Definition between Sensor Resolution, sensor sensitivity
Humans use their senses to understand the world. Our natural senses are often not enough for science or industry.
Sensors enhance our five senses. They are often called the “electronic five senses.” In automated production, sensors play a key role.
They help watch and manage processes to make operations and product quality better. We often check how well a sensor works by looking at its sensitivity, resolution, and accuracy. However, these terms can be hard to understand. Here is a clear explanation of each one.
Sensors are now widely used in many fields, such as industry, farming, space, oceans, and the environment. They also play key roles in resource studies, medical tests, biotech, and protecting cultural items. Today, nearly every modern project—from space to sea—depends on sensors.
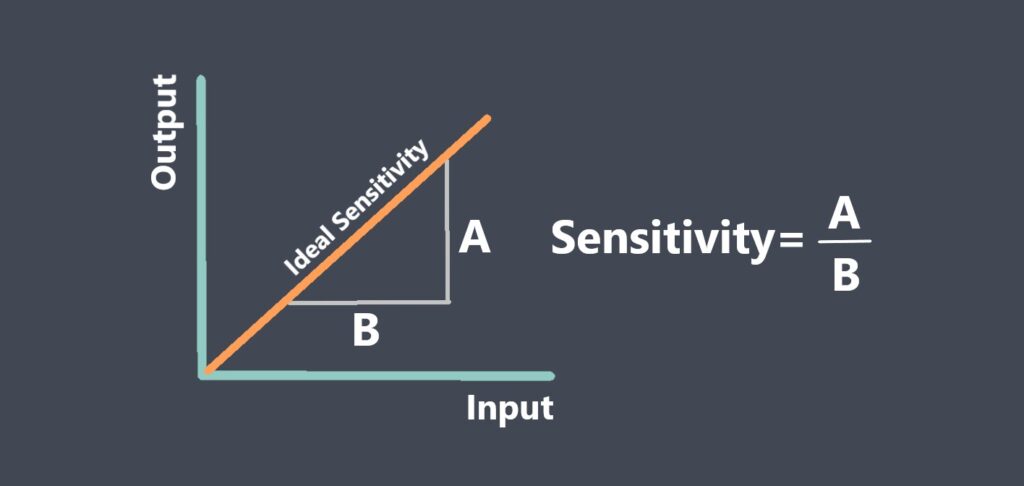
Sensor Sensitivity
**Definition:** Sensor sensitivity measures how much the sensor’s output signal changes (△y) compared to the input signal change (△x). This is done when conditions are stable. It shows how changes in what you put in lead to changes in what you get out.
In simple terms, sensitivity shows how steep the output-input curve is. If a slope of the output of the sensor and input are straight, its sensitivity stays the same. If they are not straight, sensitivity changes when the input changes.
When input and output use the same units, sensitivity can be viewed as amplification. Higher sensitivity can make accuracy better. However, it often lowers the sensor’s range and stability.
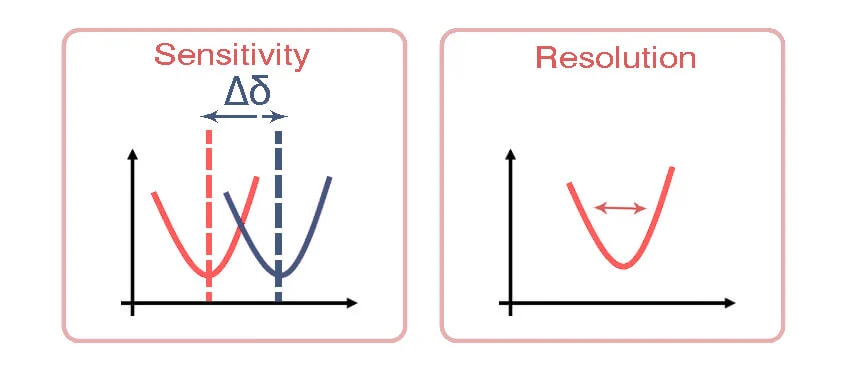
Sensor Resolution
**Definition:** Resolution is how well the sensor can see the smallest change. If an input value changes slowly from a non-zero point, the sensor may not notice this change.
This is true as long as the value stays below a certain limit. This means the change is small. The sensor only reacts when a change goes above this limit.
Resolution is about how well an analog signal to noise ratio turns into a digital one. It shows the smallest change that the sensor can detect.
Resolution depends on the sensor’s design and calibration. In digital sensors, it is set by the A/D converter’s bits. Higher resolution gives more accurate readings, but it can make stability worse.
Sensor Accuracy
Definition: Accuracy shows how close a sensor’s measurement is to the true value. The main difference is between the measured values and the real values. This difference is usually within plus or minus three standard deviations. It applies over a certain range.
Measurement accuracy includes errors from the sensor’s circuits and how it is set up. For temperature sensors, there are two grades: Class A and Class B.
Class A sensors should not change more than ±(0.15°C + 0.002 times the range of the sensor). Class B sensors can vary by up to ±(0.30°C + 0.005 times the sensor range). For more accurate measurements, it is best to use sensors with smaller ranges.
Resolution is not the same as accuracy. It shows how well we can see small changes, not just big mistakes. Higher resolution or accuracy often means we may lose some other features, such as sensitivity.
Conclusion
Knowing the differences between sensitivity, resolution, and accuracy can help you use sensors better. It also makes the system work better in many ways. Each factor matters.
They help make sure measuring devices are correct. They also make sure systems work well in various situations.
If you need better ways to watch the environment or use sensors, reach out to **Coda Sensors**. They provide modern technologies made for your needs.
Hunan Coda Electronic Tech Co., Ltd makes new sensor solutions. They have new facilities and skilled workers.
This has helped them build a strong reputation worldwide. They always deliver high-quality products around the globe. Visit Coda Sensors today to find out more!