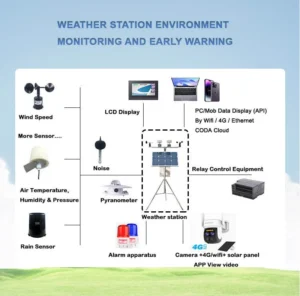
What is Black Globe Temperature
In studying thermal environments, the black globe temperature is an important measure. It provides valuable information about the heat stress people feel and how well equipment works. It is important to understand temperature. This includes how researchers measure it and why it matters. This knowledge is useful in many areas, such as health and safety, sports science, and building design.
Definition and Concept
The black globe temperature measures the average heat in an area. It looks at both air temperature and heat from nearby surfaces. This temperature shows what a person or object feels. It happens when they are exposed to two types of heat transfer. The first is heat from the air. The second is heat from the sun, warm walls, or other hot surfaces. In simple terms, it shows the temperature a black-painted sphere would reach in a certain area. This area closely mimics how the human body and other objects take in and release heat.
Measurement Principle
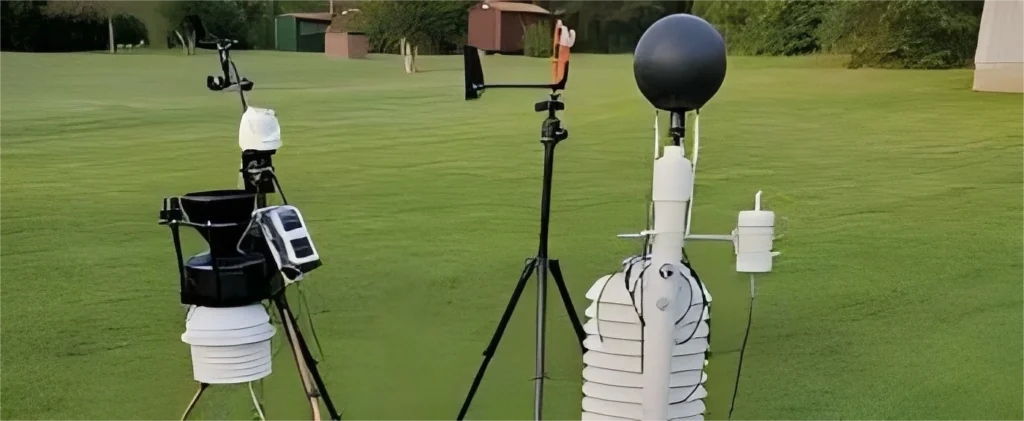
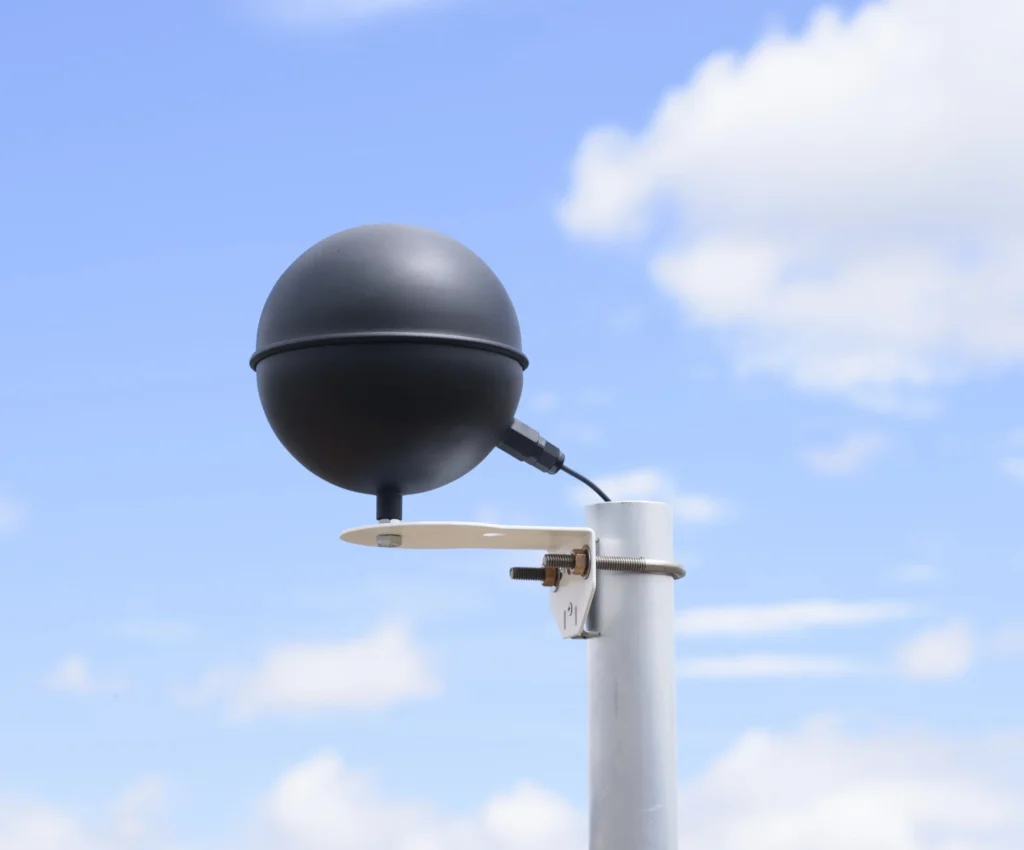
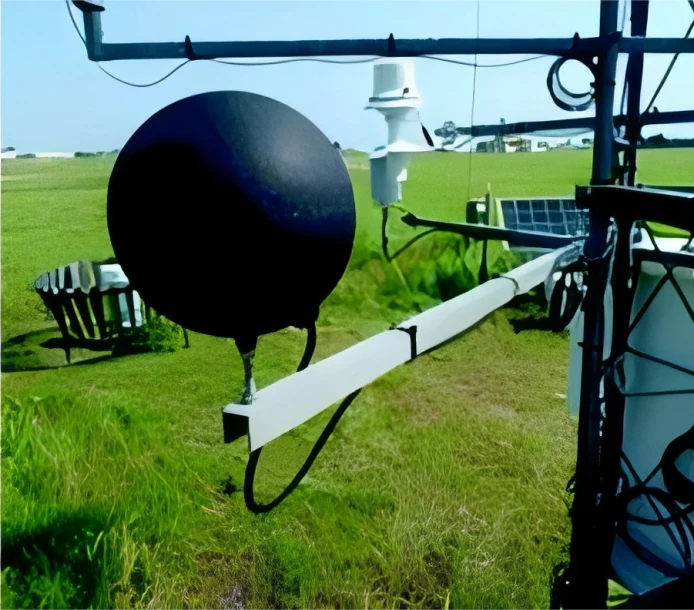
A black globe thermometer is used to measure the temperature. This device usually has a hollow, black-painted sphere made of metal or plastic. Someone places a temperature sensor, like a thermocouple or thermistor, in the center. The black color of the sphere is important. It helps absorb radiant energy well. This is like how a human body or dark-colored objects absorb heat from the environment.
When the thermometer is in the environment, it takes in heat from nearby surfaces and the air. As it takes in heat, the temperature inside the sphere goes up. The temperature sensor in the center of the sphere measures this internal temperature.
The temperature reading shows the heat absorbed from both solar radiation and convection. This gives a better measure of the thermal environment than just measuring air temperature.
Factors Affecting Black Globe Temperature
Several factors can influence the temperature in an environment:
Radiant heat index sources are important. They include the sun, industrial furnaces, and heated machines. These sources can greatly affect the environment. For example, on a sunny day at a construction site, the sun’s rays raise the temperature a lot. Inside a bakery, the heat from a large, hot oven will warm the air around it.
Air Temperature and Velocity: Higher air temperatures cause a higher temperature. This occurs because more heat reaches the black globe. Also, air velocity affects how heat moves. Faster air can help cool things down. This lowers the temperature. Slower air movement allows more heat to build up, which raises the temperature.
Surface Characteristics: The color, texture, and emissivity of surrounding surfaces play a role. Dark – colored surfaces absorb more radiant energy and re – radiate it, increasing the temperature. Rough surfaces may also have a different heat – exchange behavior compared to smooth surfaces. A room with dark-painted walls will have a higher temperature than a room with light-colored walls. This is true if all other factors are the same.
