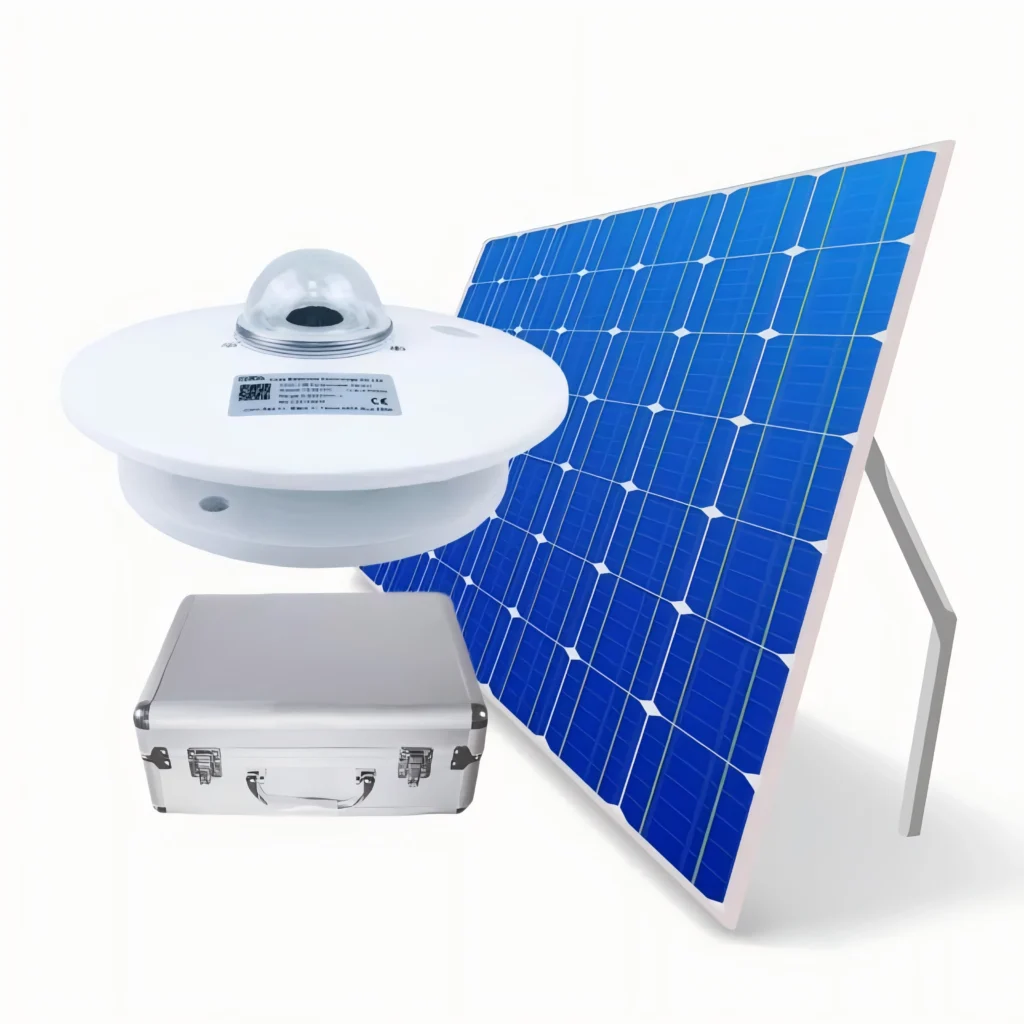
what is solar radiation measurement?
Solar radiation sensor, which is a professional-grade instrument for measuring solar radiation.operates based on the principle of thermoelectric or photoelectric induction.
This sensor can collect solar radiation data accurately. It works well with many types of solar radiation emitted recording devices and ammeters. It gives precise solar radiation measurement. This is helpful in unit area like solar energy research, weather monitoring, and farming.

