Soil moisture and temperature sensors with data loggers
1. Introduction
Soil moisture and temperature are key for plant growth. They also impact the health of ecosystems and activities in farming, environmental studies, and building. While sensors measure soil moisture and temperature, data loggers play an essential role in making the sensor data useful. They serve as a link, changing raw sensor data into useful information.
2. Basics of Data Loggers
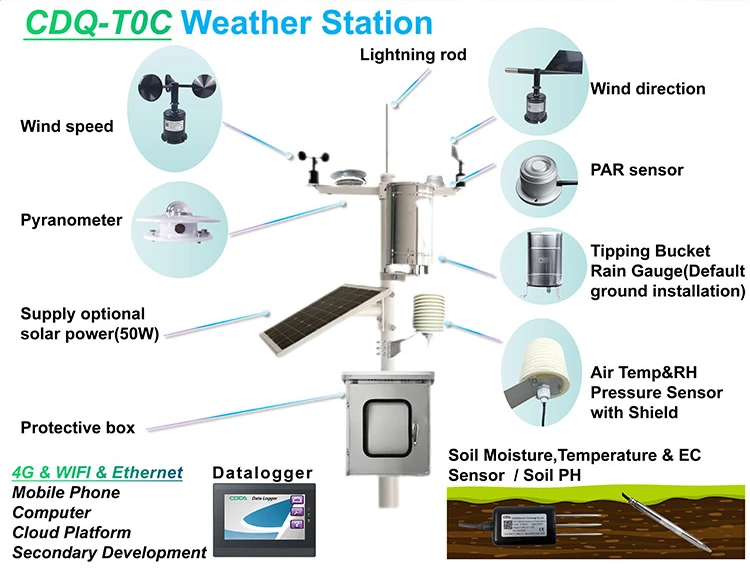
Data loggers are electronic devices that record data over time. In soil monitoring, sensors are used to collect electrical signals. The data is then stored digitally.
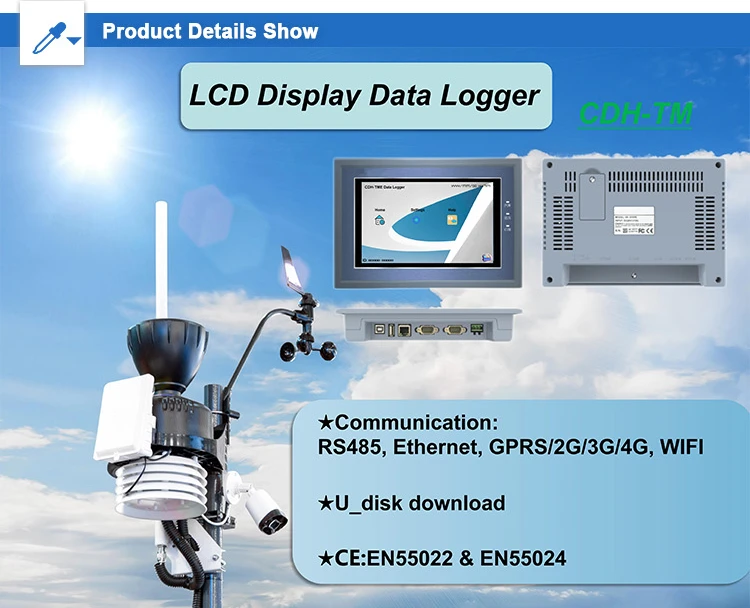
A data logger has many parts. A microcontroller controls data collection, calculations, and storage. Flash memory keeps the data. Input/output interfaces link sensors and move data.
Power management units help keep the logger working. Batteries, solar energy, or other sources provide power for them.
3. Key Functions in Soil Monitoring
3.1 Data Collection and Sampling
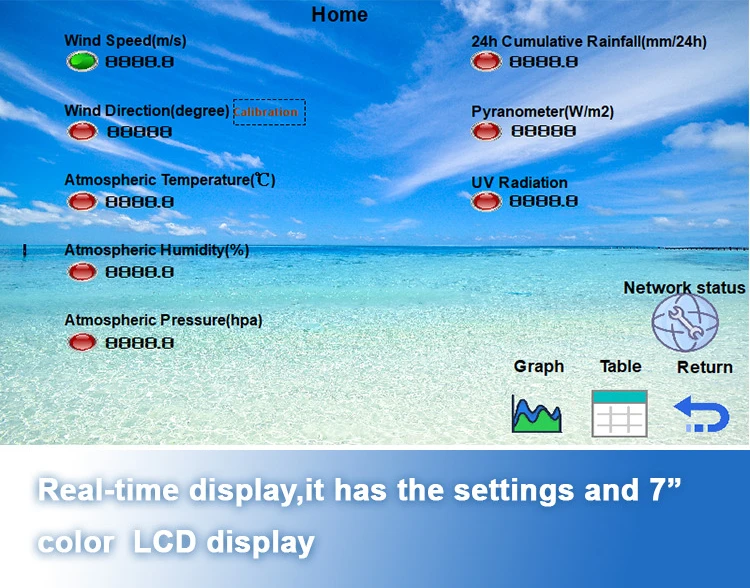
Data logger gather raw data from sensors. Sensors change soil moisture and temperature into electrical signals. The logger then turns these signals into digital values.
The sampling rate matters. For long-term monitoring, a low rate, like once an hour, is good for spotting trends. To keep up with quick changes, you need a high rate, like once a minute. This flexibility helps you get important data.
3.2 Data Storage and Management
Loggers store data reliably. Their memory can store a lot of information for a long time. Timestamping each data point helps track how soil conditions change.
Data loggers can also help with data classification. You can group data from different sensors in a field. When memory is full, some loggers remove old data.
They use a first-in-first-out (FIFO) method. Others allow users to set their own retention policies.
3.3 Data Transmission
The goal of collecting data is to use the information. Loggers can send data in wired and wireless ways.
Wired Transmission:
RS-485 is a well-known industrial standard. It allows many loggers to connect easily. It resists interference and can send data over long distances, up to 1200 meters. This is great for monitoring on a large scale.
USB: A fast and easy connection to computers. It is often used in labs or for transferring data manually.
Wireless Transmission:
Wi – Fi: Allows loggers to connect to networks. This enables remote access to data. Its high – speed transfer is great for real – time monitoring in smart projects.
Bluetooth: This is helpful for short-range data transfer. It works well between a logger and a nearby mobile device. It uses little power but has a short range of up to 10 meters.
LoRa: Ideal for remote areas. It offers communication that is low-power and can reach long distances. This makes sure data can be transferred reliably in big, disconnected areas.
4. Impact on Different Fields
4.1 Agriculture
In farming, data loggers have changed how things are done. Farmers can collect soil data. This helps them water their crops based on real moisture levels.
It saves water and boosts yields. Historical data helps farmers spot trends. It also helps them improve planting and manage pests better.
4.2 Environmental Research
In environmental studies, data loggers help scientists learn about ecosystems and climate change. Long-term data from sensors in forests and wetlands shows important information.
It shows how soil conditions impact the way plants interact with soil. This also impacts the health of the ecosystem. This data also helps validate climate models.
4.3 Construction and Geotechnical Engineering
In construction, data loggers help keep structures safe. Engineers can check soil moisture and temperature. This helps them find changes that might affect soil stability.
Too much moisture can lead to problems with the foundation. Freezing and thawing cycles can cause the soil to rise.
5. Conclusion
Data loggers are important for checking soil moisture and temperature. They gather, keep, and send data. This helps people make smart choices in many areas.
Future technology will likely improve soil monitoring. This will help with data security and reliability. These advancements will also promote sustainable practices.