how radar sensor works
In today’s industry, it is very important to measure the amounts of liquids and solids in tanks and silos. It helps with smooth operations, managing stock, and keeping things safe.
Radar level sensors are a reliable and flexible choice for measuring levels. They use radio waves to find out how much material is in containers. These sensors have many benefits compared to older methods, such as float-based or ultrasonic sensors.
In this article, we will look at how radar level sensors work. We will look at their parts and uses. This will help us understand how radar level sensor work well in different industries.
Working Principles of Radar Level Sensors
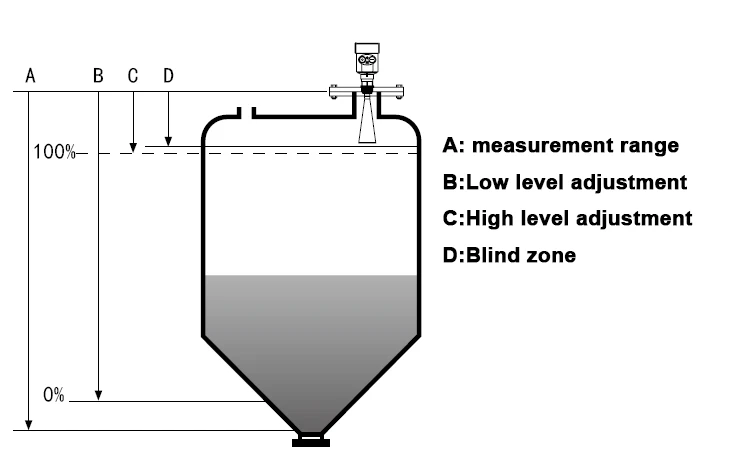
A radar level sensor works based on the time-of-flight (ToF) measurement. This is like how aviation and weather radar systems measure distance.
Radar level sensors send out high-frequency waves. These waves are usually in the microwave range. They range from 6 GHz to 80 GHz. Different frequencies give different levels of performance.
This makes them good for many uses. They send these waves to the surface of the material in a tank or silo.
When the electromagnetic waves hit the surface of the liquid or solid, they bounce back to the sensor. The sensor has an antenna that receives these reflected waves. We can measure the time it takes for waves to travel from the sensor to the material and back. This helps us find the distance between the sensor and the material level.
Key Components of Radar Level Sensors
Transmitter
The radars transmit creates and sends out electromagnetic waves. It has a microwave oscillator that makes high-frequency signals. These radar signal are made stronger and sent to the antenna to be transmitted.
The quality and strength of the waves are important for how well the sensor works. This impacts its range, accuracy, and ability to work in various materials or conditions like dust, steam, or foam.
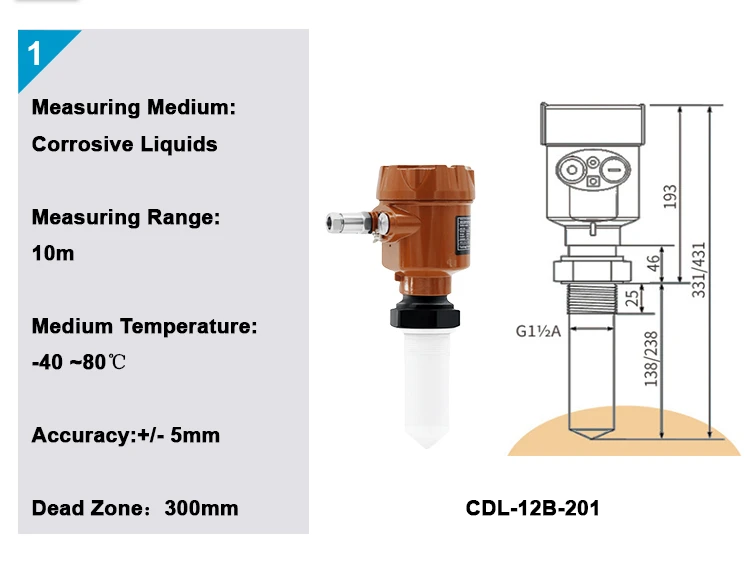
Antenna
The antenna connects the sensor’s internal parts to the outside world. Engineers create it to send electromagnetic waves in a certain pattern to the surface of the material. It also picks up the reflected waves very well.
