what is the Top 10 outdoor best weather sensor?
The best weather sensors help us learn about the environment. People use them in weather stations and for research. They are also used in networks that track the weather. Engineers create these sensors to measure local weather conditions accurately.
They provide data for professional weather forecasts, climate studies, and daily choices. This information helps people plan outdoor activities and manage their farming tasks. This article will talk about the top 10 weather sensors. It will discuss their functions, how they work, their uses, and key features.
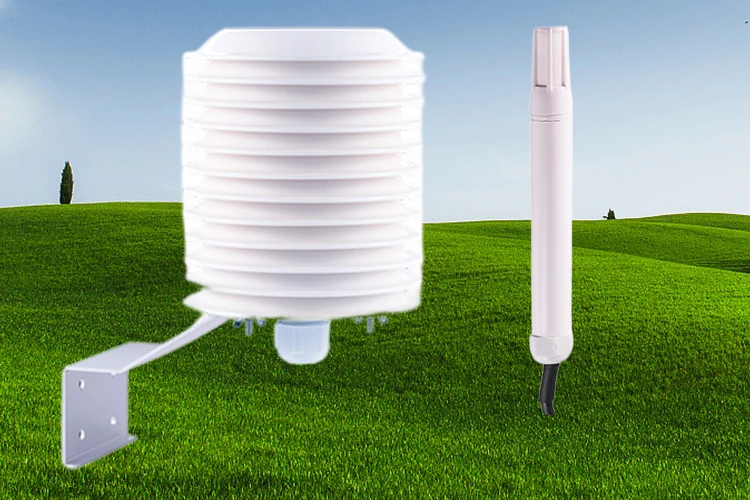
Temperature and Humidity Sensor:
This is an important part of indoor display and outdoor sensor systems. Weather enthusiasts often store it in a waterproof and dust-proof solar radiation shield.
This helps it measure air temperature and humidity well. This sensor is the most common one used. It also gives the best results.
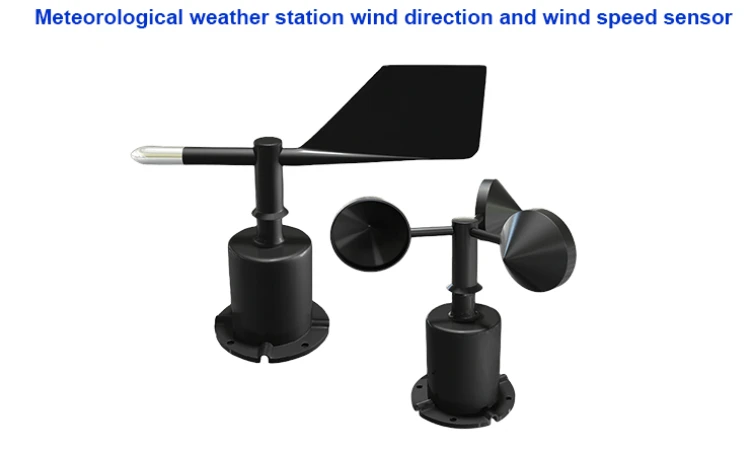
Wind Speed Sensor:
The three-cup wind speed sensor is a special tool used to measure wind speed near the ground. It adopts the traditional three – cup structure. Engineers make the wind cup from strong ABS material.
They also add a smooth internal bearing system. This helps make sure we collect accurate information.
There are two types of wind speed sensors: ultrasonic and hot-wire. Ultrasonic sensors measure wind speed by sending signals. They check how long the signals take to travel and the direction they go.
These sensors are very accurate and respond quickly. Hot-wire anemometers measure wind speed with heated wires. They depend on how heat spreads from the wires.
Wind Direction Sensor:
The main part of the wind direction sensor works like a weather vane. When the breeze hits the tail fin of the wind vane, the arrow points to the wind’s direction. It sends this information to the coaxial code disc.
The disc shows the tool that shows which way the wind is blowing. There are two ways to measure range. One is an eight-direction wind sensor. The other is a 360-degree wind sensor.
Rain Gauge:
Rainfall is very important for people who study the ambient weather. A common tool for tracking rainfall is the tipping-bucket rain sensor. This type of rain gauge is better than the standard measuring cup.
