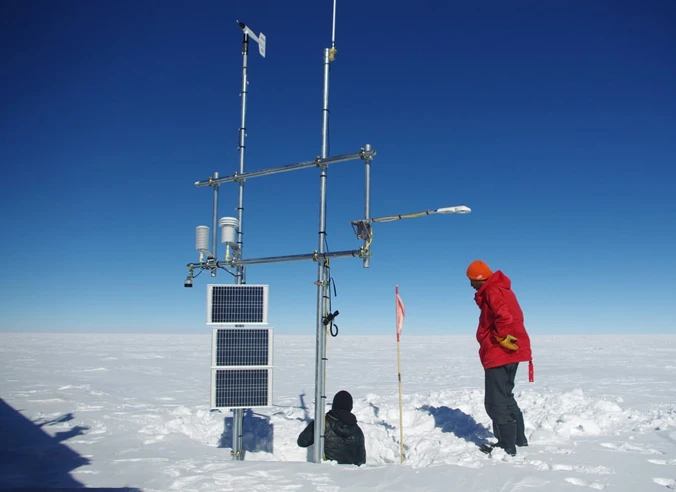
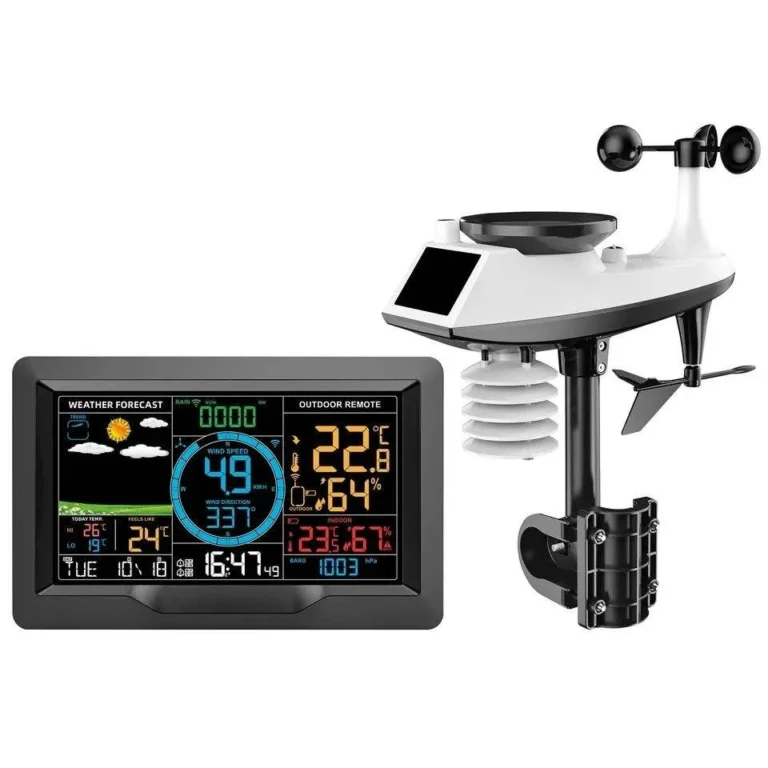
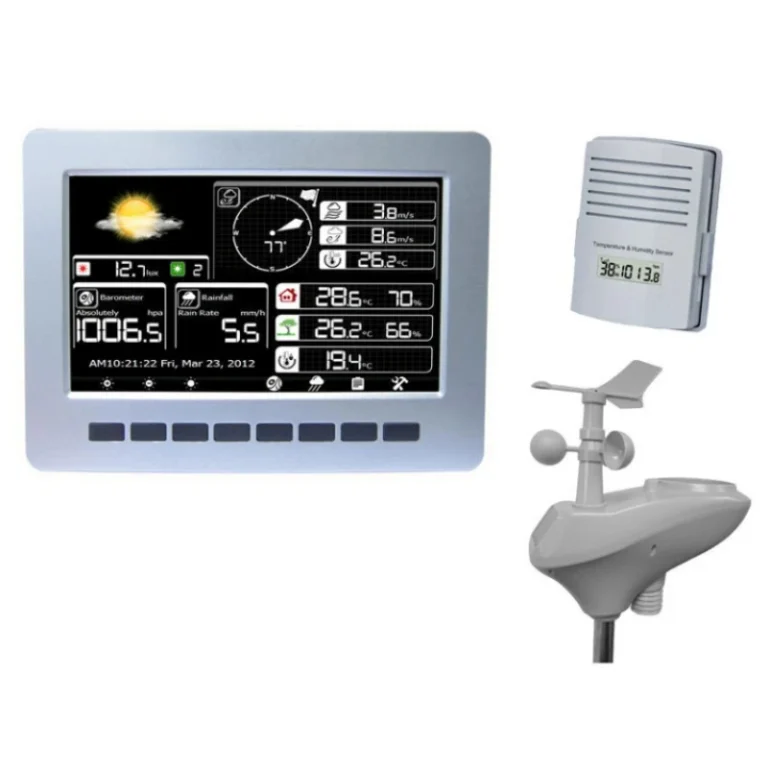
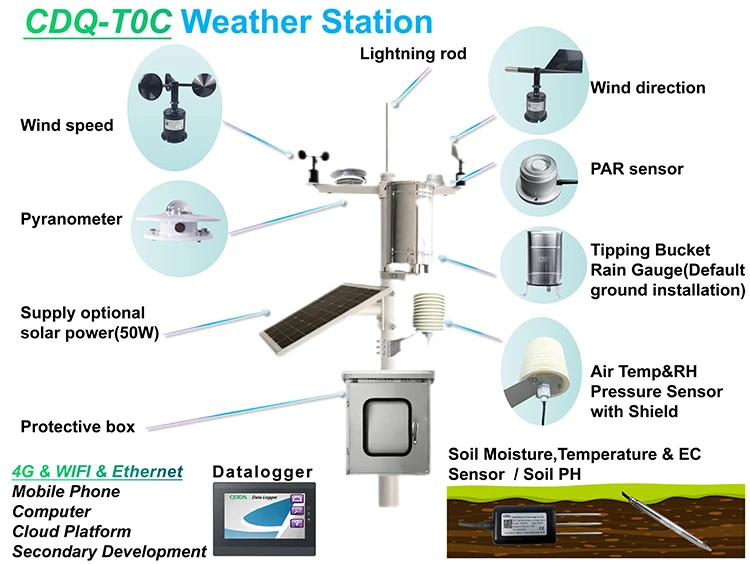
Types of auto weather station
Automatic weather stations can be grouped in different ways. Each type has its own purpose and functions. Here’s a look at the main types and their features:
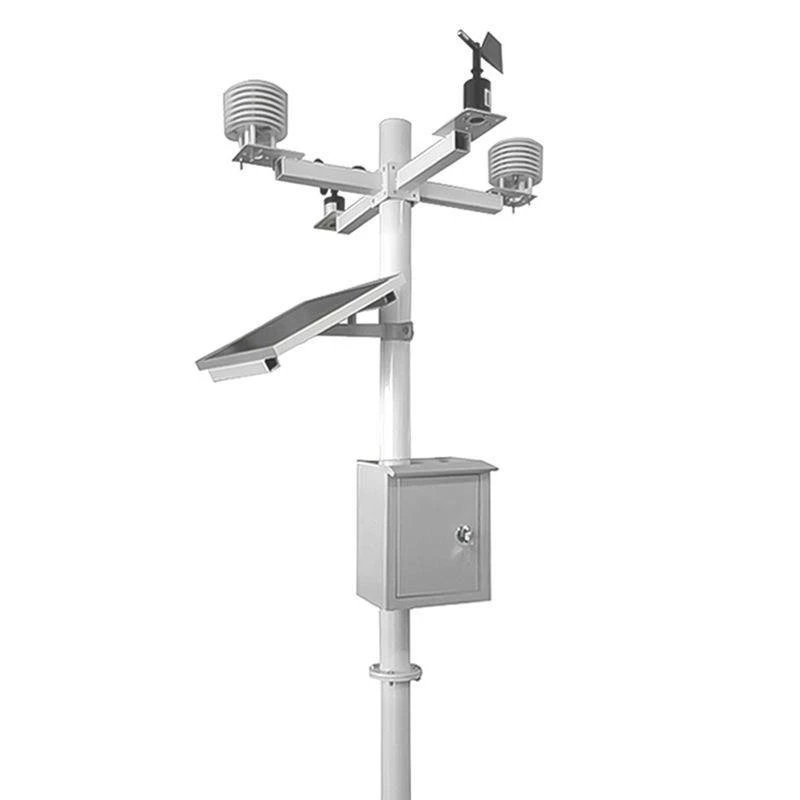
1. Automatic Weather Station
Engineers build these stations to measure and monitor automatically. This removes the need for manual work on-site. They can send and save data from far away. This gives real-time access to weather sensors information on computers, smartphones, or other devices.
