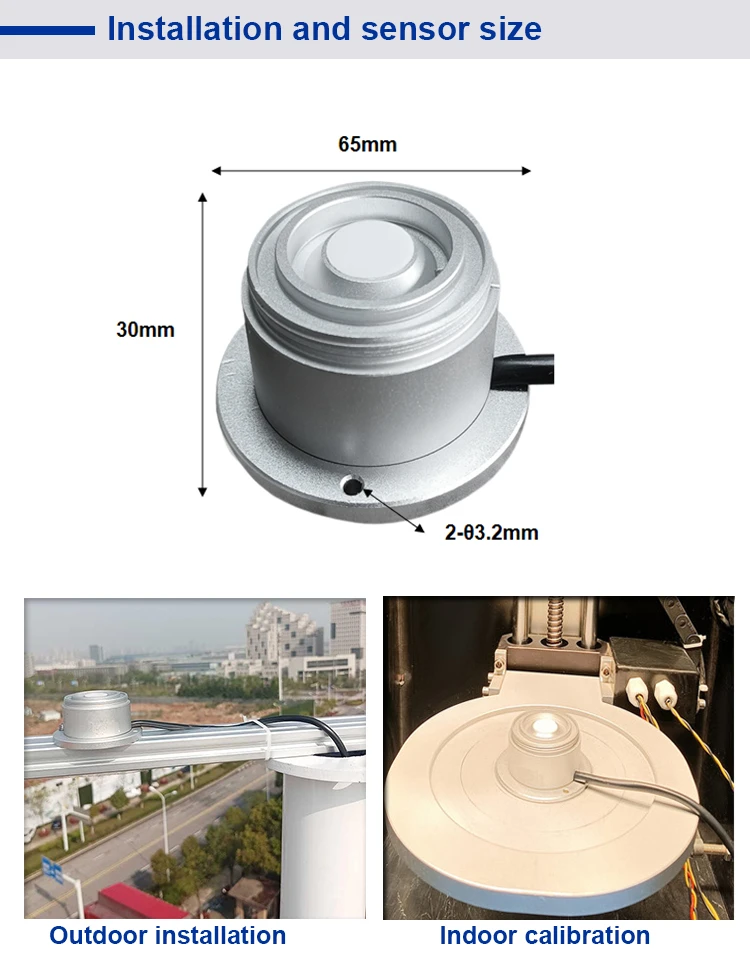
How does the PAR sensor work?
The main idea of a PAR sensor is photoelectric sensing. In this process, light exposure makes photon flux density ppfd measurements interact with the sensor’s photodiode. This interaction creates electron-hole pairs, which leads to a current in the photodiode.
The level of current matches the strength of the incoming light. This allows us to measure light intensity by looking at the current size.
In a PAR full full spectrum sensor, a glass optical filter protects the photodiode. This filter allows only visible light to pass through. This makes sure the sensor responds only to this type of light.
When the sensor measures photosynthetic photon flux density active radiation (PAR), it creates a current signal. This signal shows the intensity of PAR. You can then record and process this information.
The sensor gives an electrical signal that shows the PAR value. This value measures light intensity from 400 to 700 nanometers. This spectral range includes the light that plants need for photosynthesis. The output does not directly show how fast a plant grows or its health. It only measures light intensity.
Temperature and humidity affect how plants grow. Therefore, researchers should combine PAR sensor data with other factors and models for a complete analysis and understanding.n.
To measure photosynthetically active radiation using a PAR sensor, follow these steps:
1.Choose a suitable sensor that has a light-sensitive to light part and a light filter based on what you need.
2.Put the sensor where you want to measure. Make sure it gets the right light, like sunlight or a lamp.
3. Calibrate the sensor before you take a measurement. Calibration methods can differ by model and brand. Check the sensor’s manual for specific instructions.
4. Begin recording data by turning on the sensor. It measures PAR solar radiation sensors through the filter and sends an electric light sources signal.
5. Convert the collected data by changing the electrical signal into a PAR value. Check the sensor’s specifications and manual for the right conversion methods for your model.
Conclusion:
Understanding PAR measurements involves looking at factors like light duration, temperature, and humidity. It also requires knowing the needs and traits of plants. Different plants react closely corresponds to light levels sources in various ways. Therefore, practical uses should include detailed analysis and expert guidance based on research and experience.