It gives more accurate measurements and can take readings by itself. This means it does not need any help. Stainless-steel rainfall sensors are great for long-term outdoor use.
Atmospheric Pressure Sensor:
This tool checks the air barometric pressure. It turns this information into an electrical signal or a different type of output. It has sensitive parts for measuring and converting.
You can use it to measure air pressure and height. It works with the outdoor weather station we tested.
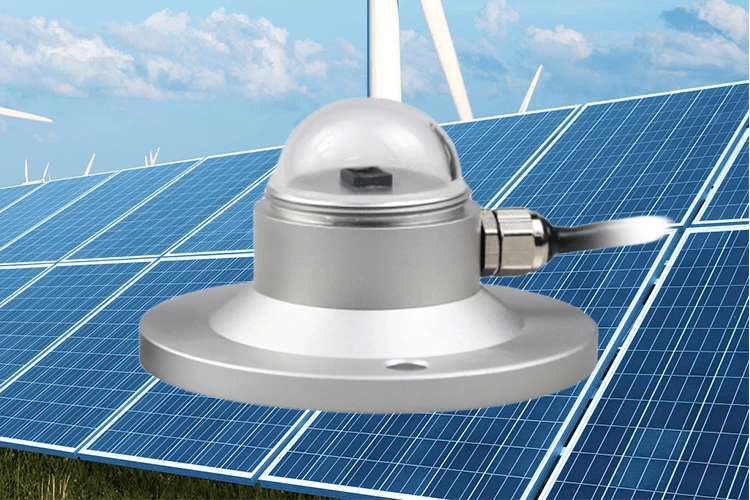
Solar Radiation Sensor:
The solar radiation sensor is a key tool for weather watchers. It helps measure solar energy and track solar power plants. People often use photoelectric and pyroelectric sensors to measure total solar radiation.
The sensor has a clear cover. This cover keeps the sensing part safe from dust. This cover allows light to pass through at a rate of 95%. A special treatment stops dust from sticking to the surface.
Sunlight Sensor:
This device measures how strong light is. It works by changing the brightness of light into a voltage or current reading. The light sensor has a very sensitive detector.
It can detect both artificial light and natural light. This makes it useful for many uses.
UV Sensor:
It measures how strong ultraviolet (UV) radiation is in sunlight. uv and solar radiation can affect health and the environment. For example, too much sun can hurt the skin and lead to other issues. Researchers use UV sensors to check the weather and protect the environment.
Noise Sensor:
It measures how loud the noise is in the environment. Noise pollution is a problem outside as well. Noise sensors can check noise levels in different areas. They give data to help with environmental protection and city planning.
PM Sensor :
This measures the tiny particles in the air, such as PM2.5 and PM10. These particles affect air quality and human health. Researchers often use PM sensors to check air quality. These sensors are important tools for environmental and home personal weather station.
Outdoor sensor installation
I. Choosing a Location: Stay Away from Interference Sources
Keep Away from Artificial Heat/Cold Sources
Temperature and humidity sensors should be at least 2 meters away from some devices. These devices include air conditioners, exhaust pipes, and heat sources like street lamps. This distance helps make sure that local weather, like outdoor temperature humidity rainfall, does not affect data accuracy.
In cities, sensors should be placed in shaded areas. This means putting them on the shady side of buildings or in green spaces. They should not be placed on concrete roads or rooftops.
Stay away from Airflow – Areas that are disturbed.
Wind speed and direction sensors should be placed in open areas. There should be no obstacles around them.
For example, in weather observation fields, nearby objects should not be taller than one-tenth of the sensor’s height. Do not install sensors in narrow alleys, between tall buildings, or in thick woods. Turbulent air can lead to wrong measurements.
Think about the features of the land and the weather.
Mountain Areas: Put wind speed sensors on high points, like mountain ridges. This helps avoid problems from valley winds. Install rainfall sensors in safe places to stop flash floods and debris flows.
Coastal Areas: Use materials that do not rust, like 316 stainless steel. Place sensors above the high-tide line. This helps stop salt fog corrosion and wave damage.
II. Installation Specifications: Height, Angle, and Fixing Methods
Standard Installation Heights
Wind Speed/Direction Sensors:
For weather observations, the height should be 10 meters above the ground. This follows WMO standards. For farming monitoring, the height can be lower. It can be 2 to 3 meters, close to the crop canopy.
