What disadvantages does an automatic weather station have?
What exactly is an automatic weather station?
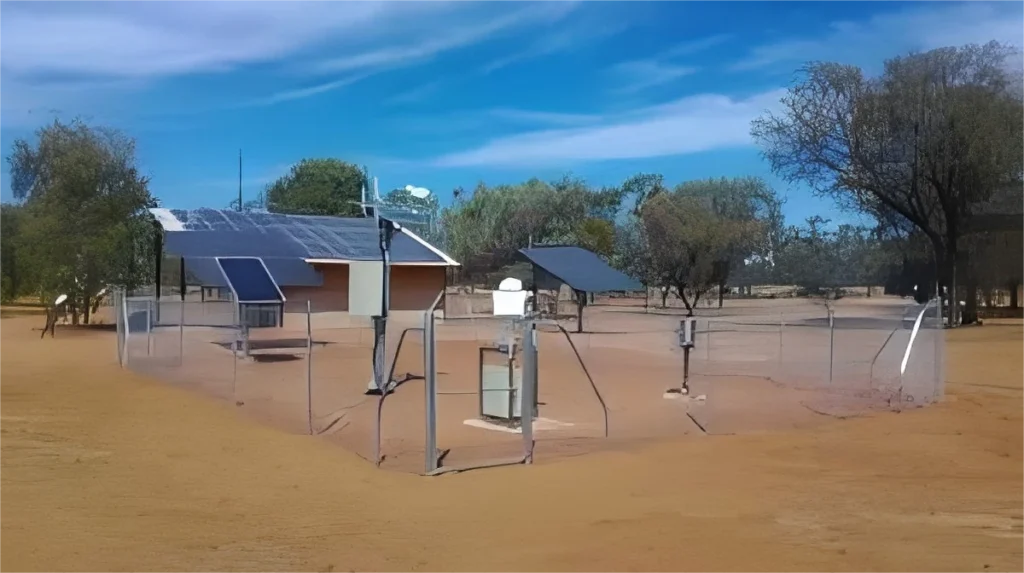
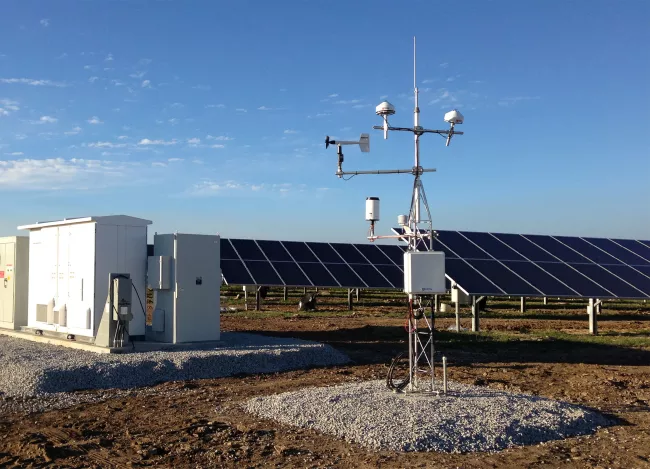
An automatic weather station is a tool used to collect weather data on its own. It has sensors that measure weather, a small computer to gather data, and a power source. – It has a vent cover that protects against radiation.
– It includes a strong enclosure.
– There is a stand for observation.
– It comes with a communication module.
– Other components are also included.
This station can automatically measure different weather factors. These include wind speed, wind direction, rain, air temperature, humidity, and light intensity. It can also make reports and send data to a central station regularly.
People rely on this equipment for weather data in different areas. It is used in fields like meteorology, farming, transportation, aviation, and marine research.
Automatic weather stations are devices that can observe and record weather data on their own. They provide benefits like high accuracy, real-time tracking, and easy data sharing. However, they also have some drawbacks. Here is a summary of the disadvantages of automatic weather stations:
Disadvantages of automatic weather stations:
Equipment malfunction and intricacy:
Automatic weather stations use advanced technology and software. Their complex design makes them hard to repair when they break. Technicians need special skills to fix them.
Susceptibility: The equipment and data loggers in automatic weather stations can be damaged or contaminated. This can affect the accuracy and reliability of weather data.
Dependence on energy and communication:
Energy reliance: Automatic weather stations need a steady power source. During power outages or when power is unstable, data collection and transmission can be affected.
Many people use solar power systems for these stations. However, long rain or bad weather can cause power shortages. This problem is especially clear in remote areas or places with weak power systems.
Communication disruptions: Automatic weather stations need a stable network to send data. If there are interruptions or a weak signal, data may not reach the central station on time. This can affect how timely and reliable the data is.
Financial Challenges:
Initial investment: Automatic weather stations can reduce labor costs in the long run. However, they have high upfront costs. This includes buying equipment, installation, setup, and training staff. For groups or individuals with limited budgets, this initial cost is a key factor in deciding to purchase.
Maintenance costs: Automatic weather stations can work on their own, but they still need regular care. Periodic check-ups are important too. We should add these maintenance costs to our overall evaluation.
Vast data volume:
Automatic weather stations gather data from many weather elements in real-time. This results in a large amount of data. For systems with limited power, storing, processing, and analyzing this data can be a big challenge.
Maintenance and calibration requirements:
Automatic weather stations lower the need for manual work. However, they still need regular maintenance and calibration. This keeps the data accurate over time. Environmental factors or long-term use can cause sensor drift.
Environmental Interference:
Electromagnetic disturbances and bad weather can impact how sensors work and the reliability of their data. This is especially true if the sensors lack proper shielding.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
Automatic weather stations send information through networks. This makes them open to data interception or manipulation. This risk is higher if strong encryption is not used.
Regional Adaptation:
In some unique places, like polar areas or deserts, automatic weather stations may need special changes. This can make things more complex and costly.
Summary of Automatic Weather Station
Automated Weather Stations consist of a network of sensors, data collection units, and communication modules. These stations can monitor weather conditions automatically. They send the data they collect to a central database using wireless or wired connections.
The goal of these systems is to lessen the need for human labor. They also improve the efficiency and consistency of data collection. Because of this, they are very important for modern weather monitoring and research. However, it is crucial to overcome the mentioned limitations for them to work fully.