where to place outdoor weather sensors
In weather monitoring, the accuracy of weather data from indoor outdoor weather sensors is very important. Where these sensors are placed matters. It can greatly affect how reliable the information is.
This is important for personal use, scientific research, and real time weather forecasting. Knowing the best places for weather sensors is key to getting accurate wireless weather stations data.
General Considerations
Before looking at where to place each professional weather station sensor, keep some key ideas in mind. The chosen spot should reflect the area for the digital weather real time data. For instance, if you want to track the weather in a certain neighborhood, place the sensors within that area. This is better than putting them on the edges, where conditions can vary greatly.
The area around the sensors should be free from artificial influences. This helps keep the weather conditions accurate. Stay away from heat sources.
These include air conditioning units, industrial machines, and large buildings that give off heat. Keep reflective surfaces like asphalt parking lots, metal roofs, and glass facades away. They can give false outdoor temperature readings. This happens because they absorb and re-emit solar radiation.
Temperature and Humidity Sensors
Temperature and humidity sensors are key parts of an outdoor home weather station. To get accurate readings, you must protect these sensors from direct sunlight and other heat sources.
A common solution is to use a Stevenson screen or a similar shelter. This is a white box with slats. It lets barometric pressure flow around the sensors. It also keeps the sensors safe from rain and direct sunlight.
The white color reflects sunlight. This reduces the heat that the shelter and sensors absorb.
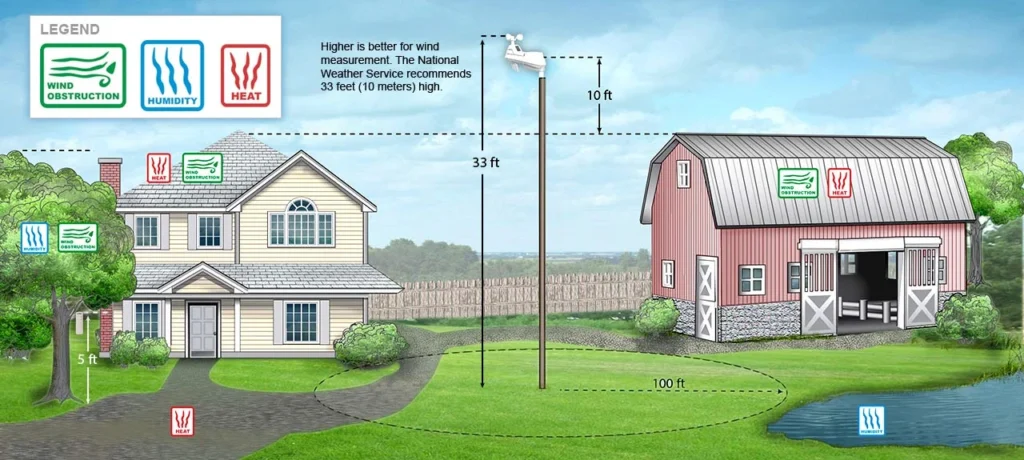
You should place temperature and humidity sensors about 1.2 to 1.5 meters above the ground. This height is standard because it shows the air temperature and humidity where people are. If you mount the sensors too low, they may pick up heat from the ground or moisture in the soil. If you place them too high, they might measure conditions that do not match the nearby environment.
