Smart Irrigation Technology and Systems
The Benefits of Smart Irrigation Systems
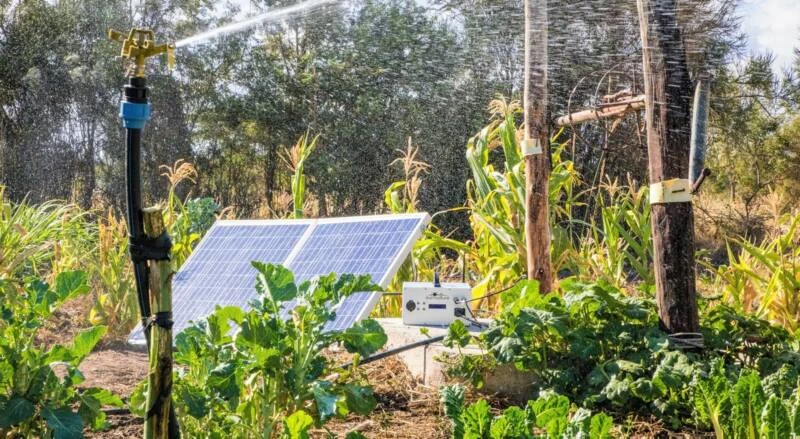
Water scarcity is a big problem in many countries. It is important to use water wisely for drinking and farming. Traditional irrigation methods, such as farming and garden drip systems, use a lot of water. This often leads to waste.Smart irrigation systems are important. They use special sensors and controls to save water and cut down on waste.
Studies show that smart irrigation technology can cut water waste by 20% to 40%. This is compared to old ways of watering plants. These systems use real-time weather data and soil moisture levels. They can choose when and how much to water the plants.
They let you change watering schedules and focus on specific areas. This helps save water, keep plants healthy, and make irrigation work better.
Smart Irrigation Technology Explained
What is Smart Irrigation?
Smart irrigation uses new science and technology to save water when watering plants. It has weather sensors, soil sensors, and controllers. These devices check the weather and soil moisture. They also control the water valves for automatic irrigation.
This technology helps make clear decisions about when and how much water plants need. It is great for saving water in lawns, farms, gardens, and more.
The use of IoT, mobile connectivity, LoRa technology, and remote sensing helps in smart irrigation systems. This allows for easy wireless control of valve switches. These systems look at soil type and weather.
They help plants get the right amount of water and cut down on waste. This new idea uses smart sensors, automatic controls, and computer systems. It works with traditional irrigation methods like sprinklers and drip systems to make them more efficient.
How Do Smart Irrigation Systems Work?
Smart irrigation systems check things like weather, evaporation, soil moisture, and plant needs. They change watering schedules on their own to be more efficient. They can be set up to water specific areas at certain times. This solves the issues that come with old watering systems.
These systems use LoRa wireless technology or home Wi-Fi to send data. Managers can control irrigation from their smartphones or computers. This means they do not need to open or close water valves by hand.
Components of a Smart Irrigation System
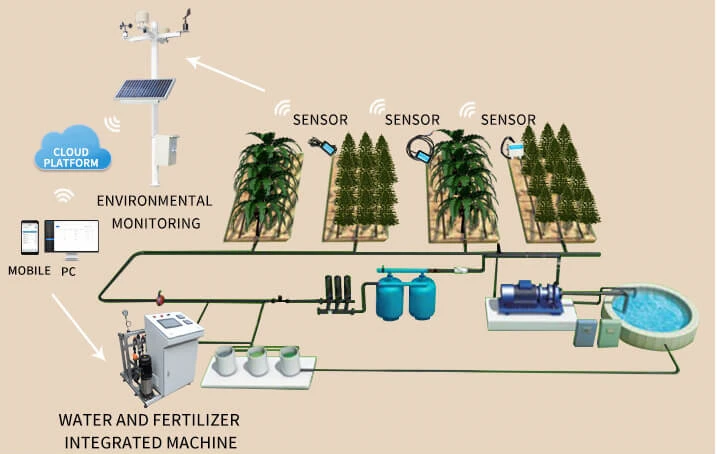
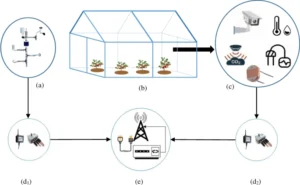
Smart irrigation works with four main parts: monitoring units, control units, transmission units, and a terminal platform. Each part is important. They work together to make sure irrigation is precise.
