Why Is IoT Used for Real-time Water Quality Monitoring?
Real-time water quality monitoring using the Internet of Things (IoT) has many benefits for industries. It can save millions in costs related to product recalls, reputation problems, and fines for not following rules.
In the United States, breaking the Clean Water Act can lead to fines of $25,000 to $50,000 each day. IoT-enabled devices help chemistry control teams check water quality data quickly. This lowers financial risks and improves how well operations run.
Industries such as food and drink, medicine, and chemicals depend a lot on clean water. This is important for human health and safety. These sectors are among the most critical when it comes to adhering to stringent water quality standards.
Unlocking IoT’s Potential in Water Quality Monitoring
The use of IoT for monitoring water quality has changed old methods. It now includes wireless data transmission and cloud storage. These advancements have greatly lowered operating costs. This is especially true for remote sites where it isn’t practical to have people there all the time.
Business owners and environmental agencies benefit from seeing data in real time. This helps them follow the rules set by regulations. We will look at how IoT-based sensors improve monitoring. We will also explore how they work, their benefits, challenges, and future possibilities.
Why Implement IoT for Monitoring Water Quality?
★ The Necessity of Ongoing Surveillance
Traditional water sampling methods often involve collecting data at set times. These intervals can be from one hour to several hours.
Changes in water chemistry in these gaps often go unnoticed. This happens until lab results are ready. Regulators are now using continuous monitoring techniques. This gives them better control over water quality.
IoT sensors help collect live data and analyze it. They can quickly find problems. This lets them take fast actions to improve water quality.
★ Real-time Decision Making
IoT-powered water monitoring systems allow instant detection of contamination events. These systems can quickly find bad water conditions and locate the source of contamination. This helps begin cleanup actions right away.
Sensors check important factors like turbidity, pH, chlorine levels, and dissolved oxygen. They work together to show a complete view of water quality. Advanced control systems make this function better by setting limits for each parameter. They also send alerts when problems are found.
★ Data-Driven Water Management
Collecting detailed data and using modern AI tools helps us take action to prevent water quality failures. This helps solve problems before they get worse. It also gives long-term insights, such as finding pollution patterns or changes in seasons.
Helpful insights allow for quick actions. They help find sensor problems or equipment failures before they occur. This improves system reliability.
Understanding IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring Systems
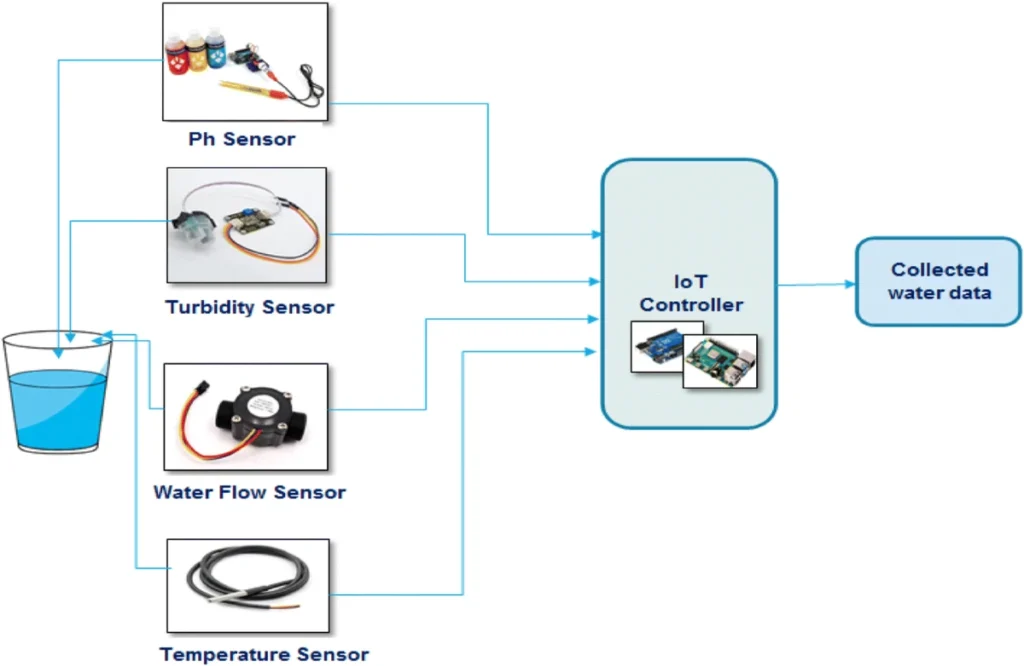
1. Components of an IoT System
An effective IoT water monitoring system depends on different parts working together smoothly. These parts are made to help specific uses and get the best performance.