Temperature/Humidity Sensors:
These sensors should be placed inside a Stevenson screen. They need to be 1.5 meters above the ground. This height helps with air circulation and keeps them out of direct sunlight.
Rainfall Sensors:
The funnel opening should be 0.7 meters above the ground. There should be no obstacles taller than half its height nearby. This will help avoid splash and rain errors.
Angle Calibration
The tail vane of the wind direction sensor needs to point to true north. Use a compass to easy to set it up. This will give you accurate wind direction data.
The sensing surface of solar radiation sensors should face the sun directly at midday. Change the tilt angle based on your local latitude.
III. Protection Measures: Weatherproofing and Anti – Damage
Waterproof and Dustproof
Make sure all sensors have a good IP rating, like IP66 or higher. This will keep water out during heavy rain or dust. Use waterproof connectors and cable glands for the wiring.
Sun and UV Protection
For sensors that react to sunlight, like temperature and humidity sensors, use covers or shades that resist UV light. This will help the sensors last longer and keep their readings accurate.
Mechanical Protection
In places where vandalism or animals are a problem, put up protective cages or barriers around the sensors. For instance, in city parks, use a metal mesh cage around rainfall sensors. This will help stop damage from falling objects or animals.
Future Development of meteorological Sensors
1. Technological Innovations
As MEMS and nanotechnology get better, meteorological sensors will be smaller and more integrated. Right now, sensors for temperature, humidity, pressure, and wind speed are separate. Soon, they will be combined into one chip.
This reduces the size and weight of the sensor device. It makes installation easier in outdoor areas. This is especially true in tight spaces, like on drones or in small home weather stations. It also lowers production costs because there are fewer parts and less assembly needed.
2. Connectivity and Data Transmission
Wireless communication technology is key for outdoor weather sensors. With the Internet of Things (IoT), sensors can talk wirelessly to other devices and cloud platforms. They will use Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks like 4G and 5G. They might use 6G in the future to send data.
In a big place like a national park, there are weather-monitoring sensors. Each sensor can connect to cellular networks. They send real-time data to a central server in the cloud.
This allows us to watch and study things from far away. It also helps us connect with other IoT devices in smart cities or factories.
3. Energy Efficiency
Outdoor weather sensors will use more renewable energy sources for power. Solar panels are now found at many professional weather station. In the future, we will develop more efficient solar cells.
We will also look at other ways to gather renewable energy. This includes capturing kinetic energy from wind or vibrations. A wind-speed sensor could be made to collect some of the wind’s kinetic energy. It could then turn this energy into electricity to power itself and other parts of the sensor system.
This method lowers the environmental impact by using less non-renewable energy. It also makes the sensor more reliable in remote areas with limited access to power.
4. Big Data and AI Integration
Outdoor weather-monitoring sensors collect a lot of data. Analyzing this data will be important for their growth. By looking at past and current data from many sensors in different areas, we can find patterns and trends.
We can predict floods by looking at different types of data. This includes data from rain sensors, river sensors, and soil sensors. Access your weather data analysis helps us see how these factors relate to each other. This can lead to better flood predictions and give early warnings to officials and the public.
Artificial intelligence, like machine learning and deep learning, will be used in weather sensors for making predictions. A sensor network in a city can use AI to look at current weather and past data. This helps predict future weather changes, like a heatwave or a sudden drop in air quality.
These predictions can help us take steps to prevent problems. For example, we can change traffic flow to reduce emissions during high-pollution times. We can also use energy-saving measures in buildings before a heatwave.
conclusion
Different sensing technologies work in different ways. For example, a temperature sensor has a special part to detect temperature changes.
An anemometer measures how fast the wind is blowing. It uses wind cups or ultrasonic methods. This gives important data support for many fields. These fields include weather research, farming, aviation, and navigation.
These climate sensors have a strong and tough casing. This helps them deal with harsh outdoor conditions. They are waterproof, dustproof, and resist rust. This means they can last a long time.
Modern outdoor wireless weather station delivers send data to weather underground without wires. They share information in real-time with a data center or user devices. This helps users get weather information quickly. It supports better decisions and early warning systems.