1. **Monitoring Units**
The system can watch the environment with sensors. The main sensors are:
– Soil moisture sensors
– Wind speed sensors
– Evaporation sensors
– Leaf wetness sensors
– Rain and snow sensors
– Data collectors
2. **Control Units**
Automated control valves are key for running things efficiently. They let you control irrigation from a distance. Common types are butterfly valves, pulse valves, and ball valves. The type of valve you choose depends on the features of the irrigation area.
3. **Transmission Units**
Data signals from monitoring units go to the control systems. They move through communication channels to the operation platform. For systems that use LoRa technology, transmission includes a LoRa gateway and a data concentrator. For people using Wi-Fi networks, routers and monitoring hosts help with this.
4. **Terminal Platform**
The terminal platform has software that helps sort and understand data. It also gives control commands. It saves data, looks at it, and makes automated instructions.
These instructions work with control units. You can usually access this platform on mobile devices or computers.
Wireless sensors send soil moisture levels and weather data to the terminal platform. The software uses this information to find out how much water is needed.
It also shows the areas that need water for irrigation. Wireless commands are sent to the control valves. This makes sure that watering is done correctly.
Factors like rising outdoor temperatures and changing rainfall are closely watched. Smart systems change watering schedules based on certain conditions. These conditions include the types of soil and the flow rates of the sprinklers.
Composition of a Smart Irrigation System
1. **Soil Moisture Sensor**
The soil moisture sensor is designed to measure the dryness of the soil directly. The probe is usually put in to the same depth as the plant’s roots.
This helps get more accurate readings. Sensors in certain places connect to nearby soil controllers. This allows for localized control of irrigation.
The management platform lets you set high and low alert levels for sensors in different areas. If the soil moisture goes over the set limit, the controller shuts the water valve.
If it falls below the limit, the valve opens. Different soil types may need special sensors. Consumers should check if the system works with their needs when buying.
2. **Evaporation Sensor and Leaf Wetness Sensor**
Evaporation sensors check weather conditions. They focus on how fast water evaporates from the soil. These sensors help decide when to water the plants. These sensors help control water flow and lower water use when watering plants.
The leaf wetness sensor acts like plant leaves. It measures changes in leaf moisture levels accurately. By looking at this data, we can tell if plants need more water or if the soil is moist enough.
Evaporation sensors check how much water is lost from the soil. Leaf wetness sensors check how much moisture leaves lose.
3. **Rain and Snow Sensor**
Watering when it rains or snows wastes water and causes runoff problems. The rain and snow sensor solves this problem. It uses metal wires on its surface to detect rain.
These wires conduct electricity when they touch rain or snow. This sends an electrical signal to the control platform. The platform then tells the controller to close the water valve.
These sensors cost about $25 each. They have a heating function that works on its own. This helps them work even in very cold winter weather. By not watering during rain or snow, users can save a lot of water and money.
4. **Wind Speed Sensor**
Strong winds during irrigation make it hard for water to spread evenly. This also makes it more difficult for the soil to take in water. Wind speed sensors can stop irrigation cycles if the wind speed goes over a set limit.
We can change irrigation schedules by checking the local weather. This helps save water in the long run.
Advantages of a Smart Irrigation System
– **Labor Efficiency**:
Smart irrigation automates tasks that used to need manual work. Users do not have to manage watering equipment or valves by hand anymore. You can manage the whole irrigation process from your mobile phone or computer. This keeps gardens and farms watered, even when you are not there.
– **Water Conservation**:
Smart irrigation systems are made to use less water. They use new methods instead of old flood irrigation. They use soil moisture data and smart methods to water plants. This helps plants grow and saves resources.
– **Remote Management**:
These systems let users analyze data and control irrigation from smartphones or computers. This allows them to manage multiple areas without being there in person. One person can run big farms effectively. This helps to reduce labor costs a lot.
– **Precision Irrigation**:
Smart systems use real-time sensor data to change irrigation methods as needed. Watering happens at set times and in specific amounts that match the needs of plant growth. This helps water all gardens evenly. It promotes healthy growth for every plant.
– **Smart Control**:
These systems have features like timed watering, remote control, and regular irrigation. They offer flexible operation modes that update quickly through cloud adjustments.