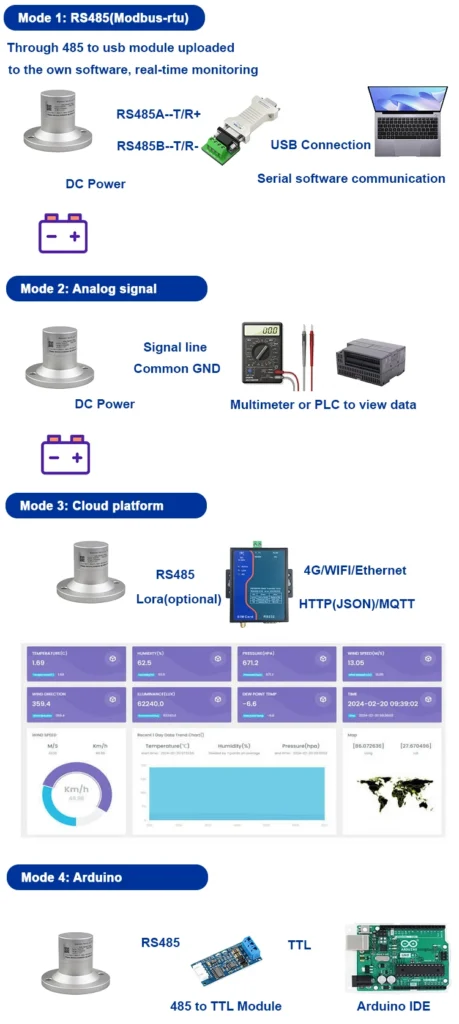
What is a Radiometer Used For?
In science and technology, a radiometer is a useful tool. It finds and measures electromagnetic radiation. This tool works with different specific wavelengths range. It can measure short gamma rays and long radio waves.
Its features make it a useful tool in many fields. It helps researchers, scientists, and professionals collect important data. This helps them see the world around us.
Astronomy: Exploring the Cosmos
One main use of radiometers is in the field of astronomy. Many objects in the universe give off electromagnetic radiation. Radiometers help astronomers find and study this radiation. They give us a look into the distant cosmos.
Astronomers look at stars, galaxies, nebulae, and other objects in space. They do this by measuring how strong the radiation is and its different features. This helps them learn about the shape, temperature, movement, and growth of these things.
For example, radio-frequency radiometers help us see the cosmic microwave background radiation. This soft light can be seen all around the universe. It comes from the Big Bang.
Studying this radiation helps scientists learn about the early universe. It shows the density and the spread of matter and energy when it formed.
Radiometers that operate in the infrared range help us study where stars are forming. In these areas, dust and gas give off infrared radiation. These observations give us important information about how new stars are born and grow.
Remote Sensing: Monitoring the Earth
Radiometers are important tools used in remote sensing. This process collects information about the Earth’s surface and atmosphere from far away.
Satellites with radiometers help watch many things on Earth. They track weather, climate change, land use, and ocean harsh conditions.
Microwave radiometers on weather satellites measure the microwave radiation from clouds, rain, and the Earth’s surface. Researchers use this data to make weather forecasts. They track storm movements and watch how heavy the rain is.
In the study of climate change, researchers use radiometers to measure changes in the Earth’s energy balance. Scientists can measure the solar radiation that comes in and the radiation that goes out from the Earth.
This helps them learn how much energy the Earth’s atmosphere and surface take in or bounce back. This information helps us learn what causes climate change. It also helps us guess what the climate will be like in the future.
Researchers use radiometers to map land use and land cover. Different land covers, like forests, grasslands, cities, and water, emit and reflect electromagnetic radiation in their own ways.
Researchers can look at radiation data from radiometers. This helps them make maps of land cover and track changes over time. This information is important for taking care of the environment, planning cities, and helping conservation efforts.
Meteorology: Understanding the Atmosphere
In meteorology, scientists use radiometers to learn about the atmosphere. For example, they use infrared sensors to check the temperature measurement at different heights.
Scientists can measure the infrared radiation from the atmosphere. This helps them see how the temperature changes from the top to the bottom. This profile helps us see how the atmosphere moves. It explains how clouds form and how weather systems grow.
Radiometers check the humidity in the air. Microwave radiometers check how much water vapor is in the air.
They do this by finding microwave radiation that water vapor molecules take in and release. Meteorologists use this data to make weather forecasts. They expect rain and high humidity.
Radiometers are tools that help us learn about the atmosphere. They can find small amounts of gases such as ozone, carbon dioxide, and methane. Scientists study how these gases take in and release radiation. This helps them track the levels of these gases and understand their role in Earth’s climate.
Industrial Applications: Quality Control and Process Monitoring
Radiometers are used in many industries. They assist with checking quality and watching the process. In manufacturing, workers use radiometers to check the temperature of materials while they are being processed.
In the steel industry, infrared radiometers check the temperature of molten steel. They do this in the furnace and when they cast. This helps workers process the steel at the right temperature. This is important for the steel’s quality and properties.
The food industry uses radiometers to check drying and baking. Manufacturers test the infrared radiation that comes from food. This helps them find the moisture level. It also makes sure the products are dried or baked properly.
In the semiconductor industry, makers use radiometers to check the temperature of wafers while they are being made. This helps manage the process settings. It also ensures the quality and performance of the semiconductor devices.
Environmental Monitoring: Assessing Air and Water Quality
Radiometers help us keep an eye on the environment. They check the quality of air and water. For example, researchers use special tools called ultraviolet radiometers. They measure UV radiation in the air.
This data shows how UV radiation impacts human health and the environment. It includes risks like skin cancer and harm to plants and sea life.
Radiometers measure how much pollution is in the air. This includes sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and small particles.
Scientists can check air quality by measuring how pollutants take in and spread light intensity. This helps them find where pollution comes from.
In water quality monitoring, researchers use special tools called radiometers. They check turbidity, chlorophyll levels, and other factors in the water. They use this data to check the health of aquatic ecosystems and to make sure drinking water is safe.
conclusion
A radiometer is a helpful tool. It has many uses in astronomy and remote sensing. It is used in weather science and industry. It also helps keep an eye on the environment.
This tool can find and measure electromagnetic radiation. This provides key information for research, technology, and taking care of the environment.
As technology keeps improving, radiometers will likely become stronger and more advanced. This will help us explore space, learn about Earth, and make our lives better.