Solar PV Industry Solution
Home » Solar PV Industry Solution
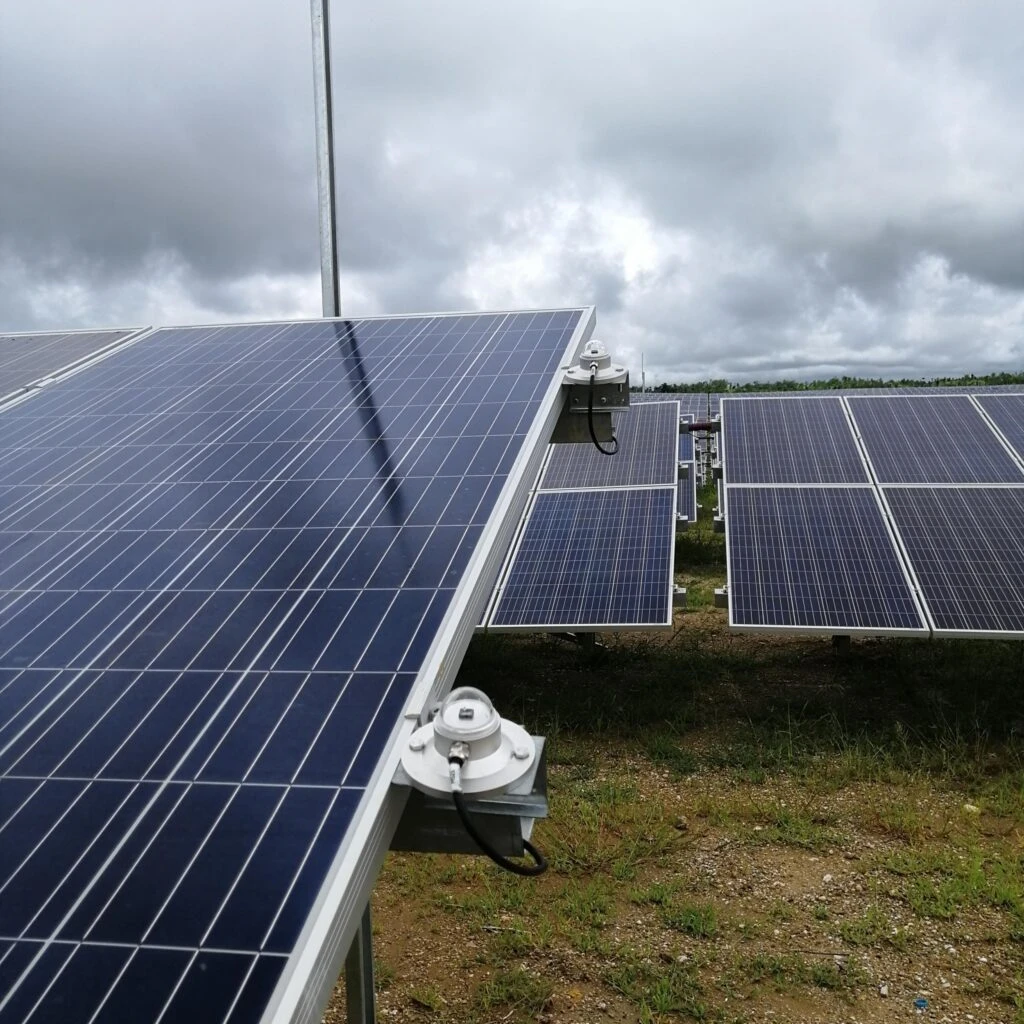
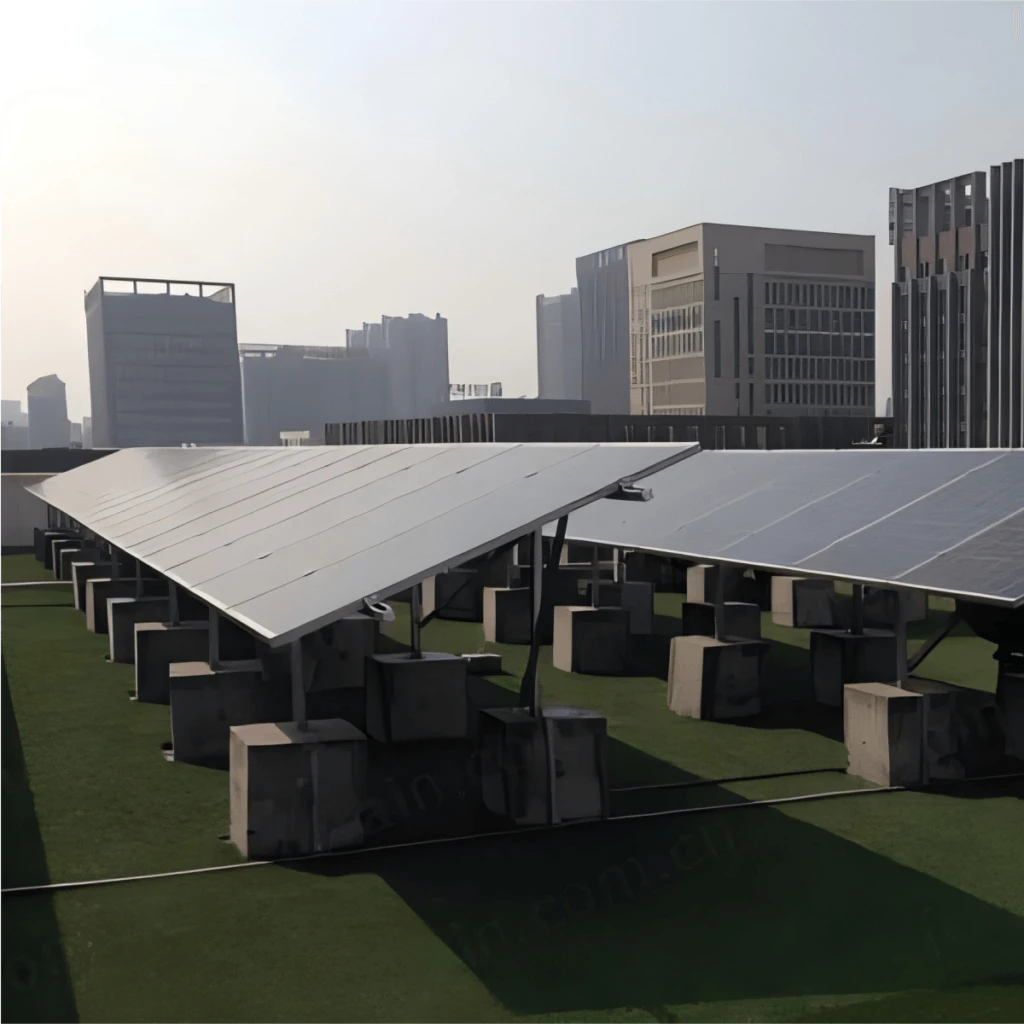
Solar industry system composition
solar cell module
The solar cell module serves as the pivotal core within the photovoltaic system. It is fabricated through the series and parallel packaging of a multitude of solar cells. Its essential function lies in the conversion of solar energy into direct current.
solar charge controller
The solar controller has battery protection function and charge control function (MPPT), which can control and adjust the charging working mode according to the battery type, output power and other factors, and make reasonable use of solar energy resources.
Battery energy storage device
When the sun is shining, the electricity produced by the solar panels may exceed the immediate demand of the load. Battery storage devices can store this excess power.
When there are clouds blocking the sun or at night, the solar panels produce less electricity, and the battery storage device releases energy to replenish the power supply.
inverter(What is an Inverter?)
As a device that converts direct current to alternating current, the electricity generated by the photovoltaic system can meet the needs of most electrical equipment and the grid.
We often apply series inverters in small and medium-sized photovoltaic systems. And we choose micro inverters for small distributed photovoltaic systems like home roof photovoltaic systems.




The application of sensors in Solar PV Industry Solution
Total solar radiation sensor
Function: It can accurately measure the total amount of solar radiation, including direct radiation and scattered radiation.
The data is of great significance for evaluating the potential power generation capacity of photovoltaic power plants, making power generation plans, and studying the distribution and change law of solar radiation resources, which helps power plant operators better grasp the generation timing and resource utilization efficiency.
