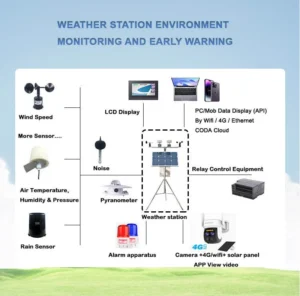
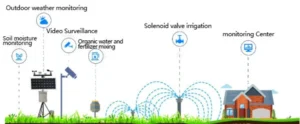
Tools and technologies for monitoring hydrometeorological hazards
The tools and technologies used to monitor hydrometeorological hazards are diverse. They include many types of sensors, remote sensing systems, computer models, and information systems. These systems work both on the ground and from space.
These parts work together to form a strong monitoring and early warning system. This system aims to reduce the impact of natural hazards on people and the environment. Here is a clear overview of these tools and technologies:
1. Sensors
Sensors are key tools for monitoring hydrometeorological hazards. They give up-to-date information on key environmental factors. Common sensors that people often use are:
1. **Rain Gauges**
**Function**: Measure rainfall amounts.
**Types**: Tipping bucket gauges, siphon-type gauges, optical sensors, among others.
**Applications**: This is often used at weather stations and in systems that warn about floods. It helps provide accurate rainfall data.
2. **Water Level Meters**
**Function**: Track changes in water levels across rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
**Types**: Float meters, pressure sensors, ultrasonic devices, radar sensors, and more.
**Applications**: Important for flood alerts, managing water resources, and tracking changes in water levels.
3. **Flow Velocity Meters**
– **Function**: Measure the speed of water flow.
– **Types**: Ultrasonic flow meters, electromagnetic devices, Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers (ADCP), and more.
– **Applications**: Help predict floods, measure water flow, and watch changes in river current speeds.
4. **Soil Moisture Sensors**
**Function**: Check how wet the soil is. See how much water it can hold.
**Types**: There are two types of devices: Time Domain Reflectometers (TDR) and Frequency Domain Reflectometers (FDR).
**Applications**: This is helpful for planning farm irrigation. It can also predict flood risks and check soil moisture levels.
5. **Temperature Sensors**
**Function**: Record air and water temperature levels.
**Types**: Thermistors, thermocouples, and more.
**Applications**: This is important for weather checks, water quality tests, and finding temperature changes in air or water.
6. **Wind Speed and Direction Sensors**
**Function**: Detect wind speed and directional patterns.
**Types**: Mechanical sensors or ultrasonic devices for wind speed and direction measurements.
**Applications**: Important for weather forecasting, storm alerts, and assessing wind-related effects.
2.Telemetry Systems
Telemetry systems gather sensor data and send it wirelessly to a monitoring center far away. They often include these parts:
1. **Data Collector**
**Function**: Gathers sensor data on its own and does some basic processing.
**Characteristics**: It works with many types of sensor interfaces. It also offers ways to store and send data.
2. **Communication Equipment**
**Function**: It is helpful to send data in various ways. These methods use radio waves, phone lines, and satellites.
**Types**: This includes radio transmitters, receivers, and devices for talking to satellites.
**Application**: Makes sure real-time monitoring data is delivered on time through remote transfer.
3.Satellite Remote Sensing
Technology
This technology uses sensors on satellites to watch the Earth’s surface. It offers broad coverage and key environmental data. People often use it for:
1. **Satellite Imagery**
– **Function**: Offers worldwide surface coverage and helps track disasters such as floods and droughts.
– **Characteristics**: It covers a wide area and captures big weather events, like clouds from typhoons and floods.
2. **Radar Satellites**
**Function**: Goes through cloud cover to get accurate ground-surface information, even in bad weather.
**Characteristics**: Works well in all weather conditions and is not affected by clouds.
4.Weather Radar
Weather radar systems use radio waves to locate the position and speed of objects. They mainly watch how much it rains and where it rains. Common types include:
1. **Doppler Radar**
**Function**: Tracks rain patterns, strength, and movement to predict events like heavy rain and floods.
**Characteristics**: Offers quick detection of changes in rainfall patterns with high time detail.
2. **Wind Field Radar**
**Function**: Measures wind speed and direction in the atmosphere in three ways.
**Characteristics**: Provides detailed wind field data to help with storm warnings.
5.Hydrological Models
These models use math and science to mimic how water works. They help predict floods and analyze runoff. They also make related assessments. Common models include:
1. **Rainfall-Runoff Models**
**Function**: Shows how rainfall becomes runoff to predict floods accurately.
**Characteristics**: Sends flood alerts by combining past records with current monitoring data.
2. **Watershed Models**
**Function**: This looks at how water moves in a watershed. It helps manage water resources and predict disasters.
**Characteristics**: It includes land features, soil types, plants, and other factors for a full analysis.
6. Information Systems
Information systems help to store, manage, analyze, and share weather and water data. They also assist with early warning systems for being ready for disasters. The main types include:
1. **Hydrometeorological Databases**
**Function**: Stores and manages weather data. This allows quick access to past records for analysis.
**Characteristics**: It has strong data storage capacity and efficient retrieval. This makes sure the information is correct and trustworthy.
2. **Geographic Information Systems (GIS)**
**Function**: It combines spatial data to assess disaster risks. It also aids in making decisions for disaster management.
**Characteristics**: Shows possible risks and helps with planning and emergency responses.
3. **Early Warning Systems**
**Function**: Combines different monitoring datasets to study possible disasters and give quick warnings.
**Characteristics**: Uses fast methods to share important information with decision-makers and the public right away.
Comprehensive Application Examples
In real life, good monitoring and early warning of weather hazards need different tools and technologies to work together. For instance, flood monitoring typically involves the following key steps:
1. **Data Collection:** We gather real-time data using tools such as rain gauges, water level gauges, and stream gauges.
2. **Data Transmission:** The collected data is sent to a central control system through telemetry.
3. **Data Analysis:** Hydrological models are used to study and predict flood patterns and trends.
4. **Early Warning Dissemination:** Alerts are sent through information systems. This informs both the authorities and the public. It helps them take quick action to prevent disasters.
Summary
The tools and technologies for monitoring hydrometeorological hazards include many sensors, modeling methods, and information systems. These tools use both ground-based and space-based resources.
These new ideas help manage water better. They support protecting the environment, public health, and sustainable growth.
Using these technologies together can greatly help us respond to hydrometeorological disasters. This helps save lives and lower property damage.