Principle and Application of Evaporation Sensors
China has a large area with different landscapes and climates. This leads to big climate differences in each region. However, due to global warming, some climate trends are similar across these areas.
For example, evaporation levels are rising in many parts of the country. Evaporation sensors are important for the surface heat balance and the water cycle. They are sensitive to changes in land use and climate. Additionally, evaporation plays a big role in heat exchange processes.
What is Evaporation?
Evaporation is when water changes from liquid or solid to gas. It then moves into the atmosphere. Researchers measure it as the amount of water that evaporates and spreads into the air over a set time.
This measurement is usually shown in millimeters. It shows how thick the layer of evaporated water is. This can come from a water surface or soil.
The effects of evaporation are clear in farming and everyday life. Knowing how evaporation changes is important for studying climate change and looking at changes in the water cycle.
In real life, this knowledge helps in many ways. It improves how we manage water and model climate. It also supports irrigation for farming and soil health for forests. Plus, it helps design infrastructure that saves water.
The Role of Evaporation Sensors
Evaporation is an important part of the weather in many places, especially in farming. However, measuring evaporation accurately is not easy. It requires special tools known as evaporation sensors. Here is a summary of how they work, why they are important, and what they do.
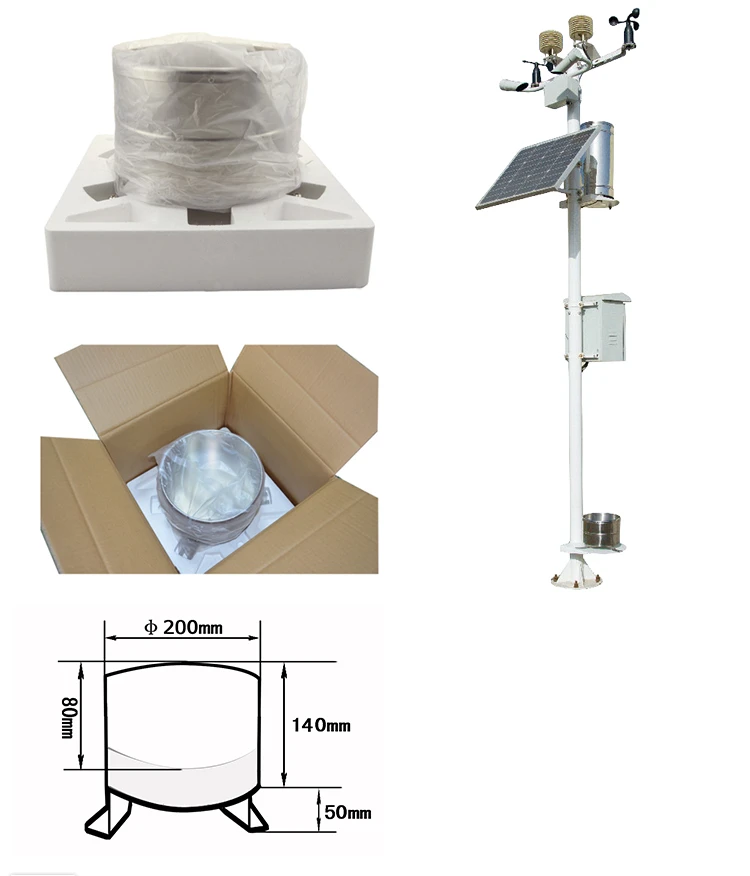
1. Principle and Definition of an Evaporation Sensor
An evaporation sensor measures changes in surface water evaporation over time. It is useful in many areas like agriculture, forestry, seed growing, geological surveys, and scientific research.
You can connect these sensors to data collection devices. This allows for automatic monitoring of evaporation processes. You can also link them to storage systems to keep track of data over time.
They use sensors to measure evaporation and rainfall. These sensors connect to data units. This setup helps them monitor evaporation and rainfall from a distance. Weather stations, evaporation stations, rainfall sites, and environmental systems often use these sensors.
2. The Importance of Studying Evaporation
Tracking changes in evaporation helps us understand climate patterns and the water cycle. Today, evaporation sensors are key in irrigation systems for using water wisely.
These sensors stop extra irrigation when the weather is bad. This includes times of rain, strong winds, or when the soil is already wet. This helps manage water use wisely.
Evaporation research helps make important choices in managing water resources. It aids in designing better irrigation systems. It also helps plan water storage solutions.
It also helps make soil better for farming, forestry, and raising animals. This research is helpful for planning irrigation and finding ways to fight drought.
3. Working Principle of an Evaporation Sensor
Evaporation sensors work by measuring pressure. They check how the weight of liquid changes in an evaporating dish. Then, they turn this into the height of water that has evaporated. Pressure-based sensors are more reliable than ultrasonic height sensors.
Ultrasonic sensors can be unreliable in icy conditions and may not work well in dry weather. On the other hand, pressure-based sensors work well in many environments. Their design also protects against damage from very low water or freezing situations.
Applications in Agriculture
In agricultural water management, irrigation acts like “income” for the land. Evaporation is its main “expense.” It is important to keep an eye on evaporation levels.
This helps us plan for water storage and supply. It also shows how much water crops need.
Evaporation affects planting systems, farming methods, and crop growth. Researchers can use data from evaporation sensors to improve water use in farming. This data helps farmers know when to water their crops or stop irrigation. It leads to better crop growth and sustainability.
By using advanced technologies like evaporation sensors in farming or environmental studies, people can manage resources better. This helps them adapt to the changing challenges of climate change.