Wind Velocity Sensors: Principles, Types, and Advanced Technologies
1. Introduction to Wind Velocity Sensor
A wind speed sensor is a key part of an anemometer. It measures how fast the wind is blowing. Anemometers are common tools in weather stations. They measure wind speed and direction at different heights in the atmosphere.
They are also used in wind tunnels to measure airflow speed and for other gas flow applications.
Working Principles of Wind Velocity Sensor
Cup Anemometers:
Cup anemometers are one of the most common types. They work on a simple and effective principle. The design has three or more cups.
These cups are on horizontal arms that connect to a vertical shaft. When the wind blows, the cups catch the wind and start to rotate around the shaft.
The speed of the cups spins faster when the wind speed increases. A generator or counting device is linked to the shaft. As the shaft turns, it powers the generator.
This generates electricity. A meter measures it based on the wind speed. Friction between moving parts can create problems in calibration. This may affect how accurate the measurements are.
Thermoelectric Wind Speed Sensors:
These sensors measure wind speed by checking how quickly the wind cools a heated wire. In a thermoelectric wind speed sensor, a wire heats up to a temperature higher than the surrounding air. When the wind blows over the wire, it takes away heat. This makes the wire’s temperature go down.
The rate of cooling is related to the wind speed. You can find the wind speed by measuring how the temperature of the wire changes. People often look at changes in resistance, since a wire’s resistance depends on its temperature. Thermoelectric sensors are very helpful for measuring low to average wind speeds.
Pressure – Tube Anemometers:
Pressure tube anemometers, like Pitot tubes, connect changes in air pressure to wind speed. A Pitot tube has one opening that faces the wind. This opening is called the stagnation pressure port. It also has another opening that is at a right angle to the wind.
This is known as the static pressure port. The difference between stagnation pressure and static pressure relates to dynamic pressure. Dynamic pressure is linked to the square of the wind speed.
People often use this type of anemometer in places where the air flows steadily. It measures high average wind speeds, like on airplanes for airspeed measurement.
Ultrasonic and Laser Anemometers:
These advanced sensors use the Doppler effect. Ultrasonic anemometers send out ultrasonic waves into the air. As the wind moves the air molecules, the frequency of the ultrasonic waves reflected from these molecules changes.
Detecting this frequency shift helps us estimate wind speed. Laser anemometers work in a similar way but use laser light instead of ultrasonic waves. They are highly accurate and are often used in research and applications where precise wind speed measurements are crucial.
2. CODA Sensors in the Realm of Wind Velocity Sensing
CODA is now an important company in making sensors. They provide different high-quality sensors. This includes sensors that measure wind speed.
CODA’s Wind Velocity Sensor Products
CDF – 10B: This is a military-grade metal sensor for measuring wind speed. It is made for extreme environments. Its strong design is great for wind energy and aviation. It is also useful in other areas where reliability in tough conditions matters.
In wind energy, measuring wind speed accurately is important for improving how wind turbines work. The CDF – 10B can handle extreme temperatures and strong winds. It also deals with other environmental stressors. This makes sure it gathers wind speed data in a steady and reliable way.
CDF – 20B: The CDF – 20B is a sensor for wind speed and direction. It has strong aluminum alloy parts. These parts make it durable and easy to install. For the wind speed part, it adopts the traditional three – wind – cup structure.
This structure provides strong initial performance. It has a wide measuring range and excellent straightness. It is also stable and reliable. In terms of wind direction measurement, it uses a low – inertia wind vane.
When the wind direction changes, the tail wheel linked to the vane moves an angle sensor. This sensor detects the change in azimuth. This results in a change in electrical signal output, which is highly linear, has high precision, and has no blind zone.
Advantages of CODA Wind Velocity Sensors
High Precision:
CODA’s wind speed sensors are designed to give very accurate measurements. The design and calibration of their sensors make sure the data collected matches the real wind speed.
The CDF – 20B has a smart angle sensor to measure wind direction. It also has a cup-based system to measure wind speed.
Together, these tools give accurate readings. This is important for meteorology. Accurate wind data helps improve weather forecasts.
Durability:
CODA sensors are made with high-quality materials, like metal in the CDF-10B. This makes them strong for extreme environments. They can handle different weather conditions, like rain, snow, and strong winds, without losing much performance.
This durability leads to fewer replacements and less need for maintenance. This makes them cheap over time. They are helpful for tasks like monitoring the environment. These stations must run all the time for long periods.
Flexibility:
CODA’s wind sensors are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. In weather stations, these tools measure wind speed and direction in real-time.
The data is sent to the meteorological processing center. In factories and workshops, technicians can install small CODA sensors. These sensors measure wind speed and direction to monitor ventilation systems.
Engineers can measure wind speed and direction in different parts of the workshop. This helps them make the ventilation system better and easier to use. The goal is to ensure good air quality for production. This also helps protect the health of workers.