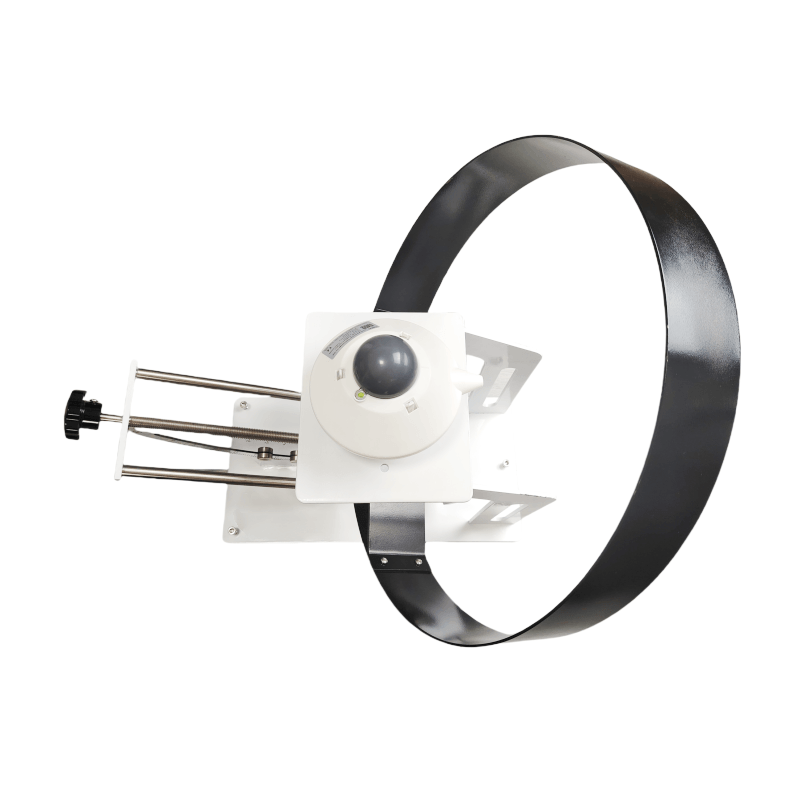
Illuminance Sensor
Function: It to measure the intensity and distribution of solar radiation and provide key data for the design, layout and power generation prediction of photovoltaic power stations. By precisely monitoring the light intensity, we can optimize the installation angle and orientation of the PV module to achieve maximum daylighting and power generation efficiency.
For example, in a large photovoltaic power station, we can adjust the angle of different regional components according to the light intensity sensor data to improve the overall power generation.
Paste Type Temperature Sensor
Function:The photovoltaic chip temperature sensor has the ability to be closely affixed to the exterior surface of the photovoltaic module, thereby facilitating real-time and highly accurate temperature surveillance.
Owing to the fact that the temperature of the photovoltaic module is subject to variation as a result of alterations in light intensity, ambient temperature, wind speed, and other elements, the dynamic temperature data of the module can be retrieved instantaneously via this chip sensor.
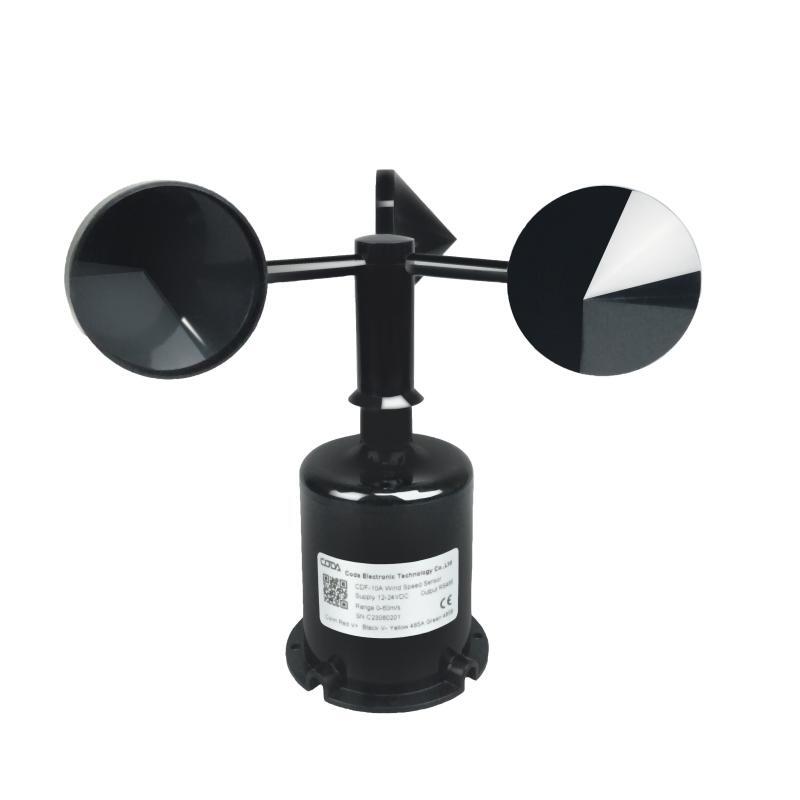
Wind Speed Sensor
Function:The real-time surveillance of wind speed is of essential significance for the secure and steady functioning of photovoltaic power plants. For one thing, the data of wind speed can be employed to appraise the effect of wind on photovoltaic modules and their supporting brackets. It also helps in refining the structural blueprint of the brackets and augmenting the wind resistance capabilities of the power stations.
