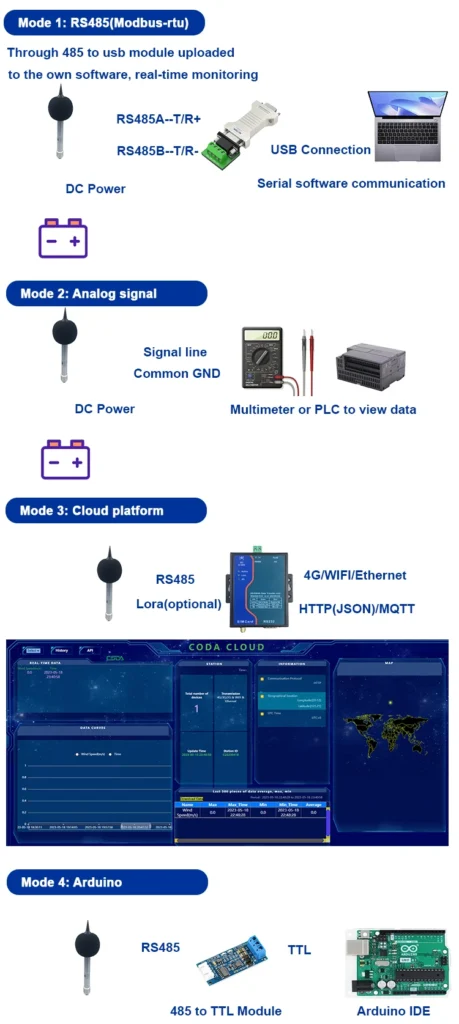
An Basic Guide to Noise Sensors: All Essential Information You Require
Picture entering a house that automatically reduces noise levels when it detects loud sounds. Or think of a factory floor that watches and reduces sound to keep workers safe. This is not merely a fantasy; it’s the truth with outdoor noise sensors. Smart devices are now a key part of homes and industries. They provide solutions to improve comfort, safety, and efficiency. Understanding noise sensors is important for both people and professionals. They want to use advanced technology to improve living and working spaces.
What Are Noise Sensors?
Noise sensors are advanced instruments crafted to assess and track sound levels in real-time. They are essential in fostering quieter environments by identifying and reacting to ambient noises. There are primarily two categories of noise sensors: acoustic and digital.
An acoustic sensor employs a microphone to detect sound waves. These instruments are ideal for conventional uses where analog technology is preferred. Conversely, digital noise sensors use sophisticated signal processing methods to evaluate sound data. They offer more accurate and dependable measurements, making them perfect for contemporary smart home and industrial applications.
Key Components and Their Functionality
Outdoor noise sensors consist of several crucial components that collaborate to execute their measurement tasks. Here’s a detailed examination of each component:
Microphones: These serve as the core of the sensor. They capture sound waves and transform them into electrical signals. Various types, like condenser or dynamic microphones, can be utilized, each offering unique advantages.
Amplifiers increase the signal strength after the sound waves convert into electrical signals. This enhances the clarity and precision of the noise for the next stages of processing.
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) serve as the sensor’s core intelligence. DSPs handle the amplified signals, employing sophisticated algorithms to determine the sound level. They are capable of filtering out unnecessary frequencies and isolating particular sounds, delivering extremely precise measurements.
When these parts work together, they keep an eye on the environment. They monitor noise levels and trigger systems to respond.
Applications and Use Cases
Noise sensors have a wide range of applications across different sectors:
In smart homes, noise sensors can turn on sound dampening systems. They can also control lighting and adjust the volume of entertainment systems. Noise sensors are also valuable for monitoring urban noise pollution, ensuring it remains within safe thresholds.
In Commercial Settings: Offices and retail environments utilize noise sensors to sustain a comfortable and efficient workspace. These sensors can trigger noise-dampening materials or notify personnel about excessive noise levels.
In Industrial Contexts: Factories and manufacturing facilities gain from outdoor noise sensors by enabling real-time monitoring of equipment and ensuring worker safety. They also play a role in quality assurance by maintaining consistent production noise levels.
Advantages and Challenges
The use of noise sensors offers numerous benefits, though it also presents some obstacles:
Advantages:
Enhanced Noise Management: Noise sensors assist in controlling unwanted sounds, fostering a more pleasant and efficient atmosphere.
Improved Security: In commercial and industrial settings, noise sensors can detect unusual sounds that may indicate security threats.
Energy Conservation: By regulating sound levels, noise sensors can help in lowering energy usage.
Challenges:
Cost: Installing and maintaining advanced noise sensors can be costly.
Accuracy Concerns: Environmental conditions such as air turbulence or improper placement can compromise sensor accuracy.
Installing and setting up noise sensors can be tricky. It requires skill in the technology and how to use it.
outdoor noise sensors Setup and Upkeep
The installation of a noise sensor involves multiple steps to ensure optimal performance:
Selecting the Appropriate Location: Position the sensor in areas where sound levels need monitoring. Important places include entrances, hallways, and open areas in homes and businesses. They also include machine areas in factories.
Installation and Connection: Firmly affix the sensor to an appropriate surface using the supplied mounting brackets or adhesive. Make sure the wiring is correctly done to link it to a power source and the monitoring system.
Calibration: Modify the settings according to the particular requirements and surroundings. This could include fine-tuning sensitivity or adapting to background noise levels.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure noise sensors operate effectively:
Cleaning: Dust and debris can disrupt microphone functionality. Regularly clean the sensor to maintain its performance and accuracy.
Software Updates: Keep the sensor’s software updated to take advantage of new features and improvements.
Power Supply: Frequently check the power source and replace or recharge batteries as necessary.
Comprehending Acoustic and Digital Noise Sensors
Digital and acoustic noise sensors differ significantly in their technological foundation, applications, and performance characteristics:
Technology: Acoustic sensors utilize conventional microphone technology, whereas digital sensors leverage advanced signal processing combined with digital processors. Digital sensors use MCU and software algorithms to analyze sound more thoroughly.
Digital sensors work well in complex environments where precise sound measurement is needed. Acoustic sensors are better for basic noise monitoring or simpler setups.
Performance Metrics: Digital sensors are superior in accuracy, reliability, and flexibility. You can customize them for specific applications and they deliver real-time data, enabling advanced analytics.
Evolving Trends in Noise Sensor Technology
Innovations in noise sensor technology are leading to smarter, more refined systems:
Artificial Intelligence (AI): The inclusion of AI enhances functionality by offering predictive analytics and enabling automatic adjustments based on historical trends.
Enhanced Precision: Advances in materials and design are boosting the sensitivity and overall accuracy of noise sensors.
IoT Integration: Modern noise sensors now integrate seamlessly with other IoT devices, promoting more comprehensive and automated noise management solutions.
The Growing Relevance of Noise Sensors
Noise sensors have changed from fun gadgets to important tools. They help manage sound levels in homes and industries. Knowing the different types, uses, benefits, and drawbacks of these devices helps you make smart choices about using them. Noise sensors are a reliable way to control sound. They can help you create a quieter home or improve safety in a workplace. Explore their practical applications and potential benefits to improve your living or working space through advanced noise management solutions.