how does a wind vane work | how do wind directions work
In the field of weather map and environmental monitoring, wind direction sensors are very important. These devices are like eyes. They help us see which way the wind is blowing.
This information seems simple, but it is very important and has wide effects. It is important to know how wind direction sensors work. This knowledge helps us predict the weather, keep flying safe, and boost wind energy production.
The Basic Structure of a Wind Direction Sensor
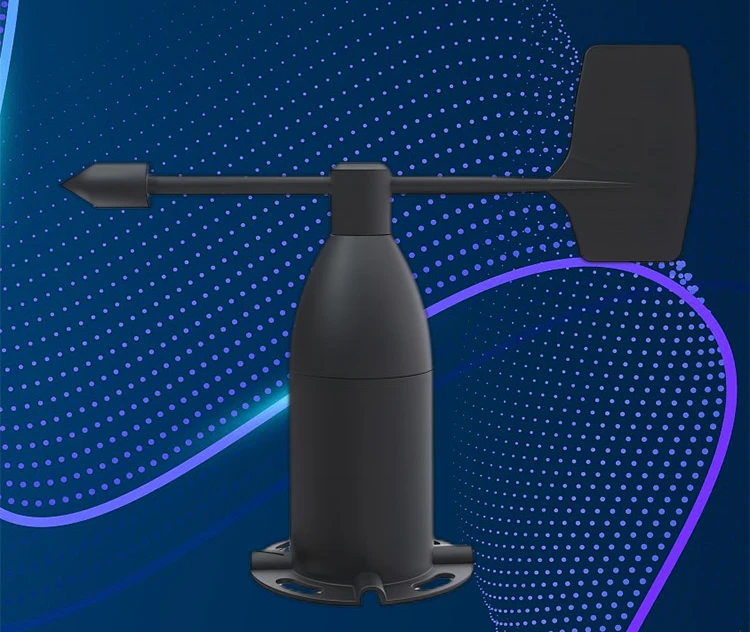
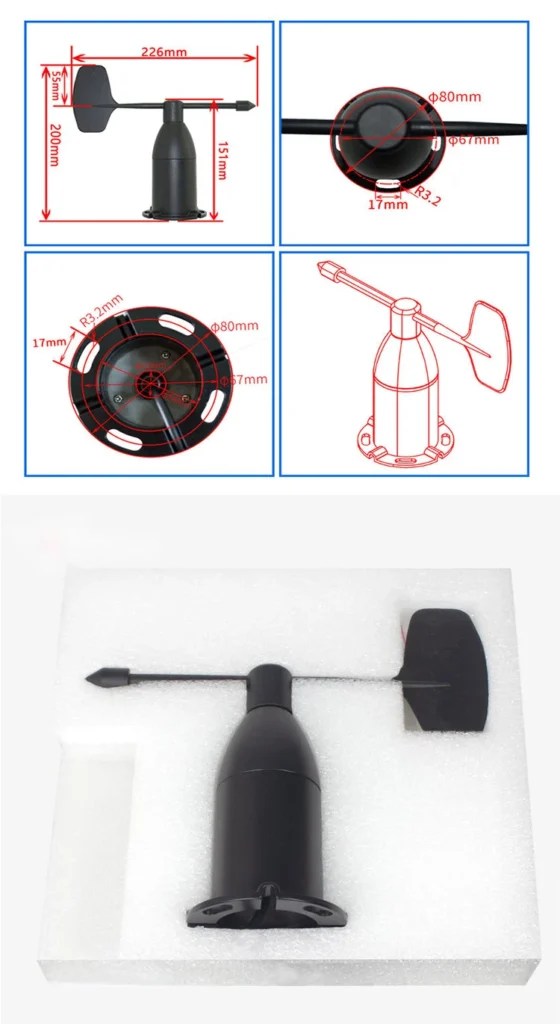
A wind direction sensor, known as a wind vane, has a simple and effective design. It typically consists of a long, slender arm, also known as a boom, with a flat, aerodynamic blade or vane at one end. The design of the vane allows it to catch the wind and rotate freely around a vertical axis.
People often place this axis on a strong base. They can attach it to a weather station, a building, or a pole. Engineers design the vane to respond quickly to even the lightest breeze. This helps make sure readings are accurate and on time.
The designer shapes the vane to make it more responsive to the wind direction. It often has a large surface on one side. This side acts like a sail to catch the wind. The other side is smooth to lower air resistance.
This design change helps the vane point in the direction of the wind. For example, if the wind comes blowing from the north, the vane will turn. The large surface of the vane will face the wind and point north.