On the other hand, when encountering strong winds, protective measures can be taken in time according to wind speed information, such as adjusting component angles or suspending power generation to avoid equipment damage.
Scattered Radiation Sensor
Function: The variation of scattered radiation will directly affect the power generation of photovoltaic system. Compared with direct radiation, the scattered radiation is relatively stable, especially when the cloud movement causes the rapid change of direct radiation, the scattered radiation can provide a certain energy supplement.
By monitoring the intensity of real-time scattered radiation and its changing trend, combined with the information of cloud cover and atmospheric transparency in weather forecast, the short-term power generation of photovoltaic system can be predicted more accurately.
Rain Sensor
Function: Rainfall serves to cleanse dust, bird droppings, and other contaminants from the surface of photovoltaic modules.
This action is beneficial in sustaining the light transmittance of the modules and, as a result, enhancing the efficiency of power generation.The rain sensor records the time and amount of rain, and operations personnel can evaluate the cleanliness of the component surface based on this information.
Atmospheric Temperature, Humidity Sensor
Function:Monitor ambient temperature. The ambient temperature affects the heat dissipation design and operation efficiency of the power station.
High humidity environments may cause condensation on the surface of photovoltaic modules, affecting their light transmission and power generation efficiency. The humidity sensor can monitor the air humidity, which provides a basis for preventing the surface condensation of components and making a reasonable cleaning and maintenance plan.
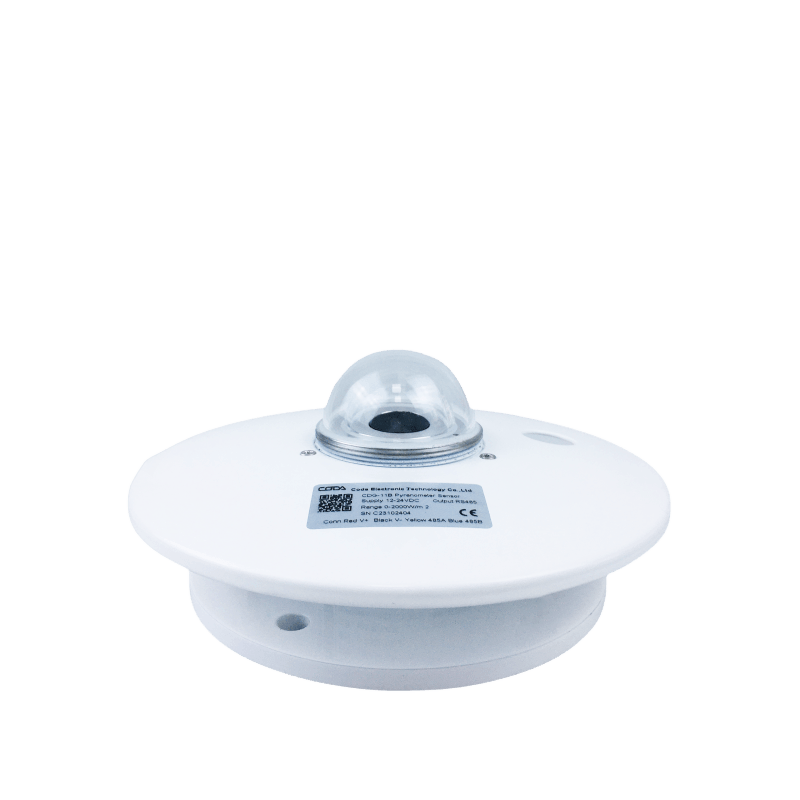
Pyranometer
Function:Pyranometer is produced based thermopile principle; sensing elements are made by winding – plated thermopiles with multi contacts.Its surface is coated by black coating with high absorption rate.
