what measures wind speed ? | wind speed measurement
Introduction of Wind Speed Sensor
A wind speed sensor, known as an anemometer, is a tool that measures how fast the wind blows. These devices are very important in many areas.
People are used in weather forecasting, studying the environment, aerospace research, marine engineering, and planning for farming. And they are often found in weather stations or towers. They collect and record important wind data.
Types of Wind Speed Sensors
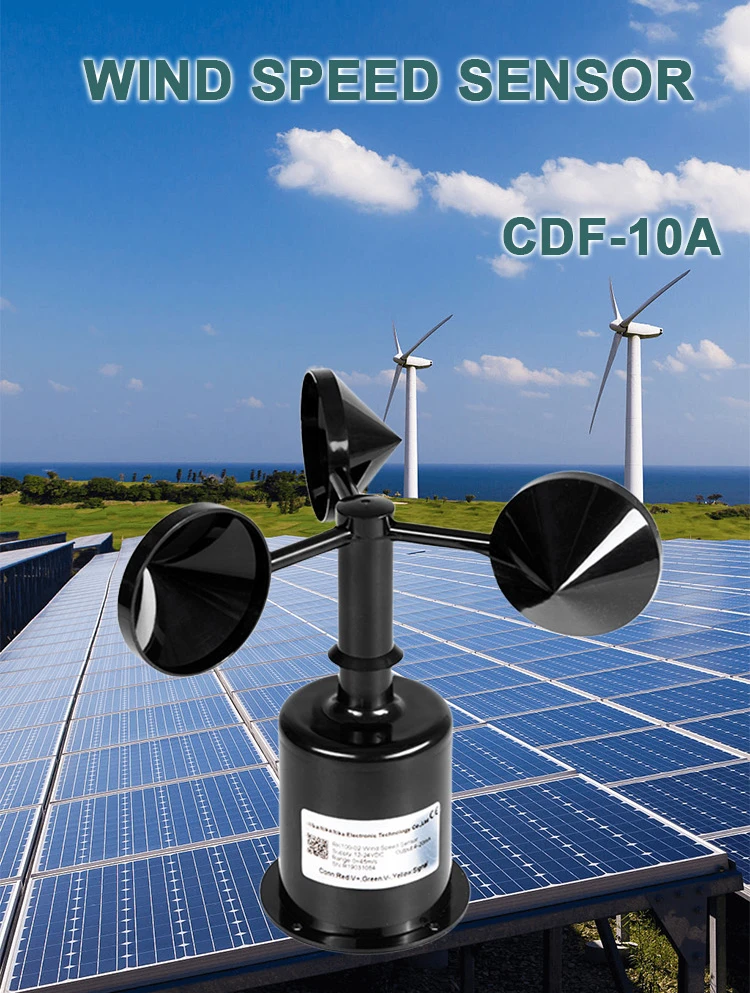
A cup anemometer is a tool that has three or more cups. These cups are on horizontal arms that turn around a tall pole. Wind exerts force on the cups, causing the assembly to spin.
The speed of rotation is linked to average wind speed. This information is changed into data that can be measured. Cup anemometers are widely used. They are easy to use and very reliable.
Hot-Wire Anemometer
A hot-wire anemometer uses electronic tools to measure the speed of moving air. It has a wire that heats up. The wire stays at a constant temperature that is higher than the air around it.
When air moves over the wire, it cools it down. This changes its electrical resistance.
The change in resistance allows for accurate measurement of recorded wind gusts speed. Hot-wire anemometers are great for detecting very low air speeds. They do this with great care.
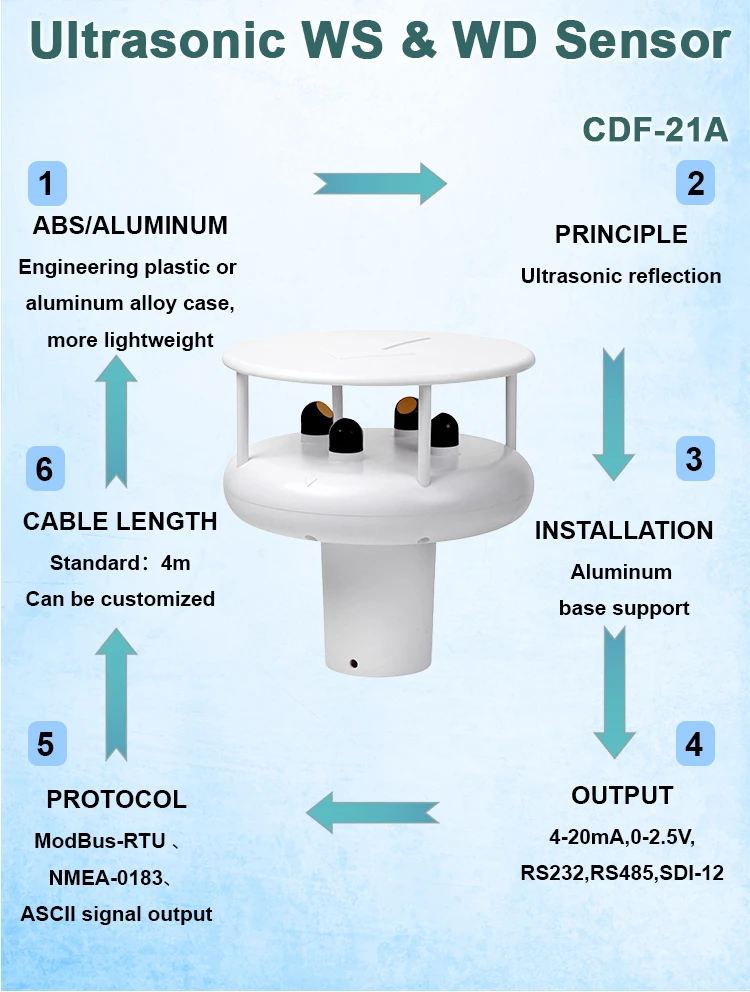
Ultrasonic Anemometer
Ultrasonic anemometers measure how fast the wind blows and which way it goes. They use sound waves that are too high for humans to hear. The device uses pairs of transducers to send and get ultrasonic pulses.
By looking at how long it takes for these waves to move between transducers, we can find the wind’s speed and direction. Ultrasonic sensors are known to be reliable and accurate. They have no moving parts. This means they need less maintenance.
Units of Wind Speed Measurement
Wind speed and wind vanes is measured in different units based on how it is used. Most units can be changed into each other. Meters per second (m/s) is the main unit used in science and weather patterns conditions studies.
– **Meters per second (m/s):** This SI unit relates to atmospheric factors like pressure and temperature. One meter per second equates to 3.6 kilometers per hour.
– **Kilometers per hour (km/h):** You often see this in weather reports.
– **Miles per hour (mph):** This is often used in places like the U.S. and the UK.
– **Knots (kt):** Used in aviation and maritime fields. One knot is equal to one nautical mile per hour. This means 1 kt is equal to 0.514444 m/s.
Conclusion
Wind speed sensors provide accurate and flexible measurements for many industries and uses. These devices help us track air currents for weather forecasts. They also help people find their way at sea. They are essential for understanding and managing air movement.
Meters per second is the main unit used to measure wind speed. Anemometer works well with other weather data.