On ships, these sensors provide real-time updates about wind conditions to the crew. This helps them adjust the ship’s course and speed for safe and efficient navigation.
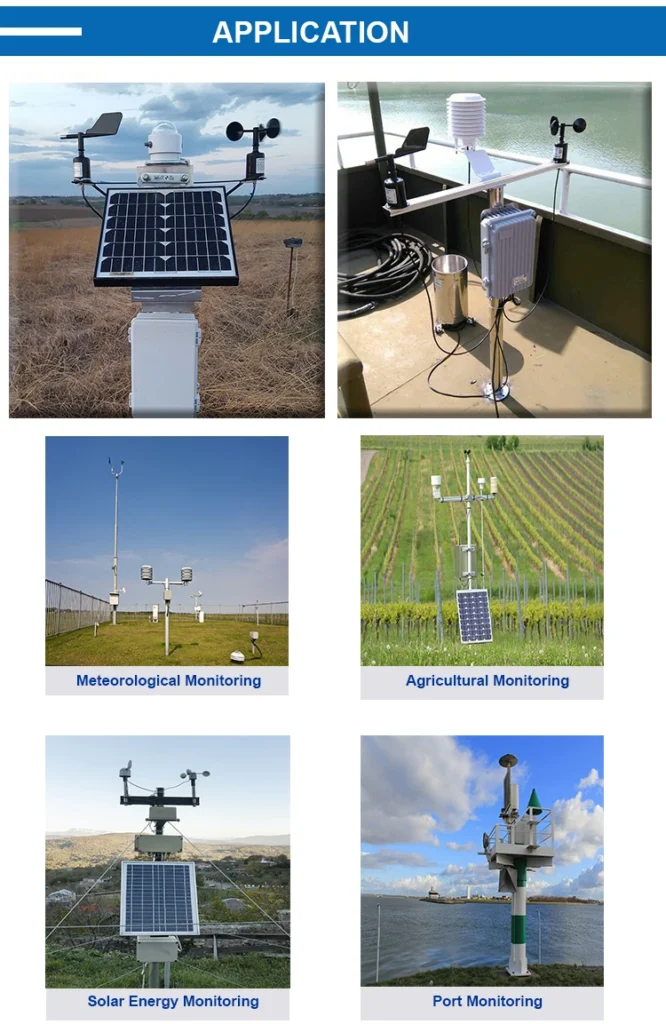
3. Applications of CODA Wind Velocity Sensors
Meteorology
In meteorology, knowing the wind speed and direction is very important for weather forecasting. Meteorological stations around the world install CODA’s wind velocity sensor, like the CDF – 20B. These sensors measure wind speed and direction. They send this data to weather data processing centers.
Weather scientists use this data and other weather information to study weather patterns. They predict how weather fronts will move and issue weather warnings. Accurate wind speed data is important for predicting how strong a storm will be and where it will go. This information helps with planning for disasters and withdrawals.
Wind Energy
In the wind energy industry, knowing wind speed is important for running wind turbines efficiently. CODA’s wind speed sensors, such as the CDF – 10B, measure wind speed in areas for possible wind turbine sites. This data helps us find the best spots for wind turbines. We should place turbines where there is enough and steady wind to generate electricity effectively.
Once installed, the sensors keep track of wind speed in real time. Turbine control systems use this data to change the angle of the turbine blades.
They also adjust the position of the turbine nacelle. This helps create more power. It also protects the turbine from spinning too fast in strong winds.
Aviation
In aviation, knowing wind speed and direction is important for safe takeoff, landing, and flying. Aviation weather stations near airports use CODA’s wind sensors. These sensors are very precise and durable.
Pilots use this wind data to figure out takeoff and landing speeds. They also use it to plan their flight routes. For example, during takeoff, wind speed and direction can change how far the plane needs to go.
They also impact the lift from the aircraft’s wings. During a flight, wind data helps pilots save fuel. They can pick the best altitude and route based on wind conditions.
Environmental Monitoring
In environmental monitoring, researchers use wind speed data to study how air pollutants spread. You can connect CODA’s wind sensors with other devices that monitor the atmosphere, like air quality monitors.
Environmental scientists measure wind speed and direction. This helps them predict how air pollutants spread. With this information, we can understand how pollution impacts air quality.
It includes emissions from industries and vehicle exhaust. This applies to cities and rural areas. It also helps create environmental policies and carry out pollution control measures.
4. Conclusion
Wind velocity sensors play a vital role in various fields, from weather forecasting to energy production and environmental protection.
CODA Sensors has made significant contributions to the wind speed sensing market. People know them for their creative designs and quality products.
Their focus is on precision, durability, and flexibility. Their sensors, like the CDF – 10B and CDF – 20B, are ready for many uses. They work well in tough military conditions and provide accurate data for weather stations.
As technology keeps improving, CODA will likely enhance and grow its wind speed sensors. This will help collect more accurate and reliable wind data for many industries.