Difference from Other Temperature Metrics
The black wet bulb globe temperature wbgt meter is different from regular temperature measurements. These include dry-bulb temperature, which is the air temperature, and wet-bulb temperature.
Dry – Bulb Temperature: The dry – bulb temperature only measures the air temperature and does not account for radiant heat. In places with strong heat sources, the dry-bulb temperature might be low. However, the temperature can be much higher. This shows that there is more thermal stress on people or objects. On a sunny day in a greenhouse, the dry-bulb temperature might be 25°C. However, the temperature could rise to 35°C because of the sun’s radiation.
Wet-Bulb Temperature: The wet-bulb temperature measures how evaporation cools us. It shows how much we can sweat. While it is important to understand comfort related to humidity, it does not directly measure heat transfer. The temperature measures the combined effects of convective and radiative heat transfer.
Applications of Black Globe Temperature
The temperature has numerous practical applications:
Occupational Health and Safety
In some jobs, workers face hot conditions. This includes foundries, steel mills, and outdoor construction sites. It is important to check the temperature in these places. This helps measure heat stress on workers. High temperatures can cause heat-related illnesses like heat exhaustion and heatstroke. By monitoring this temperature, employers can take safety steps. They can provide enough breaks, ensure good ventilation, and supply cooling equipment.
Sports Science:
In outdoor activities sports, especially in hot weather, the black globe temperature measures the heat athletes experience. Coaches and event organizers can use this data to adjust training schedules. They can also create better hydration plans. If the heat stress is too high, they might need to postpone or cancel events. This keeps athletes safe and helps them perform well.
Building Design and HVAC Systems:
Architects and engineers consider the temperature when designing buildings. This helps make indoor spaces comfortable. By understanding how materials, orientations, and designs affect heat, they can enhance windows, insulation, and shading. You can also adjust HVAC systems based on the temperature. This leads to better cooling or heating. It also boosts energy efficiency and comfort for people inside.
In conclusion, the black globe temperature is an important measure. It helps us understand the thermal environment better than regular temperature readings. Many factors can affect its measurement. Its uses in different fields show how important it is. It helps keep people safe, improves equipment performance, and helps design buildings and environments well. As we face challenges from climate change and rising heat, black globe temperature will be more important in managing heat.