Top 9 Water Quality Sensors for Water Treatment
Water quality sensors play a key role in this process. They measure different aspects of water quality and provide valuable data for researchers, engineers, and analysts.
Water is essential for life. It helps us survive and do our daily activities. The quality of our drinking water affects our health. So, it is important to keep an eye on it.
Let’s look at 10 common water sensors used in water treatment. We will explain what they do, how they are used, and why they are important.
pH Sensor
The pH sensor is important for checking how acidic or basic water is. It measures hydrogen ion levels and turns them into an electrical signal. This sensor is used in many areas, like industrial wastewater, farming, fish farming, and home sewage systems.
➥ Applications
Industrial Wastewater: pH sensors help ensure wastewater stays within safe pH limits before it’s treated or released.
Aquaculture: Monitoring water quality is essential to create a healthy environment for fish and other aquatic life.
Agriculture: Keeping the pH of irrigation water in check supports healthy crop growth and better yields.
➥ Importance
Keeping pH levels balanced is important. It controls how nutrients and metals dissolve in water. This affects chemical reactions and the health of living things.
In industrial wastewater treatment, the wrong pH can cause system failures. It can also harm the environment when the water is released.
In aquaculture, the wrong pH can stress or even kill fish and other aquatic species.
Conductivity Sensor
Conductivity sensors for water measure how well water can conduct electricity. This shows if there are dissolved salts or other conductive materials. These sensors can be electrode-based, inductive, or ultrasonic types.
➦ Applications
Drinking Water Treatment: It checks the level of dissolved solids to keep the water clean.
Industrial Processes: The team checks water quality in processes that use water.
➦ Importance
Conductivity sensors are important for testing water quality. They find dissolved salts and other impurities.
High conductivity can mean the water is dirty or salty. This can change its taste or how it is used in industries. Low conductivity shows the water is very pure, which is needed in many industries.
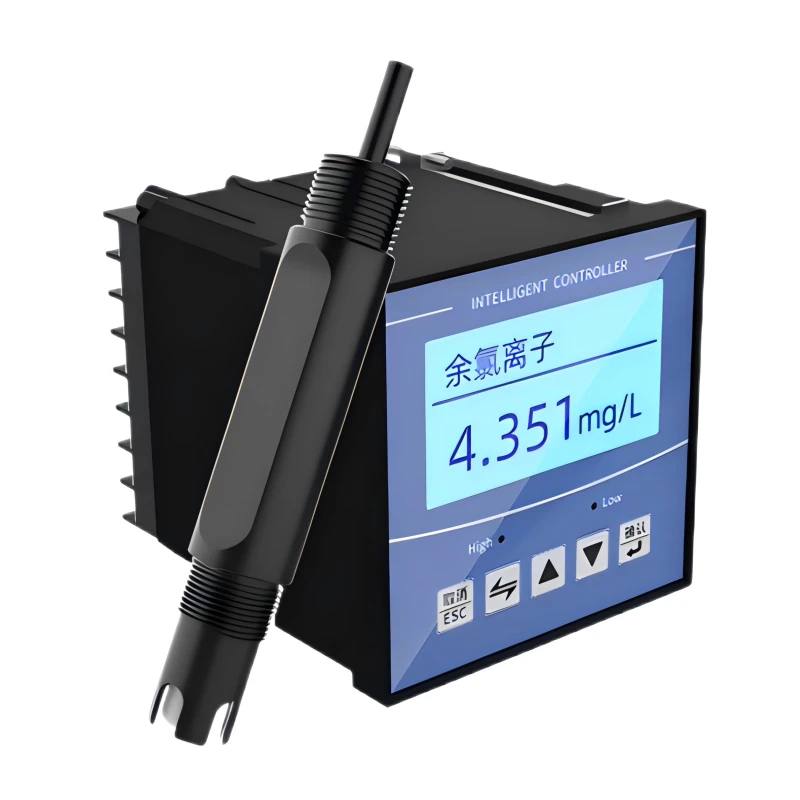
Residual Chlorine Sensor
Operators use residual chlorine sensors to check how much chlorine is left in water after disinfection. This helps make sure the water is safe to drink and free from harmful germs.