Allied Creative’s software helps users keep track of different parameters. This makes it great for tracking the weather.
2. Handheld Weather Station
Handheld weather stations are a good choice for checking some weather conditions. They work well when fixed installations are not needed. These devices are easy to carry and simple to use. They are great for times when you need quick measurements while on the go.
3. Small Weather Station
These stations are small and usually measure four to ten things. People often set them up in one place for ongoing meteorological data collection. Small weather station include run 24 hours a day. They are good for places that need moderate monitoring.
4. Portable Weather Station
Manufacturers make portable weather stations for people who are always on the go. These stations are light and simple to set up and take down.
It can measure how fast the wind blows and which way it goes. And it can also check the air temperature and humidity. It also checks the temperature and moisture of the soil and solar radiation.
It also tracks how long the sun shines, how strong the light is, and the UV levels. This flexibility makes them popular for many different situations.
Categorization Based on Installation Environment and Location
– Reference station
– Regional station
– Mesoscale station
– Photovoltaic rooftop station
According to Automation Level and Quality Control
– Manned or unmanned stations
– High-precision automated weather stations
– Semi-automatic or fully automatic stations
Categorization by Installation Type
– Fixed weather stations
– Portable weather stations
Based on Data Transmission Modes
– Wired transmission
– Wireless transmission
– Communication protocols such as RS232 or RS485
Categorization Based on Installation Environment and Location
– Reference station
– Regional station
– Mesoscale station
– Photovoltaic rooftop station
According to Automation Level and high quality Control
– Manned or unmanned stations
– High-precision automatic weather stations
– Semi-automatic or fully automatic stations
Categorization by Installation Type
– Fixed weather stations
– Portable weather stations
Based on Data Transmission Modes
– Wired transmission
– Wireless transmission
– Communication protocols such as RS232 or RS485
Types Based on Functionality, Observational Scope, and Equipment
1. Basic Meteorological Stations
These stations check many weather conditions. They check temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind speed, and rain. They use various tools to gather data in a clear and organized manner.
2. Automatic Weather Stations
These stations mostly use machines to collect weather data all the time. They need little help from people. Advanced models can analyze data on their own. They can also collect and store this real time data.
3. High-Altitude Weather Stations
They look at weather conditions high in the sky. They use tools such as weather balloons and drones. These tools measure temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, wind speed, and wind direction high in the atmosphere.
4. Special Meteorological Stations
These are focused on certain weather events. They have stations to watch thunderstorms, track typhoons, and monitor sandstorms.
5. Mobile Weather Stations
These tools are installed on vehicles or ships. They give real-time weather observations while in motion. They work well during disaster response or fieldwork that needs quick measurements.
6. Marine Weather Stations
Marine weather stations are found in oceans or near coastlines. They watch for changes in the sea climate. They also gather data for sea activities and environmental research.
Designers make each type of traditional weather station for specific needs in different places. This helps with accurate tracking and analysis for research and real-world uses.