A Beginner’s Guide to Noise Sensors: What You Need to Know
Imagine walking into a home that automatically lowers noise. Or think about being on a factory floor where loud sounds are watched closely to keep workers safe. This is not just a dream for the future. You can use noise sensors today.
These new devices are changing how we use smart homes and factories. They offer solutions that make things more comfortable, safe, and efficient. It is important to know about noise sensors if you want to use new technology. This technology can help improve homes and workplaces.
What Are Noise Sensors?
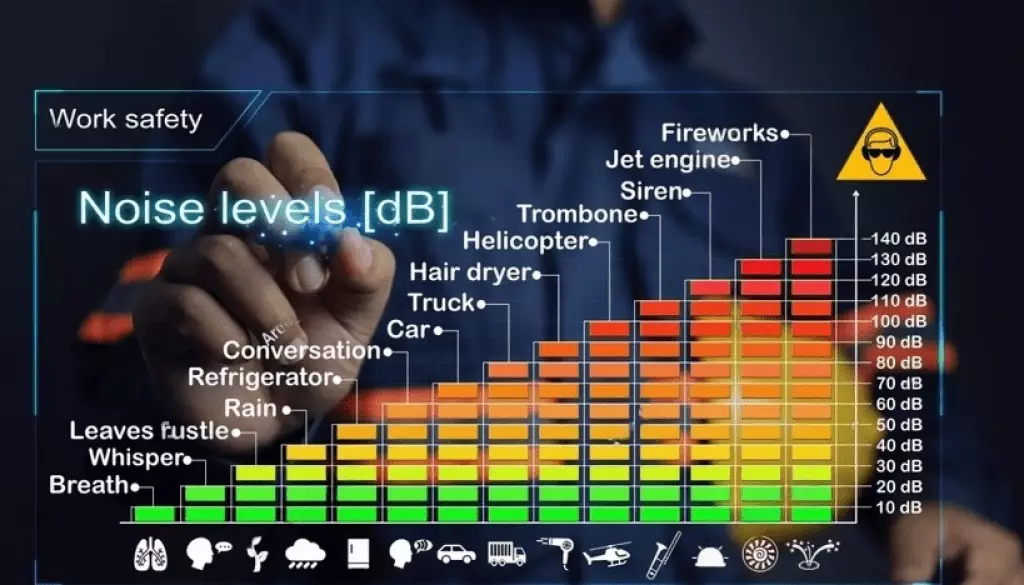
Noise sensors are special tools. They measure and analyze sound levels in real time. And play an important role in creating quieter and safer places.
They detect sounds and respond in the right way. Noise sensors come in two main types: acoustic sensors and digital sensors.
– **Acoustic Sensors:**
These devices have microphones that pick up sound waves. They are best for applications that prefer analog systems.
– **Digital Sensors:**
Digital sensors can process signals better than before. They study sound data with great accuracy. This makes them great for smart homes and industrial monitoring systems.
Key Components and How They Work
Noise sensors have several key parts that work together smoothly to do their jobs. Here is a summary of the main parts:
– **Microphones:**
The main part of the system, microphones pick up sound waves and change them into electrical signals. You choose types like condenser or dynamic microphones based on what you need and how well they perform.
– **Amplifiers:**
These devices increase the strength of electrical signals from the microphones. This helps with more accurate data processing later.
– **Digital Signal Processors (DSPs):**
DSPs act as the “brain” of the sensor system. They use smart methods to understand signal data. They remove unneeded frequencies and give precise sound level measurements.
These parts help the sensors see what is around them. They check sound levels and start the right responses.
Applications and Use Cases
Noise sensors can be used in many places.
– **Smart Homes:**
In homes, these sensors can lower noise, change lights based on sound, or control audio systems. They also help cities keep track of noise pollution to stay within safe limits.
– **Commercial Spaces:**
Offices and retail stores use noise sensors. These sensors make places more productive. They control noise with sound-dampening systems. They also let staff know when noise levels are too high.
– **Industrial Workplaces:**
Manufacturing plants use sensors to detect noise. These sensors check machines, protect workers, and ensure quality. They keep the sound levels steady while they work.
Benefits and Challenges
Using noise sensors has many benefits, but there are also some limitations to think about.
Advantages:
– **Better Noise Regulation:** They lower loud sounds. This helps you relax and focus in different places.
– **Better Security:** Noise sensors can find strange sound patterns. This helps to spot security threats.
– **Energy Savings:** Keeping sound levels in check helps save energy in smart systems.
Limitations:
– **High Costs:** Advanced models with better features can be costly to set up and keep running.
– **Environmental Interference:** Placement errors or outside factors, like air currents, can affect how precise the measurements are.
– **Setup Complexity:** You might need some technical skills to install and set up things based on what you need.
Installation and Maintenance
To install noise sensors, follow these key steps for the best results:
– **Strategic Placement:** Put the sensor where you want to check sound levels. Good places to look are entrances, open rooms in homes or offices, and areas with equipment in factories.
– **Mounting and Connectivity:** Use the brackets or glue that come with the sensor to secure it. Then, connect it to a power source and the main monitoring system.
Changing calibration settings is important. It helps boost performance for the specific environment and its needs. This means fine-tuning sensitivity levels and looking at background noise conditions.
Routine maintenance is very important to keep noise sensors working well.
Cleaning: Dust and dirt can make microphones work poorly. Cleaning them often helps keep the sensors accurate.
Software Updates: Keeping the sensor’s software updated gives you the latest features. It also makes performance and functionality better.
Power Supply: Check the power source often. Change the batteries or recharge them when needed. This will help prevent interruptions.
Understanding Digital and Acoustic Noise Sensors
Digital noise sensors and acoustic noise sensors are quite different. They differ in technology, how they can be used, and their performance measures.
Technology:
Acoustic sensors use standard microphone systems. Digital sensors use smart signal processing. They use small computer chips and software to study sound closely.
Digital sensors perform well in complex settings where precise sound measurement is important. Acoustic sensors are effective for straightforward configurations or basic sound monitoring.
Performance Metrics:
Digital sensors are very accurate, reliable, and have many options to choose from. They provide real-time data for analytics. This data can be tailored for specific uses with greater flexibility.
Emerging New Ideas in Noise Sensor Technology
New advancements are creating smarter and more precise systems. These systems can handle noise in a smart way.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) helps us use past sound data. It helps make better predictions and automatic improvements.
Improved Sensitivity: Using new materials and designs makes sensors more precise and sensitive.
IoT Integration: Modern noise sensors can now easily connect with other smart devices. This helps make automated sound control systems.
Exploring the Role of Noise Sensors
Noise sensors help control sound in homes and factories. By knowing the different types, uses, benefits, and drawbacks, you can make smart choices about how to use them.
Noise sensors provide good ways to make your home quieter. They also help keep workers safe in industrial areas. Using their potential can improve the quality of life or work with better noise control technologies.