➥ Applications
Drinking Water Treatment Facilities: They make sure the water is disinfected correctly.
Swimming Pools: Checks chlorine levels to ensure safe swimming.
Cooling Systems: Stops germs from growing in industrial cooling systems.
➥ Importance
Measuring residual chlorine accurately is important for good disinfection. It also helps lower chlorine by-products.
The chlorine level must be high enough to keep the water safe. But it should not be too high. Too much chlorine can be harmful. It can also create a bad taste and smell. This sensor helps keep the chlorine levels just right.
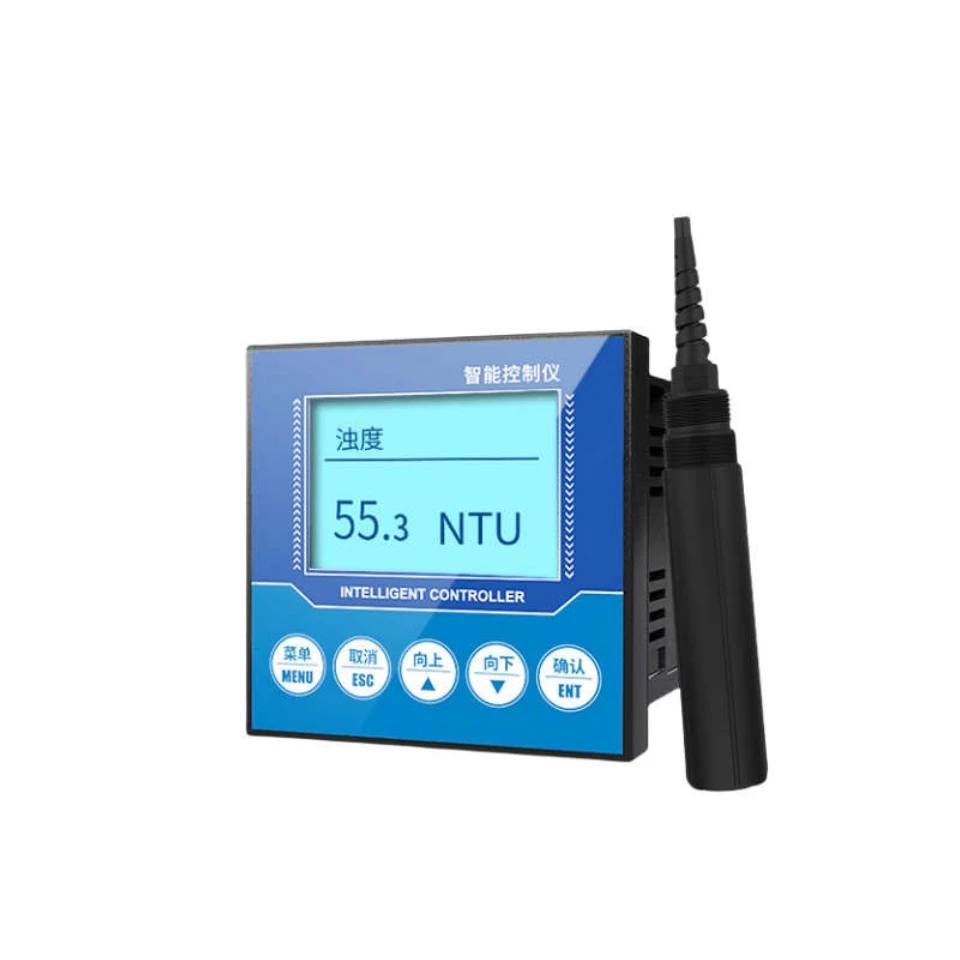
Turbidity Sensor
Turbidity sensors measure how cloudy or hazy water is because of tiny particles. They work by checking how light scatters to see how many particles are in the water.
➦ Applications
Sewage Treatment: It checks how well filtration and sedimentation methods work.
Environmental Monitoring: Checks the health of natural water sources.
Drinking Water Treatment: Makes sure that water is clear and meets the rules set by regulations.