Why is IoT Used in Real-time Water Quality Monitoring?
– **Sensors (Turbidity, pH, DO, Conductivity, TDS)**
Monitoring water quality means checking different physical and chemical factors. Sensors for turbidity, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), conductivity, and total dissolved solids (TDS) are placed in tanks or pipes. These sensors can be used in both still water and flowing water. These factors together give a complete look at water quality.
– **Turbidity**:
It shows how cloudy or hazy water is due to tiny particles in it. IoT-enabled turbidity sensors, like the Coda Turbidity Sensors, can detect slight changes as minimal as 0.01 NTU.
– **pH**:
The pH shows how acidic or basic water is. A lower pH means more acidity. The Coda measures pH with precision of 0.01. This makes it great for monitoring water quality.
– **DO (Dissolved Oxygen)**:
Changes in dissolved oxygen levels often happen due to microbial activities or reactions. This includes oxygen reacting with metal parts in power plants. Optical sensors help measure real-time dissolved oxygen (DO) levels. This ensures the right chemical balance.
– **Conductivity**:
Detects the amount of ions and salt in water. Drinking water usually needs a conductivity level of 0–2 mS/cm. An EC detector measures from 0 to 200 mS/cm. It has an accuracy of ±1 to 2%. It is important for effective IoT operations.
– **TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)**:
The amount of dissolved solids in water is important for following regulations. It varies based on how the water is used. For drinking, it should be less than 500 mg/L, according to WHO guidelines. For irrigation, it can be up to 2,000 mg/L. And for industrial use, it can exceed 10,000 mg/L. An EC sensor, such as the EC/Salinity Sensor, can calculate TDS through conversion.
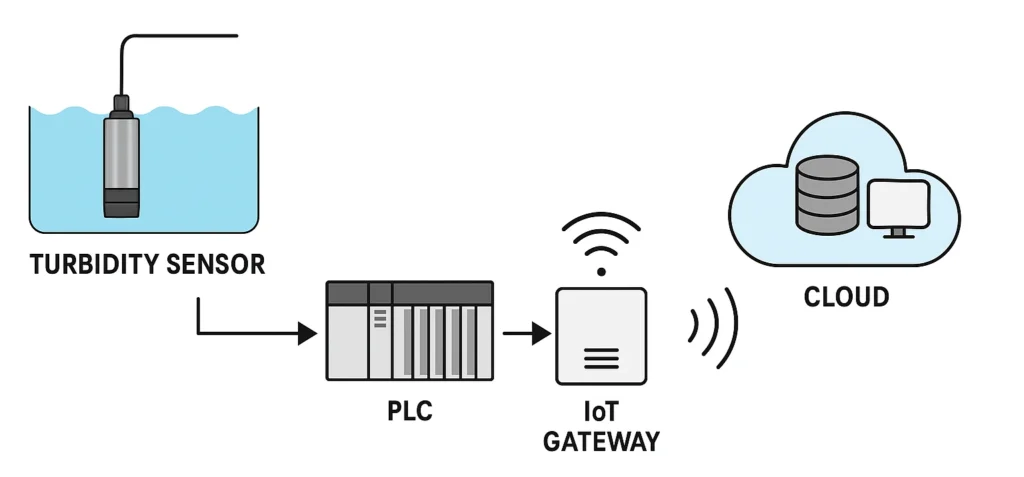
– **Gateways and PLC/SCADA Systems**
Water quality sensors collect data. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) process this data. The PLCs then send it to central systems like SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition). SCADA helps operators watch conditions and step in when needed.
– **Communication Modules (LoRaWAN, Cellular, Wi-Fi)**
Data from the sensors is sent from the field to the central monitoring system. This is done using communication modules that fit the specific situation. Short-range communication, like Wi-Fi, is great for sending data in small areas, like a plant. It removes the need for wired connections.
LoRaWAN offers low-power and long-distance connections for rural monitoring and spread-out sources. In cases where cell communication is needed, IoT devices with 4G SIM cards send data to the cloud. They use protocols like MODBUS TCP/IP.
– **Cloud Storage and Analytics Platform**
Data from sensors is sent through the communication system. It is then stored in a cloud platform for processing and analysis. This allows for better monitoring. It includes tools for predicting future trends.
It helps find patterns in preventive maintenance, sensor problems, seasonal changes, and other important issues. This leads to better decisions and more efficient water management.
2.Working Principle
The system works by combining its main parts in a step-by-step process.
