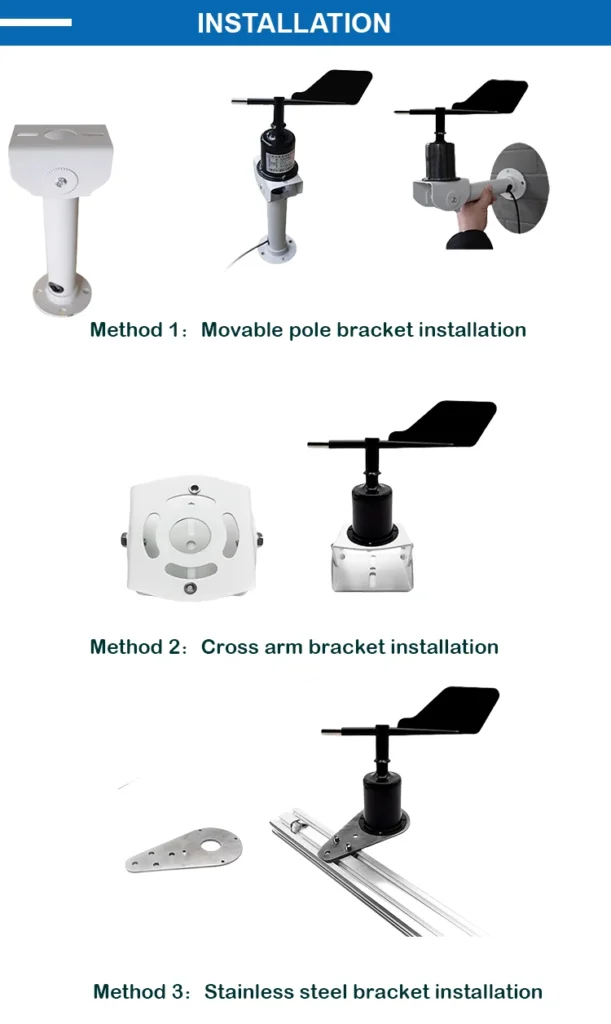
Wind Cups Anemometer | wind vane and anemometer
A wind cups anemometer measures wind speed with rotating cups. These hemispherical cups spin at rates that match the wind speed. A wind vane shows which way the wind is blowing.
It turns to line up with the wind. Together, they give important data for weather studies, forecasts, and many industrial uses.
Introduction to Cup Anemometer
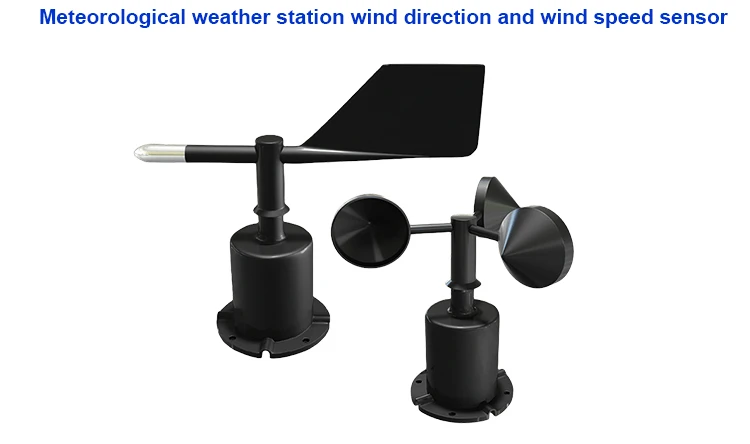
A cup anemometer, also called a wind cup anemometer, is a widely used device for gauging wind speed. Its sensing part usually has three or four hollow cups. These cups have shapes like hemispheres or cones.
The design has a bracket that looks like a trident. It has angles of 120°. They can also be on a bracket shaped like a cross with 90° angles. The curved sides of the cups point the same way.
Operation Principle:
This device is known as a rotating cup anemometer or a Robinson anemometer. It measures how fast the wind is blowing. It has cups that are linked to a shaft that spins freely.
When the wind blows, it makes the cups spin. The stronger the wind conditions, the faster they spin. The cup spins faster in revolutions per second as the wind speed goes up.
Measuring this speed helps us find the real wind speed. As the cups spin, they turn a disk or a magnetic bar. This makes pulses that match the wind speed. The system counts the pulse signal and translates it into real wind speed data.
Purpose of Cup Anemometer:
The main job is to measure wind speed correctly. This is important for weather studies, wind energy, aerospace, and environmental monitoring, among other fields. The accuracy of this device is vital for decision-making in these fields.
Key Functions:
1. Wind Speed Measurement: It gives important information for studying the weather and tracking the environment.
2. Data Recording: Lets electronic devices track and save changes in wind speed.
Application Scenarios:
– Weather Observation: Weather stations use it to give important data for forecasts and climate studies.
– Wind Power: It checks wind speeds to make sure it works well and produces energy efficiently.
– Aerospace: It checks wind speeds near aircraft to make flying safer.
– Environmental Monitoring: It keeps track of changes in wind speed. This helps support efforts to keep the environment safe.
– Agriculture helps guide how to protect crops and manage irrigation.
– Scientific Research: Helps with studies in atmospheric physics and climate science.
Introduction to Wind Vane
A wind vane shows which way the wind is blowing. Wind vane has a light arrow or pointer that is on a fixed base. It has an arrow, a counterweight, a rod, and a rotating shaft. It turns with the wind, showing where the wind is coming from.
Operating Principle of Wind Vane:
The wind vane works by balancing forces when the wind blows. When the wind blows, varying pressures affect the arrow and tail. The bigger surface area of the tail creates more wind pressure.
This causes the vane to turn around its vertical axis. It will keep turning until the arrow points with the wind direction. At this point, the arrow reaches balance with the wind pressure on both sides of the tail. This keeps the vane steady in one position.
Role of the Wind Vane:
The main job of the wind vane is to find out which way the wind blows. This information is important for weather studies, navigation, flying, farming, and more. Watching the wind change direction helps us make better choices and plans.
1. Wind Direction Indication: It provides key details about which way the wind is blowing.
2. Weather Forecasting: This uses wind speed data to help predict and study the weather.
Application Scenarios for Wind Vane:
Weather Observation: At weather stations, wind vanes and anemometers measure wind speed and direction.
Nautical: In maritime navigation, the wind vane is important for ships. It helps adjust the course based on wind changes.
Agriculture: Helps improve where to plant crops and how to water them by using wind direction information.
Aerospace: Helps measure wind changes during aircraft take-off and landing to keep flights safe.
Urban Planning: Helps design buildings and green spaces by looking at urban wind patterns.
Environmental Monitoring: It tracks how pollutants spread to understand their effects on the environment.
Summary
Cup anemometers and wind vanes are important tools for studying weather. Cup anemometers measure wind speed by how fast the cups spin. They give accurate speed data. Wind vanes show changes in direction.
These tools are important for weather observation, wind energy production, aerospace, and environmental monitoring. They greatly support progress in these fields.