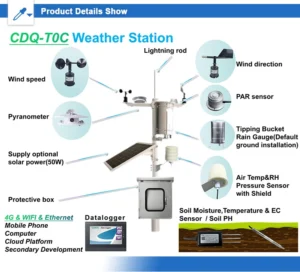
Do you know examples of various weather measurement tools?
Different types of weather measurement tools are important for collecting data. This data helps us understand and predict weather conditions. These tools are used in fields like meteorology, agriculture, aviation, and renewable energy. They provide accurate information to help us prepare for changing weather. Here are some key weather instruments and why they matter:
Thermometers: Measuring Temperature
Thermometers are important tools for measuring temperature changes. They are often used in agriculture, where temperature changes can affect crop growth and livestock care. Farmers in California pay attention to rising temperatures. These temperatures can cause pest problems. One example of a pest is the cottony-cushion scale. Modern digital thermometers offer better accuracy and are easy to use. This makes them essential for both professional meteorologists and hobbyists.
Instruments for Humidity Measurement: Hygrometers and Psychrometers
Humidity is very important in weather conditions. Tools like hygrometers and psychrometers measure moisture levels well. There are different types of hygrometers. Some use sensor technology, while others, like hair hygrometers, depend on material expansion with humidity changes. High humidity can help fungal growth in agriculture. Low humidity can cause dryness, which affects comfort and air quality. For example, farmers in the southeastern U.S. often use psychrometers. They help manage humidity-sensitive situations, like preventing mold in stored crops.
Anemometers: Gauging Wind Patterns
Anemometers are important tools for measuring wind speed and direction. This information is vital for weather forecasting, wind energy projects, and aviation. The traditional cup anemometer is still commonly used. Newer sonic anemometers use sound waves for better accuracy and detailed data. These devices help place wind turbines effectively, like in the UK. They also ensure safe takeoffs and landings in aviation by giving real-time updates on wind conditions.
Barometers: Tracking Atmospheric Pressure
Barometers measure atmospheric pressure and are important for predicting weather events like storms and high-pressure systems. There are three common types: mercury barometers, aneroid barometers, and electronic barometers. Mercury barometers are used less often because of safety concerns. Aneroid barometers are popular for home use, while electronic barometers are often used by professionals. Accurate barometric readings are essential for meteorologists and pilots. They help with storm predictions and aviation safety. In places like Houston, Texas, barometric data helps predict thunderstorms and heat waves. This ensures that locals can take necessary precautions.
These weather instruments give us the data we need to understand the atmosphere. They help us create plans to reduce weather-related risks in different areas. Their role is changing as technology improves, leading to even more accuracy in the future.
Rain Gauges: Monitoring Precipitation for Agricultural Success
Rain gauges are important for measuring rainfall. They help in planning farming activities and improving crop yields. There are different types of rain gauges: standard, self-recording, and snow gauges.
Standard gauges collect and measure rainfall easily. Self-recording gauges track rainfall data over time. They provide useful insights for long-term analysis. Snow gauges measure snowfall specifically. They give important data for climate studies and flood prevention.
Measuring precipitation accurately is important for farming. When farmers understand rainfall patterns, they can make better decisions. This includes when to plant, how to plan irrigation, and how to control pests. For example, farmers in the Northeastern United States use rainfall gauges to check water levels. This helps them know the best times for planting and harvesting.
Monitoring precipitation is important for managing flood risks. In snowy areas like New York, snow gauges measure snowfall levels. This helps assess the risk of flooding. The data allows for timely evacuations and safety measures. These actions can reduce the impact of floods.
Weather Radar: The Invisible Lens on Atmospheric Activity
Weather radars use electromagnetic waves to watch and predict weather patterns. They are very important in modern meteorology. Two common types are Doppler radar and phased array radar. Doppler radar is great for monitoring severe weather. It measures how air moves and gives detailed information about developing systems. Phased array radar uses many radar arrays to create clear images. This helps in analyzing weather dynamics more effectively.
Radar technology is essential for keeping aviation safe and managing floods. It captures real-time data on storms. This helps meteorologists give accurate weather warnings. The technology supports pilots and air traffic staff in making smart decisions for safe flights. For flood management, radar tracks storm movement and strength. This allows officials to take quick safety actions. During hurricanes like Harvey, real-time radar data helped predict storm paths and issue evacuation orders. In flood-prone areas, phased array radar helps create focused strategies by showing detailed images of storm patterns.
Visibility Meters: Monitoring Atmospheric Clarity
Visibility meters measure how clear the air is. They help us see how far we can see objects. These tools include transmissometers and visibility sensor systems. They use lasers or infrared technology to work.
Transmissometers measure how much a laser beam loses intensity as it moves through the air. Visibility sensor systems check how light scatters due to particles in the air. These tools are important for monitoring air quality and studying changes in the atmosphere.
Visibility data helps find pollutants, dust, and particles that affect air clarity over time. For example, in cities like Beijing, visibility meters check particulate matter levels. This leads to real-time public health alerts that focus on safety and well-being.
The Vital Role of Weather Instruments
Weather measurement tools are key to meteorology. They provide important data for accurate forecasts, climate studies, and safety measures. Thermometers measure temperature, while anemometers track wind behavior. Each tool helps us understand the atmosphere better. Using these instruments well improves our ability to prepare for and respond to weather events. This leads to a safer and more informed future.
Looking Ahead: The Advancement of Weather Technology
As technology improves, weather monitoring systems are becoming more accurate. These weather measurement tools help us understand the atmosphere better. These advancements are important for protecting public health and supporting industries that depend on weather data. They also help us create better plans for managing natural disasters. Each new development brings us closer to better weather predictions and a safer world.