The Working Principle
Aerodynamics laws are the basic principles that help a wind direction sensor work. When the wind blows, it exerts a force on the vane.
The shape and design of the vane make it rotate around the vertical axis. It keeps turning until it lines up with the wind direction. Once the vane is lined up with the wind, the forces on it become balanced. It stays in that position.
Most modern wind direction sensors use electronic parts. These parts change the position of the vane into a signal that can be measured. One common method is to use a potentiometer. A variable resistor connects to the axis of the vane as a potentiometer.
As the vane turns, the wiper on the potentiometer moves. This changes how much resistance there is. You can measure this change in resistance.
Then, you can convert it into an electrical signal. A microcontroller or data collection system will handle this signal.
For example, if the vane turns a certain number of degrees, the potentiometer will change its electrical resistance. The microcontroller can use a built-in calibration program.
This algorithm changes the resistance value into a wind direction reading. For example, 0° means north. 90° means east. 180° means south. 270° means west.
Different Types of Wind Direction Sensors and Their Working Mechanisms
Mechanical Wind Direction Sensors
In addition to the traditional wind vane with a potentiometer, there are other mechanical – based wind direction sensors. Some systems use gears and shafts. When the wind vane turns, it moves a set of gears. These gears then turn a set of shafts.
You can link these shafts to mechanical indicators. These indicators act like pointers on a dial. They show the wind direction clearly. These mechanical sensors are straightforward and easy to grasp.
However, they may be less accurate. They might not be as good for long-term, automated monitoring when compared to electronic sensors.
Ultrasonic Wind Direction Sensors
Ultrasonic wind direction sensors use a more advanced technology. These sensors send out sound waves in different directions. When the wind blows, it affects the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel between the transmitters and receivers.
The sensor measures how long ultrasonic waves take to travel in different directions. This helps it figure out the wind direction and speed.
For example, if the ultrasonic wave traveling in the east – west direction takes longer to return to the receiver compared to the wave traveling in the north – south direction, it indicates that there is a wind component coming from the east.
The sensor uses advanced methods to look at these time differences and find the wind direction accurately. Ultrasonic sensors are non-mechanical. This means they have no moving parts.
This lowers the risk of wear and tear. It also makes them last longer. Often, it gives more accurate and consistent measurements, especially in tough conditions.
Magnetic Wind Direction Sensors
Magnetic wind direction sensors use magnetic fields. They often have a magnetic part connected to the wind vane. As the vane turns, the magnetic part moves near a group of magnetic sensors.
These sensors detect changes in the magnetic field caused by the movement of the magnetic element. The changes in the magnetic field turn into electrical signals. The system then processes these signals to find the wind direction.
Magnetic sensors provide high accuracy and dependability. They are less affected by things like dust, moisture, and temperature than some other sensors.
Applications and Importance of Wind Direction Sensors
Wind direction sensors are widely used in various fields. In weather stations, they are an essential component for accurate weather forecasting. Meteorologists use determine wind direction data and other weather information.
This includes temperature, humidity, and wind speed. They model weather systems and predict the movement of fronts, storms, and other weather events.
In the aviation industry, prevailing winds direction is crucial for takeoff, landing, and in – flight navigation. Pilots must know the outdoor activities wind direction and speed. This helps them find the right angles for their approach. It also lets them change their flight paths.
This knowledge helps make flights safe and efficient. Wrong wind direction information can create dangerous situations. For example, crosswinds can make the plane drift off the runway when it lands.
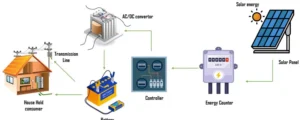
Wind direction sensors help improve how well wind turbines work in the wind energy industry. Knowing the wind direction helps operators turn the turbines to face the wind.
This makes them generate power more efficiently. This not only boosts electricity production but also helps the turbines last longer. It does this by reducing stress on their parts.
In environmental monitoring, researchers use wind direction sensors. These sensors help track how pollutants move in the air. Knowing which way the wind blows helps environmental scientists predict how pollutants spread.
This includes things like smoke from factories and wildfires. With this information, they can take steps to protect public health and the environment.
Conclusion
Wind direction sensors come in many designs and weather vane work in different ways. They are important for many parts of our lives. There are different types of wind sensors.
They range from simple traditional wind vanes to advanced ultrasonic and magnetic sensors. Each type has its own advantages and uses.
Their ability to measure measure wind speed and wind direction accurately gives important information. Meteorologists, pilots, wind energy experts, and environmentalists use this data. They rely on it for weather forecasting, aviation, wind energy, and protecting the environment.
As technology keeps changing, we can expect better and more reliable wind direction sensors. These will help us understand nature and connect with it better.