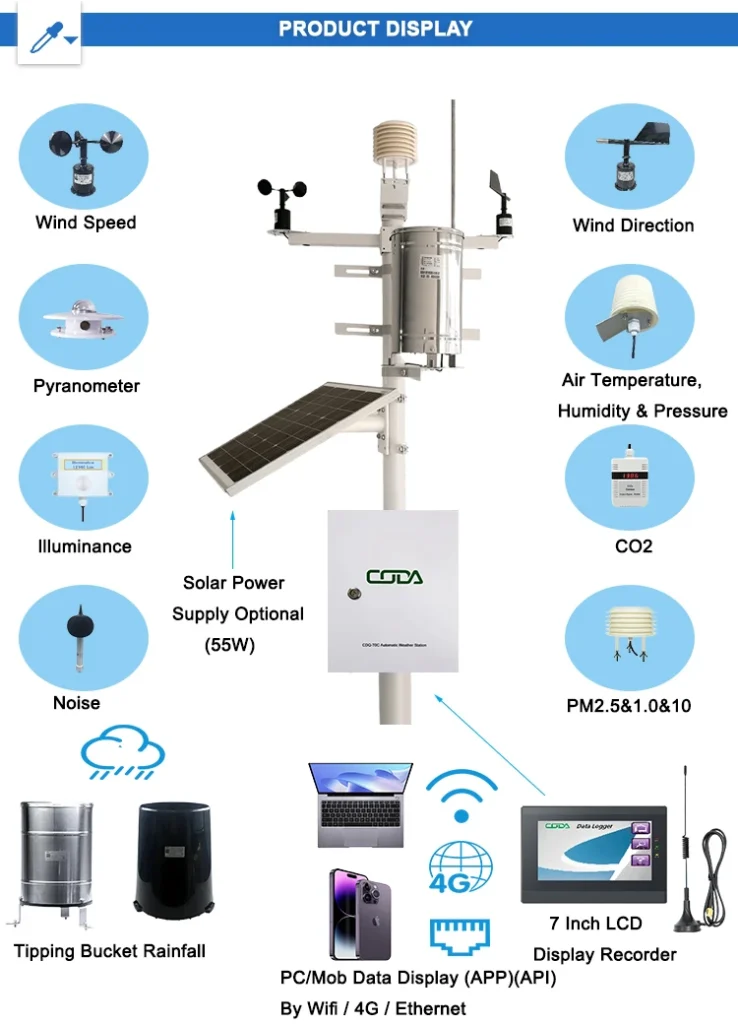
What is a GSM Weather Station?
In the realm of weather monitoring, GSM weather station have emerged as a revolutionary tool. But what exactly is a GSM weather station? Let’s delve into the details.
Definition and Concept
A GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) weather station is a new tool for checking the weather. It uses the GSM network to send data. They design it to gather various weather data from a specific place.
Then, it sends this data wirelessly to a remote location. This could be a user’s computer, mobile device, or a cloud-based server. This allows users to access weather information in real time. It does not matter how far away the weather station is.
How Does It Work?
Data Collection
GSM weather stations are equipped with an array of sensors. These sensors measure different weather conditions.
Temperature Sensors:
These can be thermocouples or thermistors. They measure the temperature of the surrounding air. A common thermistor temperature sensor changes its electrical resistance when the temperature goes up or down. The microcontroller in the weather station then measures this resistance and converts it into an accurate temperature reading.
Humidity Sensors:
Capacitive and resistive humidity sensors are often used. A capacitive humidity sensor changes its capacitance based on the amount of water vapor in the air. The microcontroller checks the change in capacitance. It then figures out the percentage of relative humidity.
Wind Sensors:
Anemometers measure wind speed. A cup anemometer has three or four cups on horizontal arms. These arms spin around a vertical shaft.
A sensor on the shaft measures how fast the cups spin. This speed is related to the wind speed.
Wind vanes help find the direction of the wind. They often look like arrows. They can turn easily and point with the wind. A sensor keeps track of this position.
Rain Gauges:
Tipping bucket rain gauges are popular. Every time a small bucket on the gauge tips from rainwater, it sends a signal to the controller. The microcontroller counts the tips to measure how much it rains.