**Why is IoT Used in Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring?**
### Advantages of IoT in Monitoring Water Quality in Real-Time
✔ **Ongoing, Automated Data Gathering**
Combining IoT with a real-time water quality monitoring system allows for constant data collection, 24/7. Wireless transmission allows remote monitoring systems with SCADA to get real-time updates and alerts from different locations.
It also gives business operators instant notifications. They can access these through web-based or mobile dashboards. Coda sensors have a fast response time of 1 second. This allows for almost constant data measurement.
✔ **Faster and More Accurate Decision-Making**
By collecting water quality data every second, IoT sensors help create clear trends. This allows for quick actions before levels become critical. This approach minimizes downtime and promotes proactive decision-making.
For example, systems that use PLCs and IoT gateways can make instant alarms. This happens if turbidity levels go above allowed limits, like more than 5 NTU according to WHO standards.
✔ **Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization**
Traditional manual sampling takes a lot of time. It also raises the risk of delaying the detection of water quality problems. IoT-enabled systems with TDS and turbidity sensors make testing easier. They achieve results with an average error margin of only 1.53% (Journal of Soft Computing Exploration).
This efficiency means using fewer chemicals, improving filtration processes, and reducing energy use during operations like filter backwashing.
✔ **Seamless Integration with Control Systems**
IoT devices that collect data can also be used to start automatic actions from control center commands. These tasks may include starting backwash cycles, operating valves, adding chemicals, or planning membrane changes. Using SCADA or PLC systems increases automation and improves process efficiency.
✔ **Regulatory Compliance and Reporting**
Following local government rules or international water quality standards requires using dependable monitoring solutions. A real-time IoT system helps organizations keep historical records using cloud-based SCADA systems.
This makes it easier to comply with audits. These records help create exportable data logs needed for regulatory inspections. This reduces penalties and possible financial issues.
Challenges and Considerations
While IoT-based water quality monitoring has many benefits, there are challenges to consider before adopting these systems.
**A. Power Supply for Remote Locations**
In places where sensors are used in remote areas, a reliable power source is needed. This power source helps run parts like PLCs and communication modules. Off-grid setups may need solar-powered systems with battery backups. This can raise initial costs, but it saves money over time.
**B. Data Security and Privacy Risks**
Wireless and internet data transmission can be risky. There is a chance of breaches or attacks. To protect information, it is important to use strong measures like encryption and secure network technologies, such as 5G.
**C. Connectivity Challenges in Rural or Industrial Zones**
Certain rural or industrial regions often lack reliable cellular or wired internet infrastructure. In such scenarios, satellite internet services may serve as a feasible alternative, albeit involving higher initial and maintenance costs.
**D. High Implementation Costs for Smaller Utilities**
Small utility providers may perceive the cost of IoT adoption as a barrier. Using cheap sensors, small computers, and shared resources can make IoT systems easier to use.
This includes shared SCADA hubs and plans for gradual deployment. It also helps to avoid expensive equipment like local servers. This approach can benefit small-scale operators.
Future Outlook for IoT Water Quality Monitoring
The fast digital change is giving businesses chances to improve efficiency and increase productivity. To stay competitive in this changing world, it’s important to adopt key innovations early. This helps ensure you remain relevant.
AI and Machine Learning-Driven Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are changing how we analyze predictions and understand behavior. These advanced algorithms can analyze large cloud databases.
They can find trends like sensor drift or unusual pump current behavior. These technologies help schedule maintenance on time. This prevents equipment failures and reduces unexpected downtime.
Integration with Smart Cities and Digital Twins
Cities using IoT systems to manage things like streetlights, sensors, and cameras can improve efficiency. They can do this by adding real-time water quality monitoring. This integration helps industries follow regulations better. It provides a clear and connected way to manage the environment.
Edge Computing and Sustainability for Rapid Processing
The trend is moving toward creating low-power IoT setups (29 W). These setups are made for continuous use and aim to reduce energy use.
This aligns with sustainability goals. Using programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and IoT gateways means less manual work is needed. This reduces travel to remote places and lowers the carbon footprint.
On-site edge computing allows for quick data processing and alarm handling. This does not depend on cloud systems. It makes sure that important actions, like turning off valves, happen even if the internet is down.
conclusion
More people around the world are starting to use IoT-based systems to monitor water quality. These systems use AI and ML to analyze cloud data. They find complex insights that humans often miss.
IoT sensors and devices are changing how we monitor water. They offer preventive maintenance, accurate control, improved surveillance, and remote management. Coda and similar companies offer full solutions to track water quality in real-time.
They use some of the most accurate and high-resolution sensors in the industry. Their new method is setting standards for easy integration and better performance in water monitoring technology.