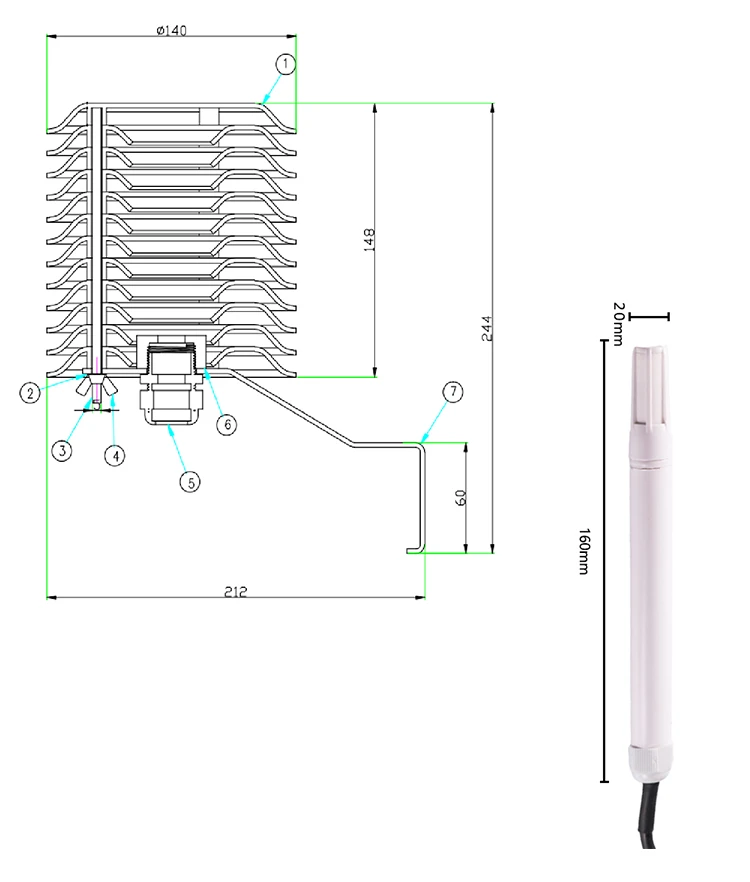
temperature and humidity sensor how does it work
A temperature and humidity sensor, known as an RH temp sensor, is a device. It converts temperature and humidity into electrical signals. This makes it easy to measure these environmental factors.
Most temperature and humidity transmitters measure the surrounding air‘s temperature and how much moisture is in it. They change these measurements into electrical signals or other types of signals. The system sends these signals to tools or software. This helps users meet their environmental monitoring needs.
How do temperature and humidity sensors function?
These sensors measure different substances. They do this by checking changes in their electrical properties. These changes happen when temperature and humidity reading change.
How they work depends on the types of humidity sensors. Below, I will explain how some common temperature and moisture sensors work.
Working principle of resistive humidity sensors
The temperature and moisture sensor checks the air’s temperature and humidity rh. It has a resistor that reacts to temperature.
It also has a part that reacts to moisture. The resistance of this material changes when the temperature and humidity change. This change makes an electrical signal. This signal shows the temperature and humidity levels.
Capacitive humidity sensors operational principle
The electrothermal sensor checks temperature and humidity. It does this by using the heating and cooling cycles of an electric heater. We find the temperature and humidity values by checking changes in resistance. These sensors usually have a heating element, a temperature sensor, and a humidity sensor.
What is the working principle of a humidity transducer?
The temperature and humidity sensor module has a capacitor that responds to humidity. It also has a conversion circuit. This capacitor can be affected by humidity.
It has a glass base and an electrode at the bottom. There is a material that responds to humidity. Lastly, it has a top electrode.
Humidity-sensitive materials are big molecules known as polymers. Their dielectric constant changes with the humidity in the air.
As the humidity in the air changes, the capacitance of these materials changes too. When the humidity rises, the capacitance goes up. When the humidity falls, the capacitance goes down.
The sensor’s circuit changes the humidity-sensitive capacitance into a voltage. This shows a humidity range from 0 to 100% RH. The sensor’s output shows a steady change from 0 to 1 volt.
Where is the optimal placement for a temperature humidity sensor?
First, stay away from any electronic or electrical devices. Next, set the sensor up straight. Make sure it is at least 6 feet off the ground.
Choose a spot in the middle of the room or a place with good air flow. This will help the sensor measure the humidity correctly.
How to Choose the Best Temp and humidity Sensor for Your Project?
The CODA sensor has a large LCD screen and buttons. It has a top-quality temperature and humidity sensor made in Switzerland. This sensor gives precise measurements and works well against interference.
This ensures great performance. The system tracks temperature and humidity levels automatically. It shows the values on the LCD display.
Devices send data to monitoring software. They use RS485 or WiFi signals. The RS485 sensor offers dependable and precise monitoring of the environment.
Our temp and humidity sensor gathers data every 2 seconds. It sends this data every 20 seconds by default.
Users can change how often they upload data. They can choose any time from 1 second to 10,000 seconds. This choice depends on their surroundings and how long they want to record. They can choose the recording time from 1 minute to 24 hours.
The sensor has an alarm built in, like a buzzer or a relay. Users can set the high and low limits for temperature and humidity with a button.
If these limits are exceeded, the sensor will sound an alarm and show a light. The sensor has good storage. It can hold up to 65,000 sets of records.
How about the CODA sensor?
The CODA sensor has a big LCD display and buttons. It has a high-quality temperature and humidity sensor from Switzerland.
This sensor provides accurate measurements and resists interference well. This ensures great performance. The system tracks temperature and humidity levels automatically. It shows the values on the LCD display.
Devices send data to monitoring software using RS485 or WiFi signals. The RS485 sensor provides reliable and accurate environmental monitoring.
Our temp and humidity sensor gathers data every 2 seconds. It sends this data every 20 seconds by default.
Users can change how often they upload data. They can choose any time from 1 second to 10,000 seconds. This choice depends on their surroundings and how long they want to record. They can choose a recording time from 1 minute to 24 hours.
The sensor has a built-in alarm, like a buzzer or relay. Users can set the high and low limits for temperature and humidity with a button.
If these limits are exceeded, the sensor will sound an alarm and show a light. The sensor has good storage. It can hold up to 65,000 sets of records.