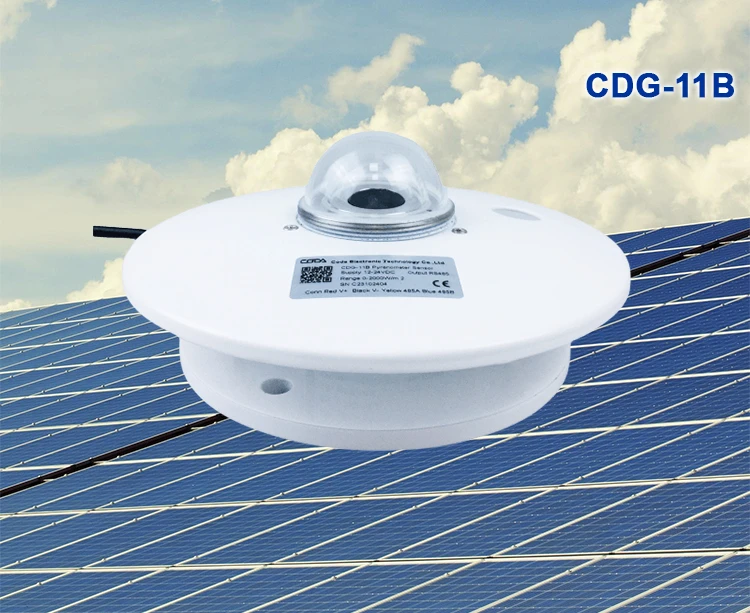
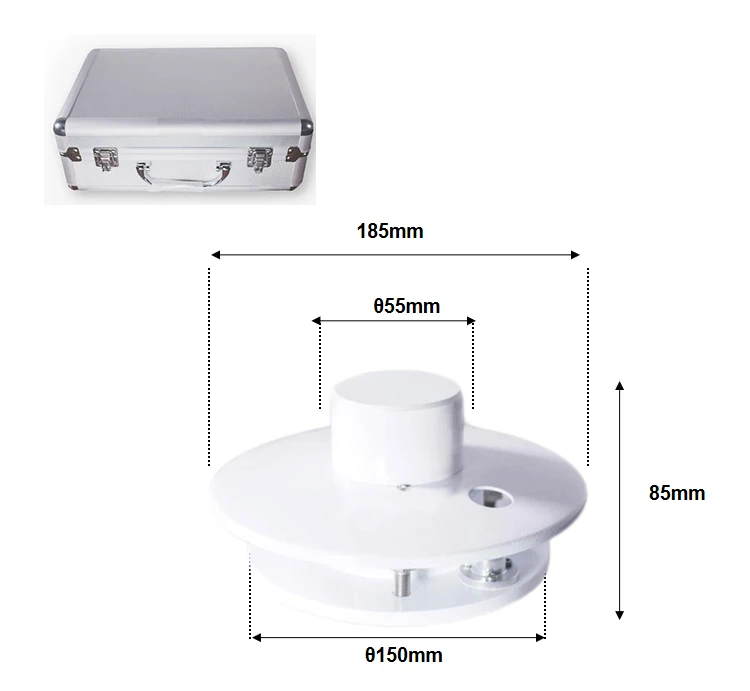
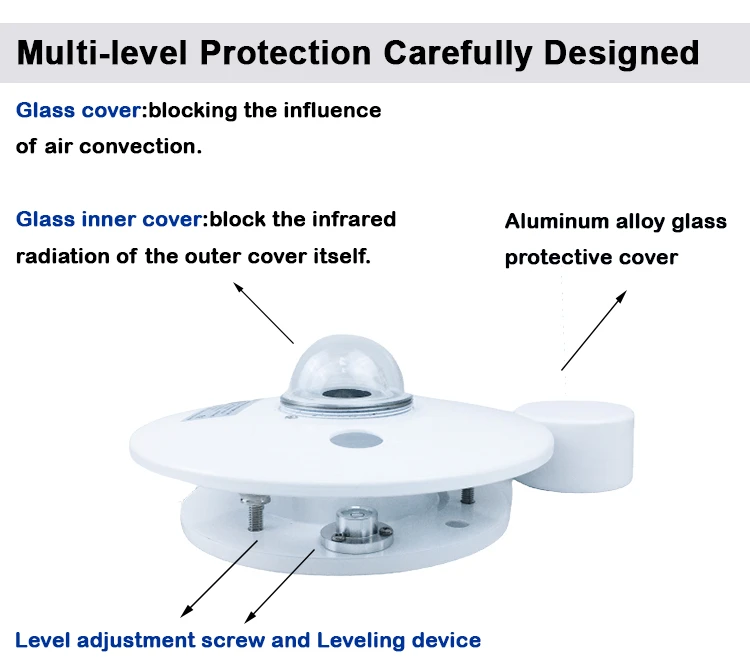
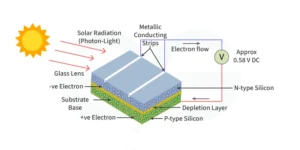
What is pyranometer used for?