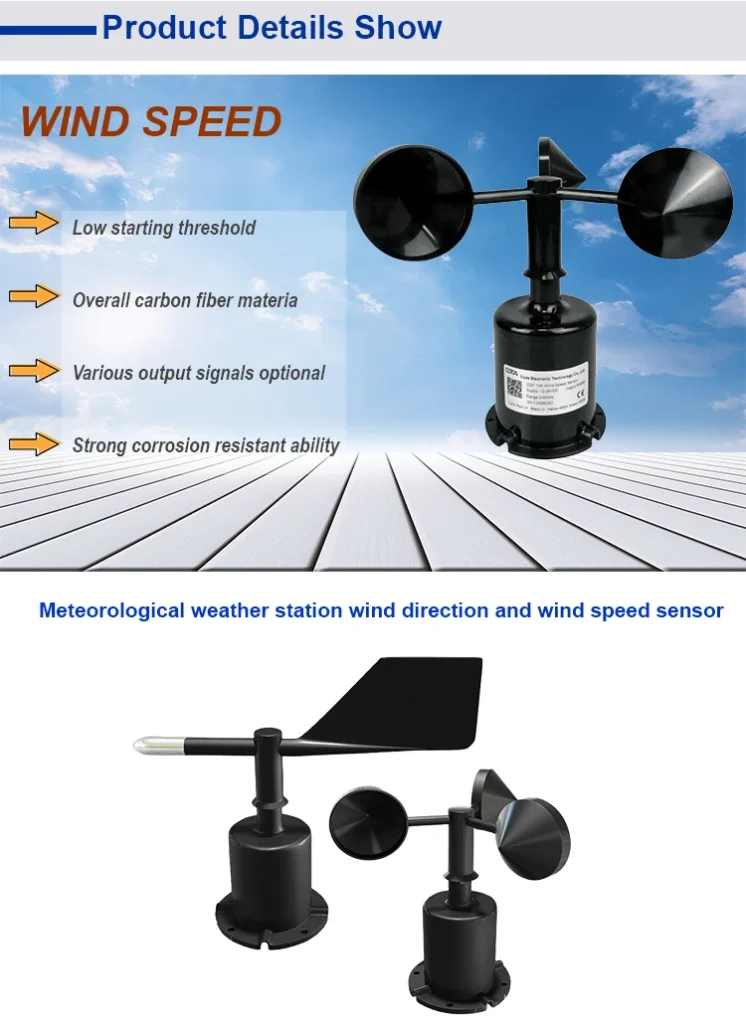
Wind Sensors
Wind sensors include anemometers that measure wind speed and wind vanes that show wind direction. They need a spot that is clear and open to the wind.
The best placement is on a tall pole or structure. It should be at least 10 meters high. This height keeps the sensors above most ground obstacles. These obstacles can block the wind flow, such as trees, bushes, or buildings.
It’s important to place wind sensors away from structures that can cause turbulence. For example, a sensor near a building’s corner can make the wind swirl. This can change the wind’s direction in surprising ways, leading to incorrect readings. Stay away from areas near large trees or in narrow alleys.
These areas can change how the wind moves. The pole or structure holding the wind sensors must be strong. It should not shake, as shaking can affect how accurate the measurements are.
Rain Gauges
Rain gauges should be placed on flat ground in an open area. The space around them must be free of branches, eaves, or other objects that could block rain. Experts suggest placing the rain gauge at least twice the height of the nearest obstacle. This helps it collect rainfall measurements accurately.
For example, if there is a tree that is 5 meters tall near where you want to put the rain gauge, place the gauge at least 10 meters away from the tree.
The rain gauge should be firmly attached to the ground. This keeps it from being moved by strong winds or heavy rain.
It is important to keep the area around the rain gauge clear. Debris like leaves and twigs can build up in the gauge.
This can change how we measure rainfall totals. We need regular maintenance for accurate data. This means emptying and cleaning the gauge.
Solar Radiation and UV Sensors
Solar radiation and UV sensors measure sunlight and UV rays. Place these sensors in a spot that gets full sun all day. Avoid areas that are shaded by trees, buildings, or other objects.
Shade will reduce the solar radiation and UV light that hits the sensors. This can cause wrong readings.
The sensors should be set at a specific angle for the best sun exposure. Solar radiation sensors work best when placed horizontally. UV sensors may need certain angles based on their design and setup.
It is important to keep these sensors clean. Dirt, dust, and bird droppings can affect their ability to measure solar radiation and UV levels.
Conclusion
Placing outdoor weather sensors correctly is very important for getting accurate personal weather station data. By following the guidelines for each sensor type, you can improve your results. Consider factors like exposure, height, and nearby sources of interference. This way, your home weather monitoring system will give weather enthusiasts useful information about local weather information conditions.
Placing your outdoor professional commercial weather station sensor correctly is important. This matters whether you love weather, work on a farm, or are a meteorologist. This will help you get more accurate and useful data for many uses.