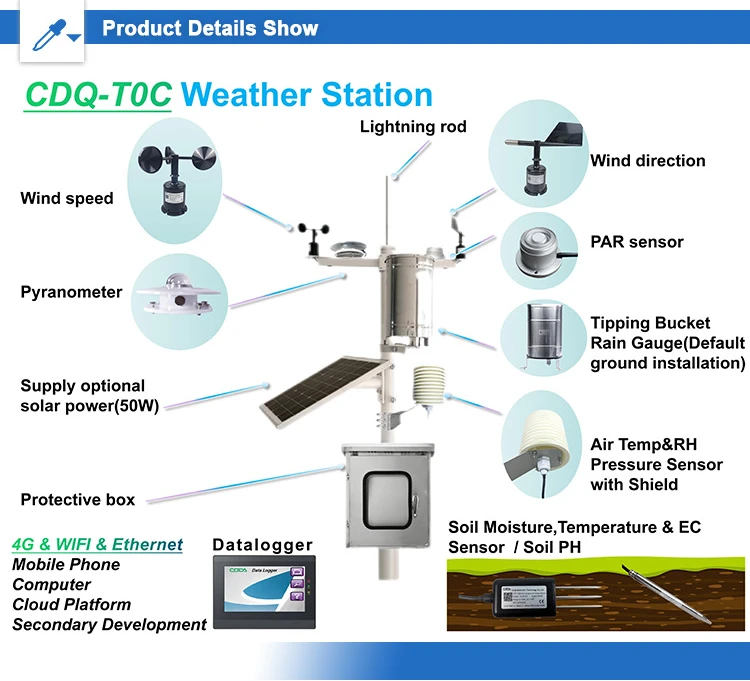
How to Understand Weather Instrument Specifications
Imagine you are a farmer planning for the next planting season. Timing is important. Knowing when to go or wait relies a lot on accurate weather data. Not all weather tools have the same accuracy or features.To choose the best tool, you must know its features well. This guide helps you learn the main factors in weather instrument specifications. It helps you make smart choices that fit your needs.
Breaking Down Weather Instrument Specifications
Specifications are like an instruction manual. They help you see what an instrument can do and what it cannot do. They give important information about how well it works and if it is right for certain uses.
This applies to different activities. You may be in charge of farm projects. You might be doing research on the weather. Or you might just be tracking local weather trends as a hobby.
Key Components of Weather Instrument Specifications
**1. Measurement Range**
The measurement range shows the limits where the instrument can record things like temperature, humidity, or wind speed. If you live in a very cold place, temperatures can drop below -40°C. You need a thermometer that can measure these low temperatures. A thermometer that measures from -40°C to 50°C is useful for both very cold and mild weather in different climates.
**2. Accuracy**
Accuracy shows how close the instrument’s readings are to the real value. This is important for tasks that need precision, like forecasting or scientific analysis. For general use, an accuracy margin of plus or minus 2% is usually enough.
A thermometer with ±2% accuracy might change a bit, but it is good enough for daily weather checks. High-accuracy instruments are essential for professional meteorologists who need detailed data.
Resolution and Response Time
**1. Resolution**
Resolution is the smallest change that can be noticed in a measured value. Instruments that have higher resolution show more detail. A wind speed meter that measures in 0.1 m/s gives more accurate readings than one that measures in 1 m/s. This is good for careful data collection or detailed analysis.
**2. Response Time**
Response time shows how fast an instrument reacts to changes in conditions. Quick-response tools give real-time data. This is important for making fast decisions in situations like storm tracking or emergency response.
A response time of 1 second is best for quick updates. However, a 10-second delay is fine for regular observations that are not urgent.
Data Output and System Compatibility
**1. Data Output**
Digital outputs are often preferred for connecting to computers, smartphones, or data loggers. They make it simple to watch and study things as they happen.
They make it easy to watch and learn about things as they happen. Analog outputs are not as common, but they are still used. They are helpful for manual setups or older systems that need special changes.
**2. Compatibility**
It is important to make sure that new systems work well with the ones we already have. A digital tool can connect easily with USB cables or wireless technology. This helps with automatic data logging and analysis. On the other hand, analog instruments may require manual recording or special converters to work with modern equipment.
Comparative Case Study: Two Weather Stations
Let’s look at two weather stations to show why specifications are important.
– **Weather Station A**
– Measurement Capabilities: -40°C to 60°C
– Precision: ±1%
– Detail Level: 0.1 m/s
– Reaction Time: 1 second
– Data Format: Digital (USB)
– **Weather Station B**
– Measurement Capabilities: -50°C to 70°C
– Precision: ±2%
– Detail Level: 1 m/s
– Reaction Time: 10 seconds
– Data Format: Analog
**Evaluation:**
– **Measurement Range:** Both stations cover wide ranges, but Station B handles slightly lower temperatures. This is helpful for very cold places.
– **Accuracy:** Station A is very accurate. This makes it great for tasks that need precision. Station B is good enough for regular use where high accuracy is not needed.
– **Resolution:** Station A gives clearer data that is more helpful for some analyses.
– **Response Time:** Station A gives faster updates for urgent decisions. Station B might be slower when the weather changes.
– **Data Output:** Station A’s digital output is easier to connect with modern systems than Station B’s analog setup.
For places with big temperature changes or needing fast weather updates, Weather Station A is the best choice. It provides accuracy, high resolution, and a fast response time. It also works well with digital devices. Station B can still meet general monitoring needs, even in tough climates.
By knowing these elements, you can choose weather instruments that meet your needs better. This will help you use their features and dependability better.
**Avoiding Common Mistakes When Checking Weather Instrument Specs**
To get the most out of weather instruments, steer clear of these frequent errors:
– Ignoring the Measurement Range: Choosing a tool with a range too small for your needs can limit its use.
– Misunderstanding Accuracy: High accuracy may seem great, but it’s important to know how it affects your needs.
– Ignoring Response Time: Instruments that respond slowly can give old data, which may lead to reliability problems.
Practical Tip:
Review each instrument’s specifications carefully. Make sure they match your specific use case. If you have doubts, consulting experienced users or professionals can provide valuable insights.
For example, meteorologists may focus on high accuracy and a small measurement range. Farmers may want faster response times, even if the accuracy is only moderate.
Mastering Weather Instrument Selection
Knowing the details of weather instruments is important for reliable and accurate data collection. Considering elements such as measurement range, precision, resolution, response time, and data output aids in improved decision-making. Choosing based on these features makes sure the tool fits your needs well.
Whether you are a skilled expert or a new fan, taking time to study specifications helps you use weather tools better. This insight helps you get ready for unpredictable weather. It also makes sure the equipment meets your specific needs.
No matter who you are, it is important to know about the weather. This includes farmers, weather experts, and anyone who needs accurate weather data. Checking specifications can help you keep up with changing conditions. Happy monitoring!