Radar level sensors can use different types of antennas. One type is the horn antenna. Horn antennas have high gain and a narrow beam. This helps with sending focused waves.
They are good for tasks that need exact targeting. This includes small tanks or measuring tools in some parts of a big container.
Other common types of antennas are parabolic dish antennas. These antennas are used for long-range measurements. They give strong signals over long distances.
There are also flat antennas. These antennas are smaller and fit well in tight spaces.
Receiver
The task asks the receiver to find the weak reflected electromagnetic waves picked up by the antenna. It boosts the received signals so they can be processed well. It also removes any unwanted noise or interference that may have come during the wave travel.
Advanced receivers use complex methods to process signals. These include frequency mixing and demodulation. They help get important information from signals we receive. This information includes the real time delay linked to wave reflection.
Signal Processing Unit
This is the brain of the radar level sensor. The signal processing unit checks the signals from the receiver. It measures the time it takes for waves to reflect back.
It also uses different methods to adjust for things that can affect measurement accuracy. These things include changes in temperature and pressure in the tank. Such changes can slightly change how fast electromagnetic waves travel.
The signal processing unit can filter and average data. This makes the measured values more stable and trustworthy.
Finally, it turns the sensor calculates distance into a useful output signal. This signal can be a 4-20 mA analog current loop.
It can also use digital communication protocols like HART, Modbus, or Profibus. It can also send data wirelessly. This allows for remote monitoring.
Types of Radar Level Sensors and Their Operation
Guided-Wave Radar (GWR) Sensors
Guided-wave radar sensors, or time-domain reflectometry (TDR) sensors, work on a time-of-flight principle. However, they differ in how they send and receive electromagnetic waves.
GWR sensors do not send waves freely into the tank. Instead, they use a waveguide. This waveguide can be a single rod, a coaxial cable, or a twin probe.
The electromagnetic waves move through the waveguide until they hit the material’s surface. At this surface, some of the wave reflects back along the waveguide to the sensor.
GWR sensors have an advantage because they guide wave movement. This helps reduce the effects of outside factors like turbulence, foam, or vapor layers in the tank.
The waves remain in the waveguide. This means they are less likely to spread out or take in things that get in the way. GWR sensors work well for measuring thick liquids, foamy substances, or materials with complex surfaces.
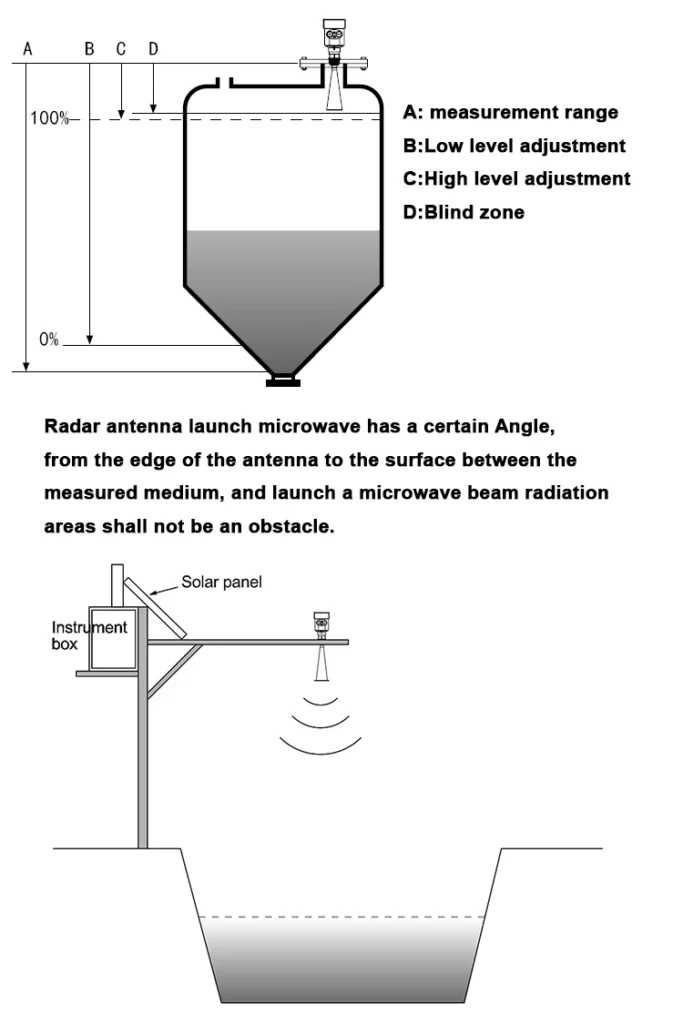
Non-Contact Radar Sensors
Non-contact radar sensors are the most common type. They work by sending out electromagnetic waves into the tank. This occurs without needing a physical link to the material.