➦ Significance
Turbidity is an important measure of water quality. It shows the presence of tiny particles that may carry harmful germs. High turbidity can hurt aquatic ecosystems and make disinfection harder. Keeping turbidity low is essential for safe drinking water and healthy aquatic life.
Dissolved Oxygen Sensor
Conductivity dissolved oxygen (DO) sensors measure how much oxygen is in water. This oxygen is vital for aquatic life. These sensors use electrochemical or optical methods to take their measurements.
➥ Applications
Aquaculture: Monitors oxygen levels to keep a healthy environment for fish and other water creatures.
Wastewater Treatment: Manages aeration processes to make biological treatment work better.
Environmental Monitoring: Checks the health of rivers, lakes, and oceans.
➥ Significance
Keeping enough dissolved oxygen is important for the health of water ecosystems and wastewater treatment. Low levels of dissolved oxygen can create dead zones where aquatic life cannot live. This sensor is vital for both environmental and industrial uses.
Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) Sensor
ORP sensors measure the oxidation-reduction potential of water. This shows how well water can break down pollutants. This measurement helps us understand the water’s ability to oxidize or reduce substances.
➦ Applications
Water Disinfection: This checks how well disinfectants, such as chlorine, work.
Aquaculture: It controls the water’s oxygen levels to keep the environment safe for fish and other aquatic life.
Environmental Monitoring: Checks the pollution levels in water bodies.
➦ Significance
ORP measurements give important information about chemical activities in water. They help improve and manage treatment processes. High ORP values show a strong ability to oxidize contaminants. This makes ORP a key factor in keeping water quality safe.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Sensor
COD sensors measure the amount of oxygen needed to break down organic materials in water. This is an important way to assess how much organic pollution is present.
➥ Applications
Industrial Effluents: Tracks the organic content in wastewater prior to release.
Wastewater Processing: Ensures that the treated water meets quality rules.
Environmental Monitoring: It checks how pollutants affect natural water systems.
➥ Importance
COD shows how much organic pollution is in water. It helps us control pollution and improve treatment. A high COD means there is a lot of organic waste. This can reduce oxygen levels and harm aquatic life.
Ammonia Nitrogen Sensor
Ammonia nitrogen sensors measure the amount of ammonia in water. They are important for showing pollution from decaying organic materials and industrial activities.
➦ Applications
Aquaculture: Helps stop ammonia poisoning in fish and shrimp farms.
Wastewater Treatment: It checks how well the nitrification process works.
Environmental Monitoring: Measures the impact of agricultural runoff on water ecosystems.
➦ Importance
High levels of ammonia nitrogen can harm aquatic life. So, it is important to monitor it. This helps protect the environment and manage fish farming. Too much ammonia can kill fish and lower water quality.
Chlorophyll Detector
Chlorophyll detectors check chlorophyll levels in water. This shows how much phytoplankton is there and warns of algal blooms.
➥ Applications
Environmental Monitoring: It checks for too many nutrients in water bodies.
Aquaculture: It checks algae growth to stop harmful blooms.
Water Treatment Facilities: This checks how well the processes take out nutrients.
➥ Significance
Measuring chlorophyll helps spot algal blooms early. These blooms can damage water quality and cause health problems. High chlorophyll means more nutrients, which can lead to too much algae and less oxygen in the water.
Innovative Water Quality Sensors by Hunan coda Electronics
Hunan Coda Electronics is a leader in making advanced water sensors. They help with accurate monitoring. With over ten years of experience, their engineers design sensors that meet high-quality standards.
Our product line has many water sensors. These include pH, conductivity, turbidity, and dissolved oxygen sensors. Engineers design each sensor to be accurate and dependable. They use these sensors in water treatment, environmental monitoring, and research.
Coda Sensors focuses on quality assurance. We provide customizable OEM services and quick delivery options. This makes us a trusted partner in water quality measurement technology.
Conclusion
In modern water treatment plants, water quality sensors are very important. They give key information to ensure safe drinking water.
These sensors also help protect aquatic habitats and meet regulations. From pH sensors to blue-green algae detectors, each tool plays a role. They help monitor water quality and improve treatment methods.