anemometer types
Numerous wind vane and anemometer models exist for measuring wind speed and direction, yet the types of anemometer include:
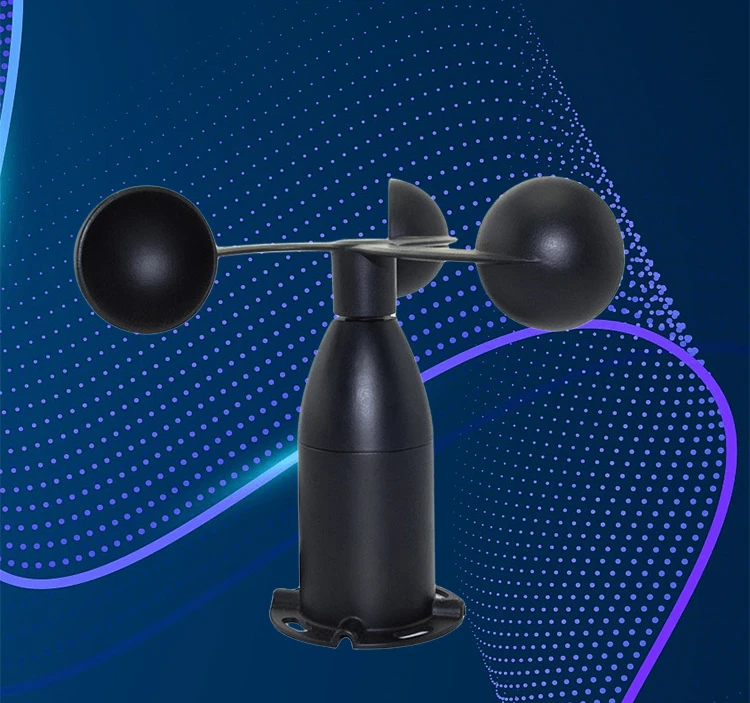
1. Cup anemometer:
This type has three or four cups that spin on a flat axis. The rotational speed depends on wind speed. Weather stations often use cup anemometers because they are simple, reliable, and accurate in measurements.
2. Vane anemometer:
This type of anemometer uses a wind vane to find the wind direction. It has a spinning propeller to anemometers measure wind speed. The vane aligns with the wind, while the propeller spins based on the wind’s speed. People often use vane anemometers in aviation and meteorology.
3.A hot-wire anemometer:
The device measures wind speed with a thin wire that heats up from an electric current. When wind blows over the wire, it cools down. This cooling changes the wire’s electrical resistance. We use this change in resistance to calculate average wind speed.
Hot-wire anemometers are very sensitive tools. They can measure low wind speeds accurately. This makes them helpful in research and development.
Below are comprehensive descriptions of the three types of anemometers:
1. Cup anemometer:
A cup anemometer usually has three or four cups mounted on horizontal arms. These arms meet at right angles. The cups are made to catch the wind. This makes them spin around a central axis.
– Function: When the wind blows, it makes the cups spin. The speed of the wind affects how fast they rotate. The anemometer has sensors that count how many times the cups turn in a certain time. This data helps to measure the wind speed.
Meteorological stations often use cup anemometers. They provide reliable and accurate wind speed measurements. Researchers commonly use them for environmental monitoring and studies.
2. Vane Anemometer:
A spinning propeller and a wind vane make up a vane anemometer. The wind vane sits horizontally and can rotate freely to align with the wind’s direction. The team sets the propeller vertical shaft and links it to a sensor.
– Function: When the wind blows, the wind vane turns to face it. The propeller spins faster with stronger winds. The sensor measures how fast the propeller spins and gives data on wind speed.
Application: Aviation and meteorology use vane anemometers to check wind speed and direction. They also use them in HVAC systems and for environmental monitoring.
3. Hot-wire Anemometer:
A hot-wire anemometer uses tungsten, which is a common choice for hot wires. This wire is made of a material that changes with temperature, like platinum. It heats up electrically and responds to air flows. The device includes temperature sensors and electrical circuits.
– Function: When the high wind blows over the wire, it cools the wire and changes its resistance. The electrical circuits notice this change in resistance and use it to find out the wind speed.
– Application: Hot-wire anemometers are very sensitive and can measure small wind speeds accurately. They are often used in research and development. This includes studies in fluid dynamics, aerodynamic research, and environmental monitoring. These tasks need precise measurements in specific situations.
These three types of anemometers have different benefits. Users choose them based on their specific needs and uses.
In addition to the types of wind speed sensors introduced above, sonic ultrasonic anemometer, wing-type wind speed sensors,laser doppler anemometer, etc. are also widely used in the market.