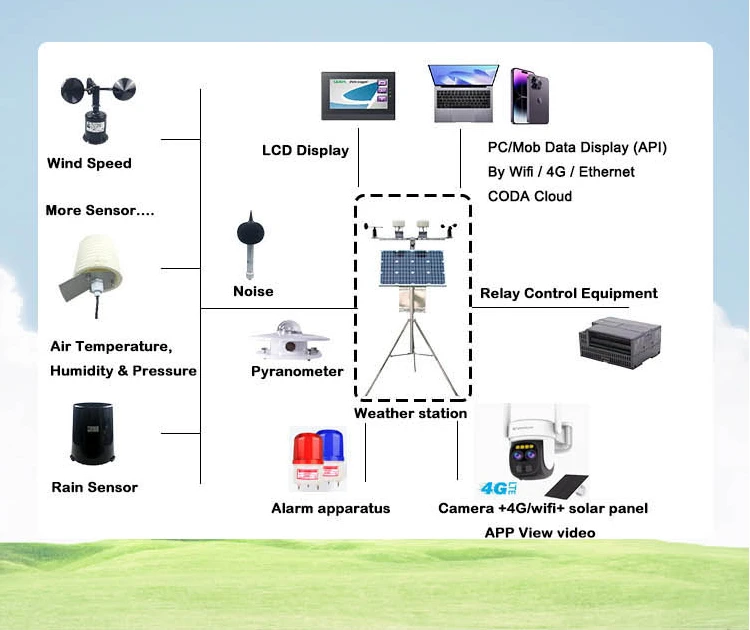
What is a Sensor and What is it Made Of?
A sensor, also referred to as a transducer, is a device designed to detect and measure specific information. It changes the detected information into electrical signals or other outputs based on set rules. This allows the data to be sent, processed, stored, shown, recorded, or controlled as needed.
Sensors have special features. These features are small and digital. They are smart, versatile, and linked to systems and networks. They are the first step in automated detection and control.
With new sensors, objects can mimic human senses like touch, taste, and smell. This makes them seem “alive.” Sensors can be grouped into ten types based on what they can sense. There are many types of sensors. They include:
– Thermal sensors
– Photosensitive sensors
– Gas-sensitive sensors
– Force-sensitive sensors
– Magnetic-sensitive sensors
– Humidity-sensitive sensors
– Sound-sensitive sensors
– Radiation-sensitive sensors
– Color-sensitive sensors
– Taste-sensitive sensors
Components of a Sensor:
A sensor usually has four main parts. These are the sensitive element, the conversion element, the conversion circuit, and the power supply. Each part is important.
1. **Sensitive Element**:
This section works with the measured variable. It makes a physical signal that matches the measurement.
2. **Conversion Element**:
It changes the physical signal from the sensitive part into an electrical signal.
3. **Conversion Circuit**:
The circuit improves the electrical signals it gets from the conversion element. This means making the signals stronger or changing them in some way.
4. **Auxiliary Power Supply**:
An outside power source is often needed to run the conversion element and the circuit.