These sensors work by reflecting waves off the surface of the material. They provide many benefits. One key benefit is that there is no contact with the measured material.
This lowers the chance of contamination. It also stops damage to the sensor from harmful, rough, or hot substances. Non-contact radar sensors are very useful.
They can be used for many applications. For example, they check chemical levels in industrial reactors. They also keep track of grain stored in big silos.
Factors Affecting Radar Level Sensor Performance
Many factors can affect how well radar level sensors work and how accurate they are. The dielectric constant of the material we measured is an important factor. The dielectric constant shows how well a material can store electrical energy in an electric field. It also changes how electromagnetic waves interact with the surface of the material.
Materials with a high dielectric constant, such as water or some water-based solutions, reflect electromagnetic waves more effectively. This leads to stronger signals and more accurate measurements. Materials with a low dielectric constant, such as hydrocarbons or dry powders, do not reflect waves well. You might need to use higher-frequency radar sensors or extra signal processing methods for accurate level readings.
Environmental conditions also play a significant role. Changes in temperature and pressure inside the tank can change the density of the air or gas above the material.
This can affect how fast electromagnetic waves travel. Dust, steam, or condensation on the sensor’s antenna can disrupt wave transmission and reception. This can cause measurement errors.
To reduce these effects, modern radar level sensors often have built-in features for temperature and pressure compensation. They make their antennas strong against dirt and other harmful things. They also make them easy to clean and take care of.
Applications of Radar Level Sensors
Radar level sensors find extensive use in a wide variety of industries. In the oil and gas industry, workers measure crude oil, refined products, and chemicals in storage tanks. This helps keep track of inventory. It prevents both overfilling and shortages.
In the chemical processing industry, radar sensors help monitor the levels of reactants and products. They are used in reactors, distillation columns, and other process vessels. This allows for precise control of chemical reactions and improves production processes.
The food and drink industry uses radar level sensors. These sensors measure liquid levels like milk, juice, and syrup. They also measure granular materials such as flour and sugar.
These sensors do not come into contact with food and manufacturers can make them from safe materials. This means they meet the strict hygiene rules of the industry.
Radar level sensors are used in water and wastewater treatment. They help keep track of water levels. They are used in reservoirs, tanks, and treatment plants.
This technology helps manage water efficiently. It makes sure that pumping and treatment systems work well.
conclusion
Radar level sensors find extensive use in a wide variety of industries. In the oil and gas industry, workers measure crude oil, refined products, and chemicals in storage tanks. This helps keep track of inventory. It prevents both overfilling and shortages.
In the chemical processing industry, radar sensors help monitor the levels of reactants and products. They are used in reactors, distillation columns, and other process vessels. This allows for precise control of chemical reactions and improves production processes.
The food and drink industry uses radar level sensors. These sensors measure liquid levels like milk, juice, and syrup. They also measure granular materials such as flour and sugar.
These sensors do not come into contact with food and manufacturers can make them from safe materials. This means they meet the strict hygiene rules of the industry.
Radar level sensors are used in water and wastewater treatment. They help keep track of water levels. They are used in reservoirs, tanks, and treatment plants.
This technology helps manage water efficiently. It makes sure that pumping and treatment systems work well.
Radar level sensors have changed how we measure levels. They are accurate and reliable. They do not interfere with the process.
These sensors use electromagnetic waves and smart signal processing. They can provide precise level measurements in many industrial uses.
This works well, regardless of the material or the environment. As technology improves, radar level sensors will get better too. They will provide better performance, improved connections, and easier use. This will expand their use in today’s industrial world.