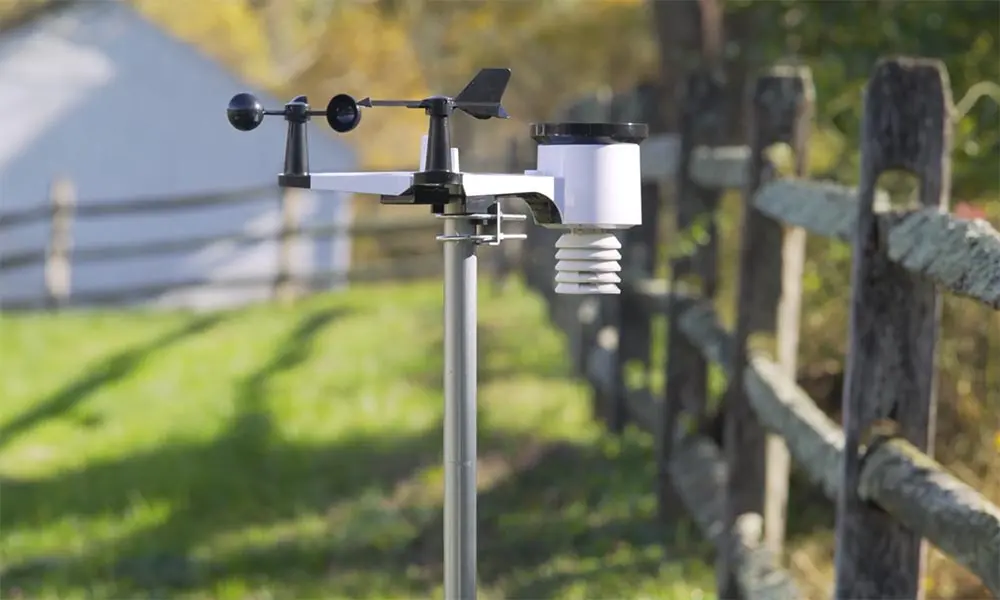
where to mount weather station
The location of a weather station is very important for accurate weather data. Proper placement helps ensure that measurements like temperature, humidity, and wind speed reflect real conditions. This avoids interference from human-made or natural factors. Here are some key tips for placing weather stations effectively:
1. Far from Obstacles
We should place a weather station in a clear area. It must be away from tall buildings, trees, or other things that could block the wind.
These barriers can create small weather patterns that do not show the larger area. Wind sensors should be placed at least 10 meters (about 33 feet) above the ground. This helps reduce interference from wind at the surface.
2. Above Natural Surfaces
We should cover the area around a weather station with natural grass or plants. Surfaces like asphalt or concrete can trap heat. This can change the temperature and humidity readings. It can make the area warmer than the places around it.
3. At Prescribed Heights
We should install temperature and humidity sensors 1.25 to 2 meters (4 to 6.5 feet) above the ground. This height helps us collect data that shows average conditions. It also allows us to compare different stations in a consistent way.
4. Far from Artificial Heat Sources
To avoid high temperature readings, stations should be placed away from certain areas. They should not be near buildings, parking lots, or air conditioning units. Also, keep them away from machines that make heat or steam. To lessen the effect of nearby objects, we suggest a distance of at least four times the height of the nearest obstruction.
5. Safe and Reachable
While environmental factors are very important, practical considerations matter too. The station should be located in a safe area. This will help stop vandalism or damage.
It should be easy to reach for regular maintenance, calibration, and data collection. This way, we can protect the environment.
6. Consistent with the Purpose Intended
The station’s purpose can affect where it is placed. For farming, farmers might put it near crop fields. This helps them get important data for their decisions.
Meteorologists should set up weather stations in cities. These stations measure local conditions that differ from those in rural areas.
7. Taking Elevation into Account
Elevation affects temperature and wind patterns. Higher areas are often cooler and can have stronger winds. Weather stations need to be at the right height to show the area’s usual conditions.
8. Regarding the Surroundings
The land cover near weather stations is very important. Weather stations should be far from buildings, trees, and water. This helps stop shadows and changes in airflow.
Being near water can create small climate zones. These zones can have different temperatures and humidity levels than the area’s averages.
9. Minimizing the Impact of Microclimate
Small features like hills, valleys, and water can create small climate areas that change readings. We should place stations in areas with low influences. This will help keep the data consistent.
10. Tracking Atmospheric Conditions
We should set the installation height based on the atmospheric layer we are studying. In most cases, we install sensors between 1.5 to 2.5 meters (5 to 8 feet) above the ground in rural areas. In urban settings, we may need to make adjustments to account for heat island effects.
By thinking about these factors, we can place weather stations in good spots. This will help us get reliable data for many uses, like farming, city planning, and climate tracking.