Data Transmission
Once the sensors collect data, the GSM module in the weather station takes over. It works like a phone’s GSM module. It uses a SIM card to connect to the network.
The microcontroller at the weather station gets the data ready to send. It sends the data as SMS messages.
For weather stations with GPRS, data can be sent this way. SMS works well for small amounts of data. A station might send hourly texts with temperature, humidity, wind speed, and rainfall.
GPRS allows for continuous data streaming. It sends data straight to a server for live web monitoring.
Components of a GSM Weather Station
Sensors
The sensors are the “eyes and ears” of the GSM weather station. We use different sensors based on what we need to measure. Good sensors are important for getting accurate data.
For example, a professional GSM weather station used in farming needs precise temperature and humidity sensors. These sensors give precise readings for studying how crops grow.
GSM Module
The GSM module is the main part of the data transmission system. They create it to connect with the GSM network. There are many types of GSM modules on the market. Each type has its own features.
These features include different data transfer speeds, power use, and compatibility with various SIM cards. Some advanced GSM modules have extra features like voice calls.
These are not often used in weather stations. They can be useful when sending an alarm or voice message. This is especially true during severe weather events.
Microcontroller
The microcontroller acts as the brain of the GSM weather station. It controls the sensors and collects data from them. It processes this data, like changing raw sensor readings into useful units, such as degrees Celsius for temperature.
Then, it sends the data to the GSM module. The module will transmit the data. Engineers write programs for microcontrollers. They use specific algorithms to make sure the whole system works well.
For example, they can set up the microcontrollers to adjust sensors often. This helps keep the data accurate.
Power Source
GSM weather stations can be powered in several ways. Many have rechargeable batteries, and you can charge them using solar panels.
Solar-powered GSM weather stations are very helpful in remote areas. These places often have limited access to electricity. The solar panels change sunlight into electrical energy. This energy charges the batteries and runs the weather station.
Advantages of GSM Weather Stations
Remote Monitoring
One of the biggest benefits of GSM weather stations is that they can monitor weather conditions from a distance. This is very helpful in places that are hard to reach, like remote mountains, deserts, or offshore areas.
For example, researchers can set up a GSM weather station deep in the Amazon rainforest for a research project. Researchers can get weather data from their labs, even if they are far away. They do not have to go to the weather station in person.
Real – Time Data
GSM weather stations give real-time data. After the sensors collect new data, you can send it through the GSM network. This is important for things like weather forecasting. It needs up-to-date information about temperature, humidity, wind, and rain.
For example, weather agencies can use GSM weather stations. This helps them update their weather models more often. As a result, they can create more accurate weather forecasts.
Easy Installation and Setup
GSM weather stations are simpler to install than traditional systems. They do not need complex wiring or infrastructure. To set up a GSM weather station, first mount the sensors. For example, place the wind sensor on a tall pole.
Next, connect the sensors to the main unit. Then, insert the SIM card and turn on the power. This ease makes it good for many users, from hobbyists to small farmers.
Data Security
When using GPRS and cloud – based storage, data security is enhanced. For example, on a construction site with a GSM weather station for safety, users can still access its data. Even if the station is damaged, they can reach both historical and real-time information stored in the cloud.
Applications of GSM Weather Stations
Agriculture
In agriculture, people use GSM weather stations to optimize crop growth.Farmers can monitor temperature, humidity, and rainfall data. For example, if the humidity is too high, it can indicate a higher risk of fungal diseases in crops. With real – time data from GSM weather stations, farmers can act preventively, adjusting irrigation, applying pesticides, or boosting greenhouse ventilation.
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, especially in wind and solar power plants, GSM weather stations play a vital role. Wind speed and direction data are crucial for wind turbine efficiency. A GSM weather station monitors parameters, enabling operators to reposition wind turbines for more energy capture. In solar plants, its temperature and sunlight data predict output and maintain panel efficiency.
Construction
Construction sites can benefit from GSM weather stations in terms of safety and project planning. Extreme weather conditions such as high winds, heavy rain, or low temperatures can affect construction activities. With a GSM weather station, construction managers can receive real – time weather alerts. For example, if they predict strong winds, they can halt crane operations to prevent accide