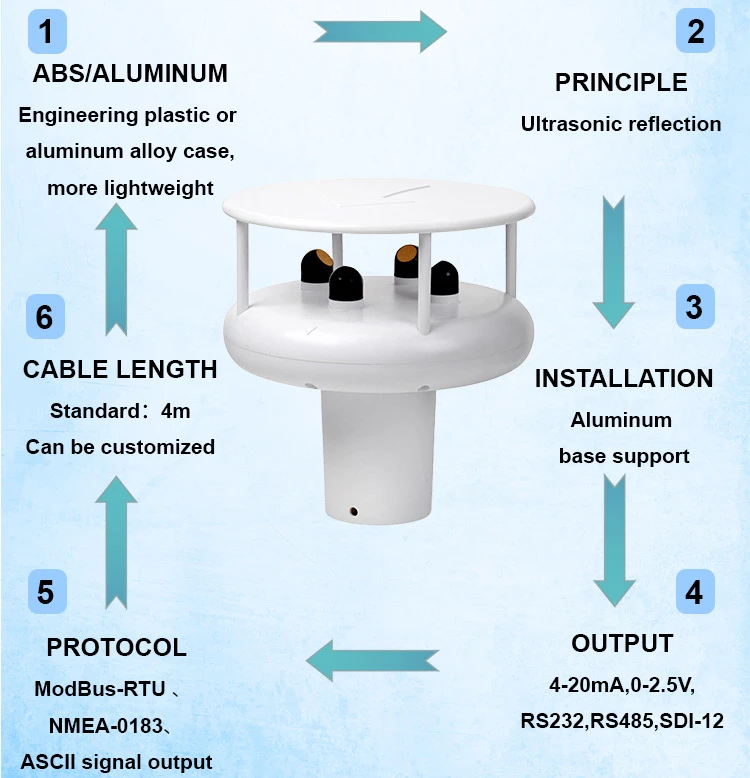
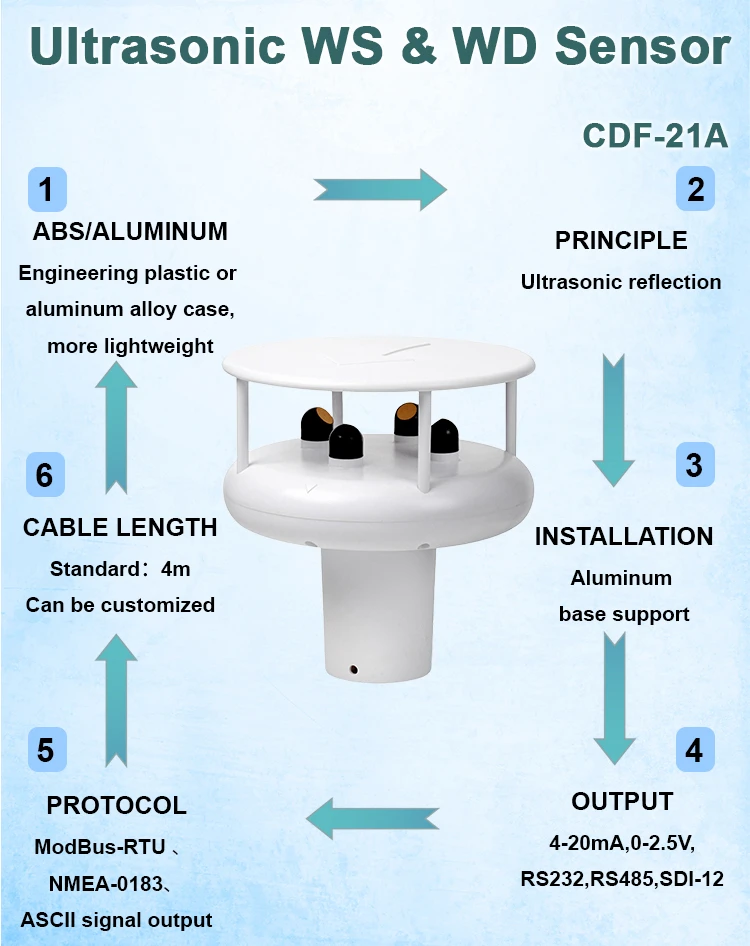
Ultrasonic wind speed and direction sensors: principle and applications
Ultrasonic wind speed and direction sensors are important for weather studies. They give helpful information about weather conditions. Let’s see how they work and where they are used:
Principle of Wind Speed Measurement:
The sensor works on the time-of-flight principle. It has two or more ultrasonic transducers placed in specific spots. These transducers send out and receive ultrasonic waves. When there is no wind, the travel time of these waves stays the same.
When wind is present, it changes how fast the ultrasonic waves seem to move to the sensor. The sensor measures the time differences of the waves traveling with and against the wind. It then calculates the wind speed using vector addition principles.
Principle of Wind Direction Measurement:
To find wind direction, the sensor uses pairs of ultrasonic transducers. These are arranged in a circle or a specific shape. By checking wind speed data from different pairs, it can determine which way the wind is blowing. This direction is found by comparing wind speeds at various angles.
Ultrasonic wind speed direction sensors Applications
Agricultural Meteorological Monitoring:
We watch wind conditions on farms to see how they affect crop growth. This includes pests, diseases, drying crops, and wind damage. For example, strong winds can make some fragile crops fall over. By measuring wind speed and direction, farmers can take steps to lower these risks.
Greenhouse Environment Control:
In greenhouses, knowing the wind speed and direction helps improve ventilation systems. Changing vent openings based on the wind helps control temperature, humidity, and gas exchange. This creates a better environment for plants to grow.
Irrigation System Management:
Data on wind speed and direction helps irrigation systems work better. For example, strong winds can affect how sprinklers spray. Adjusting the spray range and direction can stop uneven watering and water loss from wind drift.
Farmland Micro-Climate Research:
Scientists use ultrasonic sensors to measure wind speed and direction in farms. This research helps us see how wind, temperature, humidity, and other factors work together. It gives important data to improve farming methods and support better decisions in farm management.