Principle of a soil temperature sensor
A soil temperature sensor measures the temperature of soil, air, and water. Experiments and studies are important. Soil temperature, also known as ground temperature, includes surface and underground temperatures. It provides valuable data for research.
Soil temperature is important for growing crops. It affects how fertilizers break down and how organic matter forms. Soil temperature is a key part of farming. It helps shape the microclimate.
Measuring and studying soil temperature is very important. It helps us understand microclimates and agrometeorology.
Soil heat flux affects how soil temperature changes. Researchers link this to soil properties like heat capacity, thermal conductivity, density, specific heat, porosity, and moisture content. In sloped areas, the slope’s position and size also play a role.
So, what is the operational principle of a soil temperature sensor?
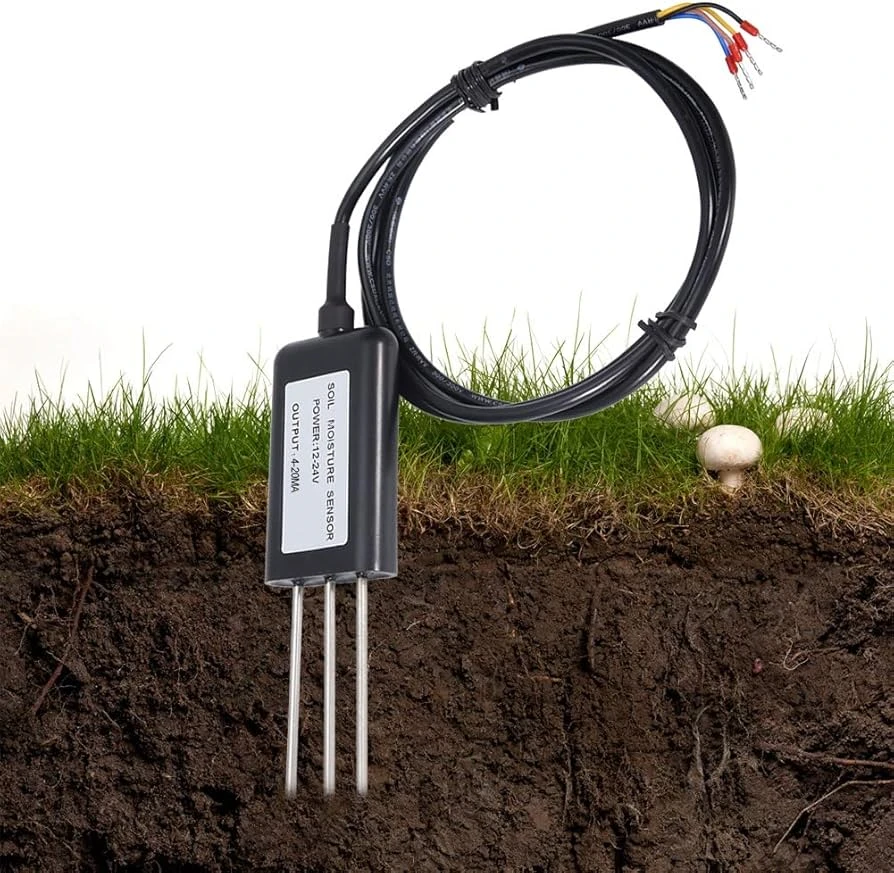
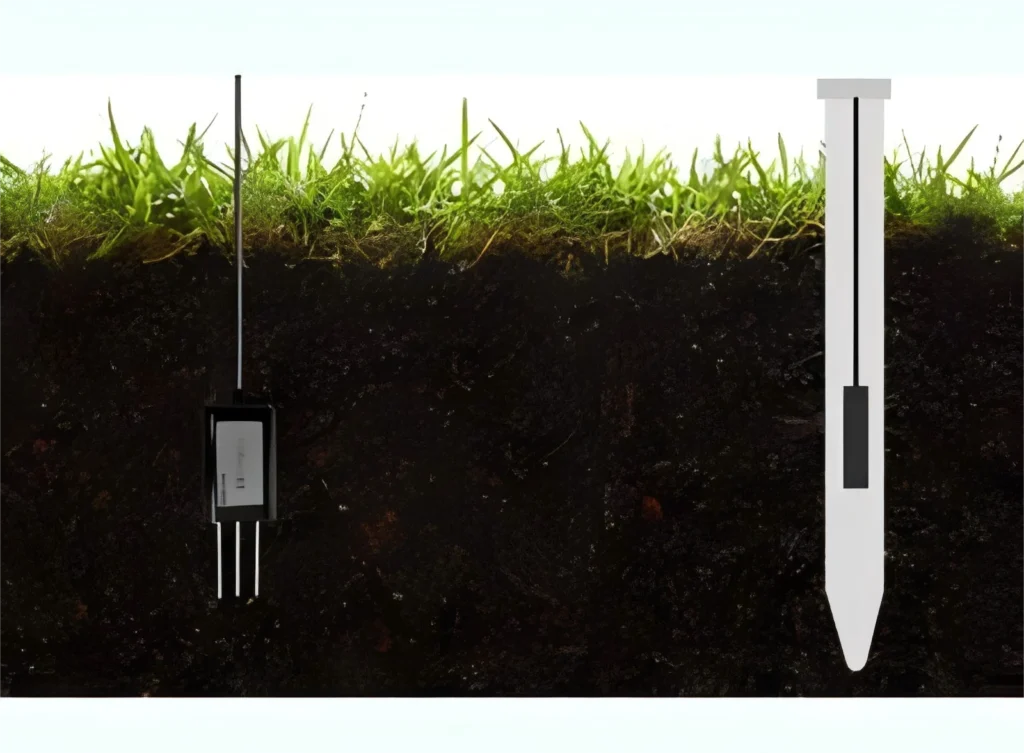
Many friends want to know how this type of sensor works. It works like a regular temperature sensor. It uses the thermistor principle. However, the soil temperature sensor has a stronger sealed casing.
This design helps the sensor work well, even when buried deep in the ground.
Sources of error in soil temperature sensors
The temperature sensor has inaccuracies from two main sources. First, the error comes from the measurement and control circuit. However, the sub-microwatt detection circuit can greatly reduce the sensor’s self-heating error.
The signal detection circuit can measure temperatures with a resolution better than 0.01°C. Its accuracy can be 0.1°C or more. We also find that solar radiation causes some error. When solar radiation hits the sensor, it raises the temperature.
The sensor adds this increase to the atmospheric temperature it measures. This effect is like heating the sensor directly. People call the rise in temperature from radiant heating solar radiant heating error, or radiant error for short.
Application of soil temperature sensor
Many people use soil temperature sensors in farming, forestry, geology, and water management. They help with fields, forests, lawns, and keeping highways and railways in good shape.
The smart soil temperature monitor is rainproof. It is made to work well in wet conditions. It can track the temperature of soil, air, and water at the same time. This device gives accurate measurements and dependable performance.
The soil temperature sensor is small and can store a lot of data. It is portable and monitors soil temperature all the time. This gives it stable performance and high reliability. Also, it needs no maintenance.