Working of solar radiation sensors:
Principle of thermoelectric:
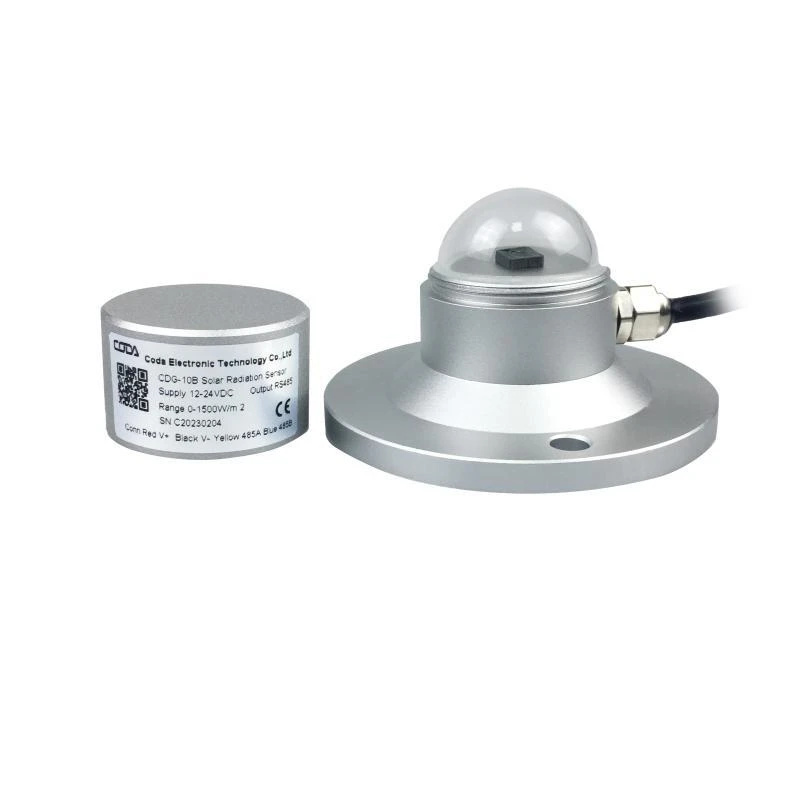
The CDG-11B Pyranometer uses blackened thermopiles to absorb sunlight. A thermopile has several thermocouples. When sunlight hits the sensor, it only gets scattered light from the sky. This happens under the shadow ring.
The sensor can be a thermopile or a photocell. It creates an electrical signal based on how bright the light is.
The Seebeck effect states that a thermocouple creates a thermoelectromotive force at both ends. When solar radiation is stronger, the heating end of the thermopile gets hotter. This increase in temperature leads to a greater electromotive force.
By measuring this force, we can learn the total strength of the emitted by the sun’s radiation. The output signal is usually a millivolt voltage. This signal has a direct link to the strength of solar radiation.
Principle of photoelectric:
Photoelectric CDG-10B total solar irradiance sensors use photoelectric elements (such as silicon photocells) to detect solar radiation. A silicon photocell is a semiconductor device.
The short-circuit current of a photocell is linked to the strength of solar radiation. In real life, we can measure solar radiation by looking at the short-circuit current of the photocell.
To get accurate measurements, we must adjust for factors like the temperature of the photocell. The photocell works best at certain temperatures. If we don’t consider this, it can lead to errors in measuring solar radiation intensity.
What is the Scattering Radiometer?
A scattered radiation sensor is a tool that measures the sun’s diffuse horizontal irradiance scattered radiation. When diffuse solar radiation hits the ground, particles like gas molecules, dust, and cloud droplets in the air scatter some of it. This scattered light is known as scattered radiation.
