how is rain measured
Rainfall is a key part of Earth’s water cycle. It impacts ecosystems, weather, and human life. Accurate rainfall detection is crucial for weather forecasts, water management, farming, and flood control.We often use inches to measure rainfall. This article looks at the methods, tools, and importance of precise measurements.
Understanding Rainfall Measurement in Inches
In the imperial and US customary systems, an inch is a unit of length. When we measure rainfall, it tells us how deep the water would be on a flat surface. This is true if there is no runoff, evaporation, or soaking into the ground.
For example, 1 inch of rain makes a water layer that is 1 inch deep. This unit helps us look at rainfall data from different times and places.
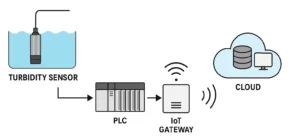
types of rain gauges
Standard Rain Gauges
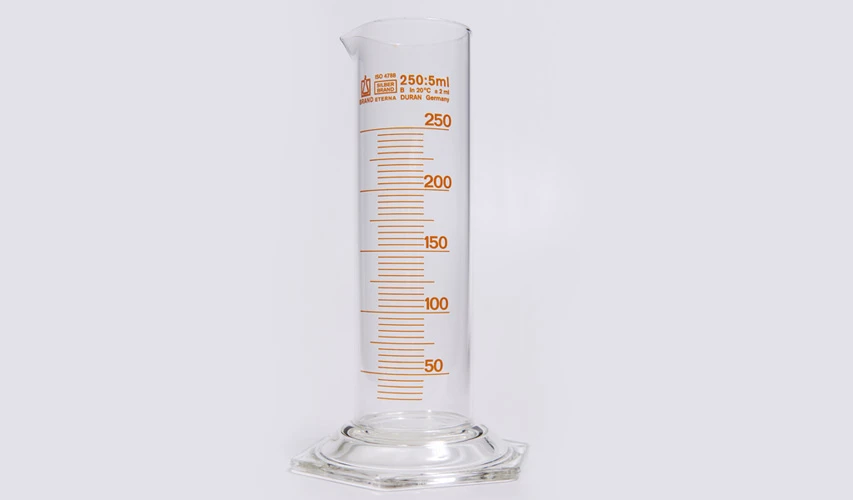
Standard rain gauges are simple tools that have been used for a long time. They are often round containers made from metal or plastic.
These tipping bucket gauges are set upright in the ground to measure the water level. Rain gathers inside them. After the rain stops, a ruler checks the collected water depth in inches.
These gauges are simple to use and cheap. You can find them in weather stations and homes. But they do have some problems.
They measure rain in just one place. Wind can make rain splash out or not come in correctly. Manual readings need regular checks, and mistakes can happen.
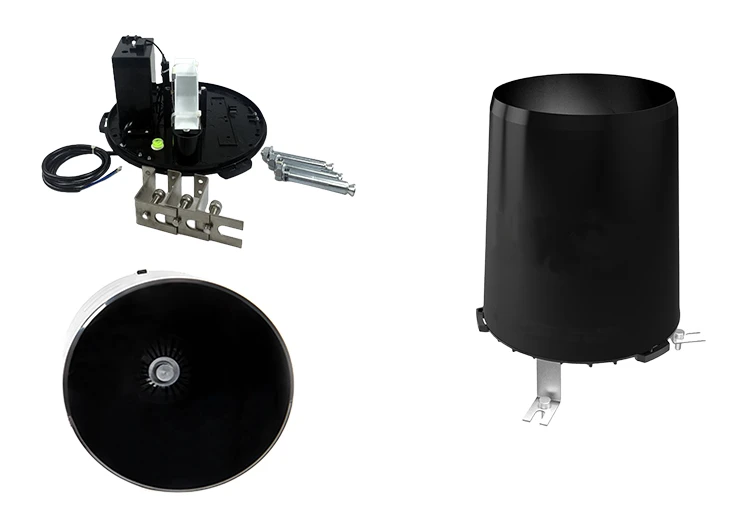
Tipping – Bucket Rain Gauges
Tipping bucket rain gauges have two small buckets that move on a pivot. When one bucket fills with a small amount of rainfall, like 0.01 inches, it tips over.
This empties one bucket and lets the other fill. Each time a bucket tips, it triggers a mechanism.
This system keeps track of the event. The data is sent to a logger. By knowing how much rain causes a tip, we can find the total rainfall.
These heavy rainfall sensors give automatic and ongoing measurements. They are helpful for watching things from a distance and for a long time. They are not as affected by wind. However, they need regular cleaning and checking to work well.
Radar – Based Rainfall Measurement
Radar rainfall sensors use microwave signals to measure rain in large open areas. The signals hit raindrops and bounce back.
The strength of the signal that comes back shows how much rain has fallen. Meteorologists use this collect data to predict how much it will rain and the total rainfall. They use algorithms to change signals into inches.
Radar shows a wide view of rainfall in real-time. It helps predict the weather and track storms.
The distance from the radar can change how accurate it is. Things that are not rain can give wrong readings. Weather can also change the signals.
Satellite – Based Rainfall Estimation
Satellites with special sensors measure rain all over the world. Passive microwave sensors pick up microwave radiation from the Earth. This radiation is linked to water vapor and raindrops, which helps estimate rainfall. Visible and infrared sensors look at cloud properties, such as temperature and cover, to measure record rainfall.
Satellites are helpful in places with few ground measurements, such as oceans and deserts. They help study long – term rainfall trends. But they have a lower resolution than ground instruments. Cloud complexity and other factors can affect accuracy too.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
Environmental Factors
Wind is a big problem. It can make rain fall at an angle. This causes rain gauges to collect rain too little or too much water.
High temperatures speed up evaporation in rain gauges, leading to underestimates if not measured quickly. Humidity can mess with electronic rain – measuring devices. Obstacles like buildings change wind patterns and affect measurements.
rainfall sensor – Related Factors
Calibration is key for all rain – measuring tools. Uncalibrated gauges give wrong readings. The design of a rain gauge is important.
A narrow opening can get blocked. A bad design might not measure rainfall rate well in different amounts. For radar and satellite methods, the quality of sensors, calibration, and algorithms can impact accuracy.
Why Accurate Measurement Matters
Weather Forecasting
Accurate rain sensor data helps weather experts predict the weather. It also helps them track storms. This gives fast warnings that help keep people and property safe.
Water Resource Management
Rain is the main water source in many places. Precise measurement helps manage water use for drinking, farming, and industry, and plan water treatment and reservoir operations.
Agriculture
Farmers use rainfall sensors to help them plan irrigation, planting, and crop choices. Knowing how much it rains helps them use water wisely. This can lead to bigger harvests.
Flood Prevention and Mitigation
Real–time rainfall monitoring helps predict floods. This helps officials move people to safety and open floodgates. They can use accurate data to check for flood damage.
rainfall sensor Conclusion
Measuring rainfall in inches uses different methods, each with its own pros and cons. Environmental factors and tools can impact accuracy. Accurate measurement is important for many fields.
Future technology will likely make measurements more precise. This will help us manage our environment and resources better.