Hot contactson the sensors surface, while the cold junction is located within the body,temperature difference between the hot and cold junction generates electromotive force, the thermoelectric effect is proportional to the solar radiation. In order to reduce the ambient temperature effect.
Solar PV Industry Customer Case
Background:
In recent years, Southeast Asia has experienced remarkable progress in the realm of photovoltaic power station parks. This growth is spurred by the escalating need for clean energy and the copious solar resources available in the area.
Weather station equipment:
According to the local climatic conditions and lighting characteristics, the high efficiency polycrystalline silicon photovoltaic modules were selected.
Polysilicon components in the local high temperature and high humidity environment, with better stability and cost-effective, in the selected power station construction area, further installed meteorological monitoring stations, including light intensity sensor, temperature sensor, wind speed sensor, radiation sensor, etc., for micrometeorological environment analysis.
Results:
The execution of the photovoltaic project has yielded remarkable economic advantages for the local community. Firstly, the establishment and operation of the power station have generated a substantial quantity of employment prospects. This encompasses the design and construction phases during the initial period, as well as the subsequent operation and maintenance management.
Secondly, the electricity produced by the power station is either integrated into the grid or directly furnished to local consumers. This diminishes the reliance on conventional fossil fuels and curtails energy expenditures.
Background:
In order to meet the power needs of remote areas in Australia, the development of distributed photovoltaics and microgrids has become an effective solution.
Weather station equipment:
By building microgrids, distributed photovoltaic systems are integrated with energy storage systems (such as lead-acid battery storage) and diesel generators.
In microgrids, power sensors are used to monitor photovoltaic power, charge and discharge power of energy storage systems, and load power.
The intelligent control system is able to realize coordinated control among different power sources inside the microgrid by relying on the data from these sensors. For instance, when there is sufficient sunlight during the daytime, photovoltaic power generation will be given preference for use.
Results:
Distributed photovoltaic and microgrid application models effectively solve the problem of power supply in remote areas and improve the quality of life of local residents. At the same time, this application model also provides a sustainable energy solution for other resource-rich countries and regions with weak power infrastructure.
Background:
The Netherlands represents a country where agriculture has reached a high level of development. Nevertheless, the energy consumption of agricultural greenhouses is considerably large.
With the aim of diminishing energy costs and realizing the sustainable progression of agriculture, the adoption of small photovoltaic systems within agricultural greenhouses has evolved into an inventive and pioneering resolution..
Weather station equipment:
In the Netherlands, translucent photovoltaic modules are fitted on the rooftops of agricultural greenhouses. These modules serve a dual purpose. They permit a certain amount of sunlight to pass through, fulfilling the requirements of plants for photosynthesis, and simultaneously generate electricity from sunlight.
To enhance the lighting effect of the photovoltaic modules, light intensity sensors are placed both inside and outside the greenhouse. Through comparing the light intensity data from the interior and exterior, the transparency and arrangement of the photovoltaic modules are modified to guarantee the equilibrium between plant growth and photovoltaic power generation.
Results:
This diminutive photovoltaic agricultural greenhouse setup has attained favorable economic and environmental outcomes in the Netherlands. For one thing, it curtails the energy expenditure of agricultural greenhouses and augments the competitive edge of agricultural produce.
For another, it diminishes greenhouse gas emissions and accomplishes the seamless integration of agricultural production and the utilization of renewable energy.
LEAVE A MESSAGE
Just tell us your requirements, we can do more than you can imagine.

Welcome to Hunan CODA Electronic Technology Co., LTD
- Building S5, Oakes Plaza, Changsha, Hunan
- Monday to Friday: 9:00 a.m. to 20:00 p.m
- (+86)17775769236
- [email protected]