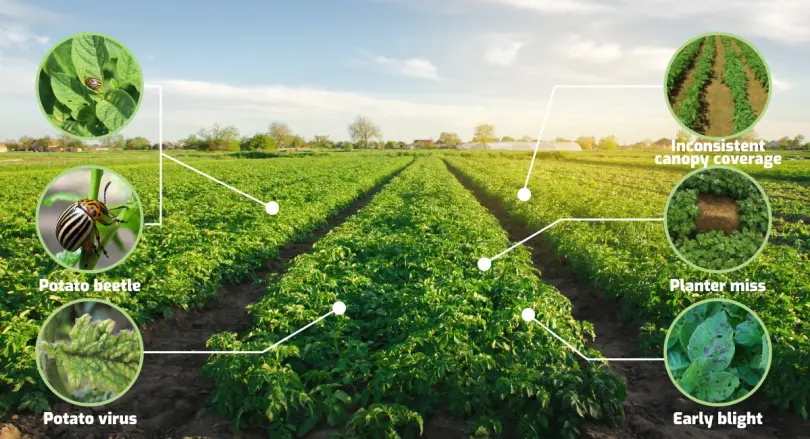
List of Agricultural Sensors and agricultural sensor station
An agricultural sensor station is a device that detects important information. These sensors turn this information into electrical signals or other forms. This process uses rules to help send, process, store, show, record, and manage information. New advances in Internet of Things (IoT) sensor technology are helping many industries, like agriculture, use sensors more often.
Agricultural weather stations measure air temperature, humidity, soil moisture, soil pH, light, and carbon dioxide levels. These sensors gather data during the crop growth process, from nursery to harvest. We use sensors to check the conductivity and pH of water and fertilizers. These sensors help keep track of mixed fertilizer solutions.
Agricultural Sensor Overview
Agricultural sensors come in two types: plant information sensors and environmental sensors. Plant information sensors track how plants grow. They collect data on plant health and analyze the conditions needed for growth.
Environmental sensors check the conditions of water, soil, and air. They help us notice changes in the environment. These sensors support healthy plant growth.
Common farm sensors measure temperature, humidity, pH, gas levels, and pressure. They also have biosensors and light detectors.
Agricultural Sensors List
Agriculture sensors are key for IoT applications that track plants and animals in real time. In farming, sensors play a key role. They help with tasks like fertilizing, spraying, and watering plants.
Farmers can check the soil, pests, and humidity levels. This helps them know when to fertilize, spray, or water. This helps save resources and lowers the environmental impact of traditional methods.
1. Temperature and Humidity Sensor
The temperature and humidity sensor checks changes in air temperature and humidity on farms. It works in temperatures from -40°C to +80°C. It can also handle humidity levels from 0% to 100%.
You can put it on walls in greenhouses or places with good air flow. For outdoor use, place it in a solar radiation shield to check the weather.
Coda’s temperature and humidity sensor uses a Swiss measurement unit. It has a microprocessor chip made in the US. This helps give accurate measurements and steady communication.
2. Soil Moisture Sensor
Soil moisture sensors are important. They show how much water crops have. The right moisture levels help roots take in water and leaves let it out. This balance helps crops grow healthy.
Coda’s soil moisture sensor checks how much water is in the soil. It uses the dielectric constant for this. This method meets international standards. It shows the moisture content in different types of soil accurately.
3. Soil pH Sensor
The right soil pH is important for healthy crop growth. The Coda soil pH sensor uses electrodes to touch the soil. This starts a reaction that creates a current. The current relates to the pH value shown as a number.
The sensor has an electrode that does not corrode. It is made from a special alloy. They seal it with flame-resistant epoxy resin. This gives it IP68 protection.
4.Light Sensor
The light sensor has three main parts: a transmitter, a receiver, and a detection circuit. All these parts are made from electronic parts.
It quickly measures light intensity from 0 to 200,000 Lux. The sensor has a fast response time.
In greenhouse farming, sensors help farmers track the sunlight that plants get. They can sense when there is too much light or not enough light. This information helps control light better. As a result, crops grow healthier and produce more.
5.CO2 Sensor
Plants take in CO2 from the air for photosynthesis. This process is important for their health and growth. Studies show that more CO2 in the air helps photosynthesis grow a lot.
Coda’s CO2 sensor uses special infrared technology to check CO2 levels in the air. It responds fast and accurately. This avoids the issues found in older electrochemical sensors. The sensor measures CO2 in a range of 0-5000 ppm and has temperature compensation to reduce outside effects.
6.Barometric Pressure Sensor
The barometric pressure sensor measures air pressure changes. This helps farmers predict the weather. They can see drops in pressure or changes in wind speed. With this knowledge, they can prepare for disasters and reduce crop damage.
For example, if air pressure is set to drop, farmers can pick their crops early. This helps avoid losses from bad weather.
7.Rain Gauge
The rain gauge shows how much rain falls. It gives important information about soil moisture from rain and snow.
Tipping bucket rain gauges are commonly used. They give accurate measurements with little error.
These gauges often work with evaporation sensors. This helps analyze soil moisture correctly.
Rain gauges are useful tools for measuring how much it rains. They also help with managing irrigation in farming.
Benefits of Farm Sensors
Irrigation System Control: precision agriculture sensors can check soil moisture, humidity, and weather data from stations. This helps them find soil moisture levels accurately. This allows us to use water on time with automated systems.
One example is the Coda multi-layer soil sensor. It connects to irrigation systems. This helps manage when and how much water is used through mobile apps.
Pest and Disease Monitoring
We use insect traps and pesticide sprayers that have sensors for farming. These tools help us check temperature, humidity, and air pressure on farms.
The monitoring takes place in real time. This helps with effective pest and disease management.
Insect monitoring devices have weather sensors. These devices help farmers choose the best insecticides. They make choices based on the data they collect.
Optimizing fertilizer management involves meticulously
Measuring soil parts like dissolved oxygen, metal ions, and hydrogen ions is important. Knowing these elements helps us check soil health and the nutrient needs of crops. This improves our use of fertilizer.
A water-fertilizer machine can test the nutrients in the soil. It can also change fertilizer levels on its own. This helps farmers work better and cut down on waste.
Improve planting efficiency
Using sensor stations in agriculture to study weather data can make planting easier and more efficient. They also help with crop management during growth cycles. For example, sensors that measure light and temperature can change based on the weather and local climate. This creates the best environment for crops and boosts production efficiency.
promote sustainable development
Using farm sensors helps promote sustainable development. These sensors give precise calculations for land use. They also cut down on agricultural wastewater and emissions. This lowers the impact on the environment and helps reach sustainability goals.
Agricultural sensor stations are important for monitoring in the water and fertilizer system. Researchers use them to measure conductivity, pH levels, and temperature of fertilizer solutions after mixing.
The system shows and uploads data to the control system using LCD screens. These sensors have memory chips that store data for up to three days. They use precise AD conversion and microchip technology. They also provide features such as data collection and automatic temperature adjustment.
Traditional farming relies on manual work and basic tools. It has its limits when compared to modern farming.
Modern farming uses the Internet of Things and sensors. These tools give accurate and timely data on crop growth. This information helps with planning and saves labor. It also improves crop types and boosts both quality and yield.