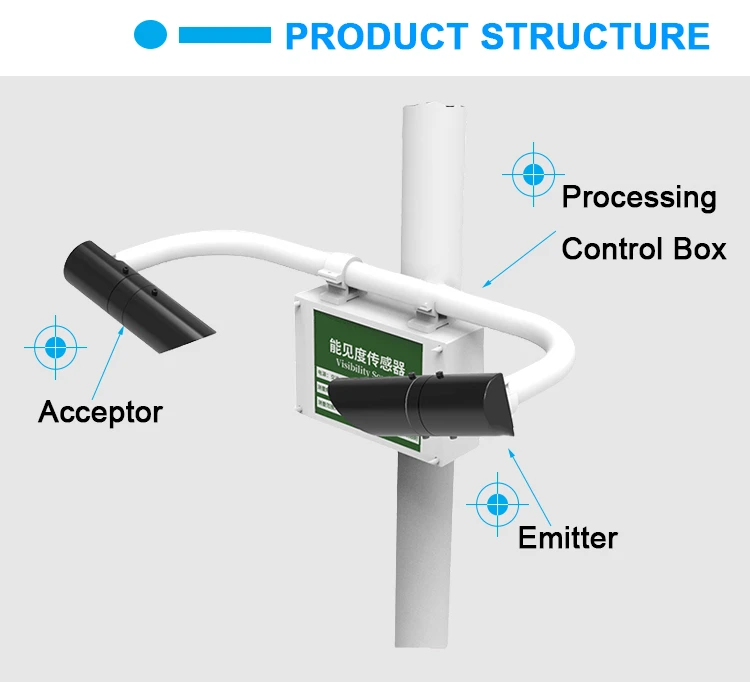
What does visibility mean in weather?
Visibility is how far a person can see and recognize objects clearly. It depends on the weather and how clean the air is. This step is very important for predicting the weather.
Many important factor affect it. These include water droplets, ice crystals, dust, smoke,dense fog and pollution. The angle of the sun compared to the horizon also plays a role.
In weather science, horizontal visibility shows how clear the air is. It impacts daily life, travel, and the safety of flights.
How is visibility assessed?
Researchers often check visibility by studying how light moves through the air. Here’s a simple explanation of the process:
Ground-based observation
Manual Observation: This is the oldest and most common method. A ground observer looks at a target that is far away.
This target could be a black panel or a light tower. Observers use their eyes or binoculars to see how clearly they can view it. This method is easy to use, but it depends on the observer’s judgment.
Employment of specialized equipment:
New technology uses tools like visibility meters and scattering meters. These tools check how clear things are. These devices send out a laser or light beam. They measure how much the beam is scattered or absorbed as it moves through the air.
Satellite:
Satellite images can show good visibility data over large areas. Weather scientists study the light that bounces off the Earth. This helps them see how clear it is in different areas.
Aerial surveillance
In aviation, pilots check visibility while flying. They depend on their eyesight, which is key for safety.
Some aircraft have automated systems. These systems check how well we can see. They give correct information. How do they check visibility?
How is visibility determined?
Researchers study how light travels through the air to see how well we can see. Here’s a simple explanation of the process:
The climatic optical visual range (MOR) is a standard measure. MOR shows how far a straight beam of light can go.
This light comes from a lamp with a color temperature of about 2700 K. The light’s brightness drops to about 5% of its original level due to the atmosphere weakening it.
In practical use, an automated device sends out a light beam. It shows how much light gets weaker as it moves through the air. This weakening occurs because of scattering or absorption. You can find the current visibility value by using this data and the definition of MOR.
Reduced visibility depends on many things, like dust, humidity, and temperature. Because of this, researchers use special tools to get accurate measurements.
Visibility shows how clear the air is. It can be measured in different ways. It can also change with the weather. Visibility affects flying, driving, and outdoor fun. Because of this, weather agencies around the world keep a close eye on it.