A pyranometer is a tool that measures solar energy. It tracks the sunlight that hits a specific surface. This tool measures the total solar radiation a surface gets over a set time.
They are important for studying solar power and for checking solar potential. Here are six common uses of class A thermopile type of pyranometer:
1. Evaluation of Solar Energy:
We use pyranometers to measure solar energy. This energy is important for making solar power, especially in solar electric (PV) systems. Engineers and developers study the solar resource.
This helps them figure out how much energy a solar power facility can make. This helps them design and place solar panels better.
2. Agricultural pyranometer Research:
In agriculture, solar radiation sensors help researchers see how light affects crop growth and plant production. Farmers and researchers can see how much light plants get and what type of light it is. This helps them change their irrigation, fertilizing, and planting schedules. These changes can increase crop yield and make things more efficient.
3. Climate Research:
Pyranometers are key tools used in climate research. They measure solar radiation patterns that can change the world’s climate.
Scientists look at long-term trends in solar energy. This helps them see and guess changes in the weather. It also helps them forecast temperature and air cloudy conditions.
4. Building Energy Analysis:
In building science, researchers use pyranometers to measure the amount of sunlight that buildings get. This information is key for designing energy-efficient buildings. It helps us find the best way and understand how passive solar gain works. It also helps us figure out if we need shading solutions.
5. Solar Water Heating Systems:
Solar radiation sensors are important for checking solar water heating systems. Engineers measure solar irradiance to see how well these systems work. These systems use sunlight to warm water. This information helps to design and size solar water heating systems for homes and businesses.
6. Weather Monitoring:
In weather stations, pyranometer sensor measure sunlight. This helps us learn about and forecast the weather.
Solar radiation sensors are key tools for collecting solar energy. They help make farming better and understand climate change. They also improve building design and make sure solar water heating systems work well.
pyranometer advantages
Class A thermopile pyranometers are tools that measure sunlight. They have several benefits, which include:
Wide spectral response range:
We design pyranometer to be able to respond to a wide range of wavelengths. They usually detect light from the ultraviolet all the way to the near-infrared spectrum. This allows them to measure total solar irradiance, which covers much of the solar energy spectrum. It provides a full view of the solar energy that is available.
High accuracy and precision:
Modern solar radiation sensors can provide accurate solar irradiation and precise radiation measurements. We change them to meet global standards. This makes sure that the solar irradiance values are trustworthy.
High accuracy is important for research on solar energy, weather, and climate. Exact data is needed for analysis and predictions in these fields.
The sensor can talk to RS485 Modbus RTU. It has passed the international ISO 9060:2018 certification. This means it measures accurate data very quickly.
Simple operation and maintenance:
These tools are simple to use. They have a simple design. The interface is easy to use. This helps users set up and start measuring fast.
For maintenance, they do not need complex steps. Regular cleaning and occasional checks are enough to keep them working well.
pyranometer Remote sensing capabilities:
We equip some advanced pyranometers with remote sensing and data transmission functions. We can place them in wireless sensor networks.
This lets us monitor and collect data in real – time from far – off places. This is very useful for large solar farms and distant weather stations. Since it’s hard to reach the equipment there frequently, this solution works well.