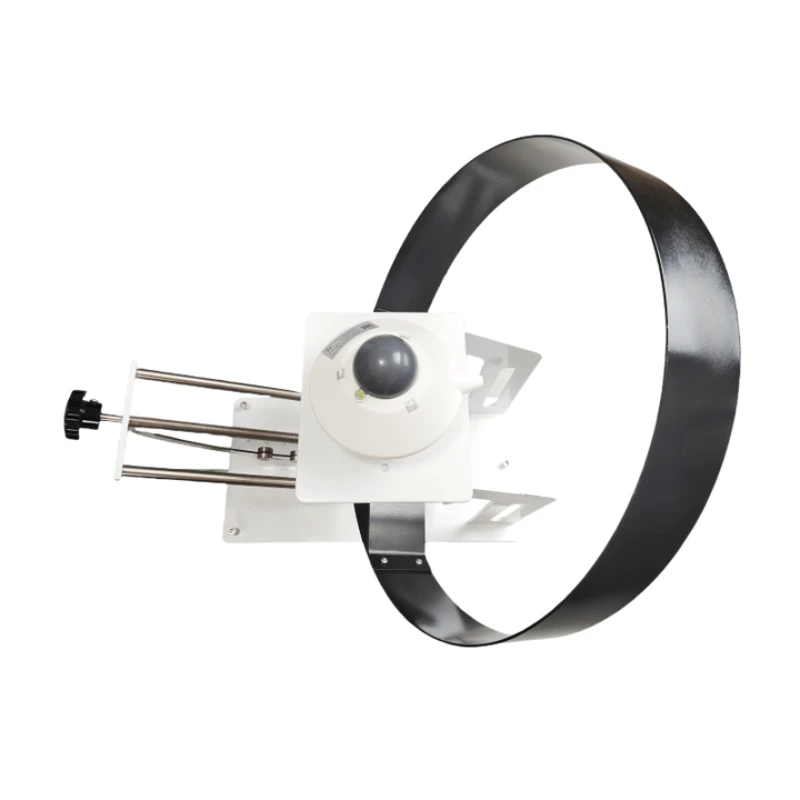
Shadow ring method:
This is a common method to measure scattered radiation. Scattered radiation sensors often have a total radiation meter with a shadow ring. The shadow ring blocks direct sunlight. This lets only scattered radiation reach the sensor’s surface.
Designing and installing a shadow ring needs careful calculations of the sun’s position. This is key for blocking direct light well.
When sunlight reaches the sensor, it only picks up scattered light from the sky. The sensor uses an induction element, such as a thermopile or photocell. This happens under the shadow ring and creates an electrical signal.
Installation:
We usually install the beam solar radiation solar irradiance is measured in an diffuse sky open area. It should not be blocked to work well. We need to keep its sensing surface flat. This helps it get global solar radiation from all parts of the sky.
We often use a special bracket for installation. We choose the height of the bracket based on what is around it. This helps us avoid nearby buildings, trees, and other objects.
Avoid large reflective surfaces, such as big metal roofs or water. These reflections can confuse the sensor. They might cause extra radiation to be detected. This can disrupt normal measurements.
The amount of solar radiation sensor should be placed flat. This is important because scattered radiation comes from everywhere in the sky. A level horizontal surface helps the sensor get this radiation evenly from all sides.
You can use a level for the installation. This makes sure the sensor is installed correctly.
The diffuse irradiation horizontal irradiance measurement surface error should not be more than ±0.5°. If the installation is not level, the sensor will get uneven radiation from different directions. This can lead to biased measurement data.
application:
solar energy industry
In the early planning of large solar panel PV plants, radiation sensors are designed are very important. They help evaluate solar resources. Measuring total solar radiation over a long time at potential sites shows how much solar energy source is available.
In a finished PV solar power station, a radiation sensor is set up to monitor solar radiation in real time. We can analyze how efficiently power is generated. We will do this by combining the data from the station with the power generation data. This will help us evaluate the performance of the PV modules.
Meteorological Monitoring
A radiation sensor is a key tool in a local weather station. It measures total solar radiation, scattered radiation, and direct radiation. This data helps meteorologists see how solar energy spreads on the reaches the earth surface.
Radiation sensors on weather balloons or planes measure radiation at different heights. This helps us study how solar radiation moves, is absorbed, and scatters passes through the atmosphere.
agricultural
In greenhouse farming, we use sensors to measure amount of sunlight inside the greenhouse. We check the total sun visible light and scattered light. This helps growers decide how much to open or close sunshade nets and insulation curtains.
For agricultural researchers, radiation sensors can help study the effects of solar electromagnetic radiation on crop growth and development. Different crops have different demands for solar radiation at different growth stages.
building trades
In the building design process, radiation sensors measure solar radiation at the site. Designers use these measurements and the local climate to plan the building’s orientation. They also choose the right window sizes and design shading devices.