How to Define hydrology ?
Hydrology looks at how water moves and spreads across the Earth. It also looks at the properties of water and the processes that cause changes. Researchers can split it into different branches. This is based on various research angles and uses.
They mainly classify it by the subject being studied and how it can be used. How do we definition for hydrology?
At first, the study divides hydrology by its focus:
– Research Focus:
This study looks at how rivers work. Rivers get their water from various sources.
This text explains how runoff happens and how floods form. It also talks about how sediment moves. It also shows how rivers connect with other water sources like groundwater, lakes, and swamps.
– Real-World Uses:
River hydrology gives us ideas and support for managing rivers. It helps stop floods and control drainage. It also helps to manage water.
– Research Focus:
This text looks at the water balance in lakes. It studies how water on earth moves in lakes and how sediment builds up. It also looks at issues like flooding and cyanobacteria outbreaks.
– Real-World Uses:
Lake hydrology is the study of how lakes work. It helps keep lakes safe. Also helps us make water resources and keep water clean. It also helps us to predict disasters.
Subsurface Water
Research Focus: This area looks at how groundwater forms, moves, and spreads. It also looks at how we develop, use, and protect groundwater resources. It also looks at how ground water interacts with earth surface water.
Real-World Uses: Groundwater hydrology helps water supplies manage our groundwater. It makes sure we have safe drinking quality of water and stops contamination.
Glacier
Research Focus: This area looks at how glaciers form, grow, move, and melt. It also looks at how we use and save glacier water. It looks at how melting glaciers impact global climate change.
Real-World Uses: Glacier hydrology helps us take care of our water resources. It also aids climate change studies and restores ecosystems in glacier regions.
Other Types
Swamp: This field looks at how water river flows in swamps. It also looks at how plants and water interact.
Estuarine: This field looks at the water features of estuaries. It looks at changes in salt levels, tidal effects, and how sediment builds up.
Next, let’s look at the work done in the hydrology division.
1. Engineering Hydrology – Research Focus:
This field provides data and calculations about water. It helps to plan, design, and manage water projects. These projects include hydroelectric power, water transport, roads, bridges, and other engineering works.
Environmental engineers use hydrology in many ways. They make plans for water resources and predict floods. They also manage reservoirs and plan for urban drainage systems.
2. Agricultural Hydrology
– Research Focus: This study mainly looks at how to develop and use water resources for farming. It includes irrigation, drainage of farmland, soil moisture, crop water needs, and other related topics.
3. definition for Forest hydrology
– Research Focus: This field looks at how forests impact process by which water. It looks at how forests influence rainfall, surface runoff, evaporation, and soil moisture. This means looking at how forests affect water systems. It also includes learning how we develop and use water resources from forests.
– Application Context: Forest hydrology helps us learn how to protect forests. It helps create forests that save water and stops forest fires.
4. Define Urban Hydrology
– Research Focus: This field looks at solve water related problems in cities. It covers urban stormwater runoff, flood control, drainage, and the use and protection of city water resources.
– Application Context: Urban hydrology helps with city planning. It is important for managing rainwater. It also helps with flood control and drainage in cities.
5. Additional Categories
Environmental hydrology looks at how changes in the environment impact water. This includes how climate change impacts water resources. It also looks at how pollutants move in water systems.
Ecohydrology looks at how water cycles impact ecosystems. It looks at wetlands and checks the health of river ecosystems.
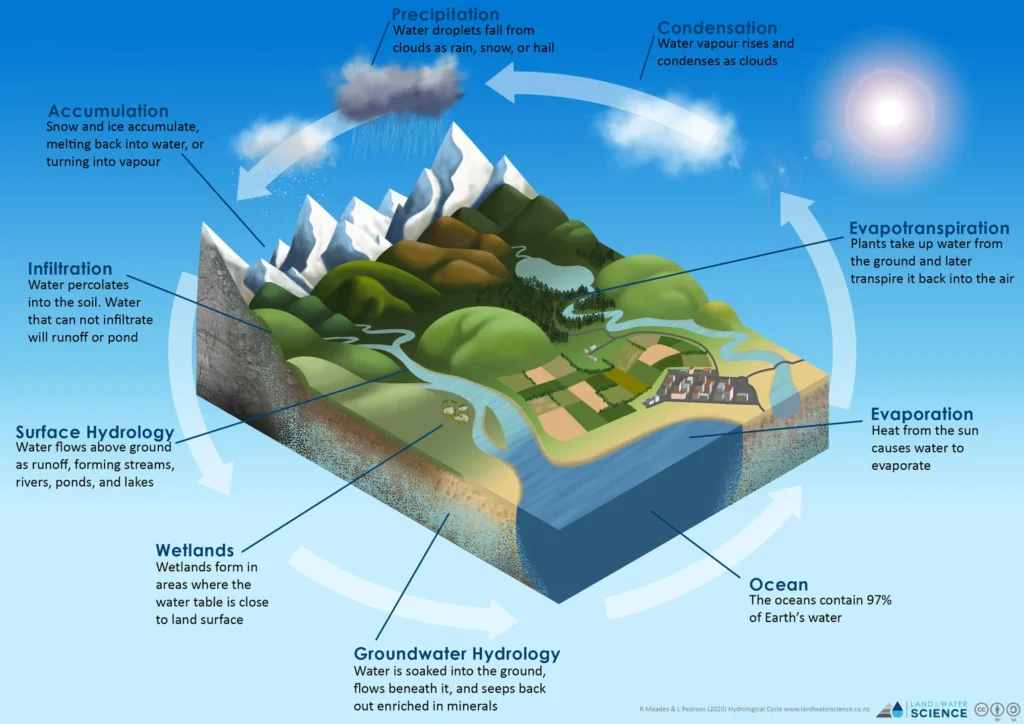
Third, let’s look at the water cycle. We can also divide hydrology by the different phases of the water cycle.
1. definition for Precipitation hydrology
Research Focus: This field looks at how precipitation works and what its features are. It examines where rain and snow occur. It covers types and sources, like rain, snow, and fog. It also looks at the amount, strength, and timing of these events.
Application Context: The study of precipitation hydrology provides crucial insights for water resource management, flood forecasting, and agricultural irrigation planning.
2. definition for Surface Water hydrology
Research Focus: This field studies how surface water bodies, like rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, are spread out and move. It also looks at evaporation, infiltration, and how we collect and analyze this movement of water.
Application Context: Surface Water Hydrology is used in flood warning systems, water management, and water resource occurrence distribution. Groundwater is also important.
Research Emphasis: Looks at how ground water flow is shared, moves, is stored, and is taken out.
Practical Application: Groundwater hydrology helps us take care of our groundwater resources. It also helps give clean water and stop contamination.
3. Hydrometeorology
Research Focus: This study looks at how water processes connect to weather elements. It looks at how rainfall, evaporation, and transpiration impact water activities.
Meteorologists use hydrometeorology to forecast weather. They also handle water resources and get ready for floods. It helps predict how changes in the weather affect the water cycle.
Hydrology can be classified in different ways:
By object of study: This looks at different water bodies and natural places. These include rivers, lakes, groundwater, and ice from glaciers. This field looks at how areas like engineering, farming, forestry, and city planning use hydrology.
The hydrologic cycle looks at the stages of the water cycle. These stages are precipitation, surface water, groundwater, and hydrometeorology.
Each classification has its own focus, but they are linked and work well together. They help scientists study how water moves and changes. These categories provide a scientific way to manage water resources. They help keep the environment safe and support growth that lasts.