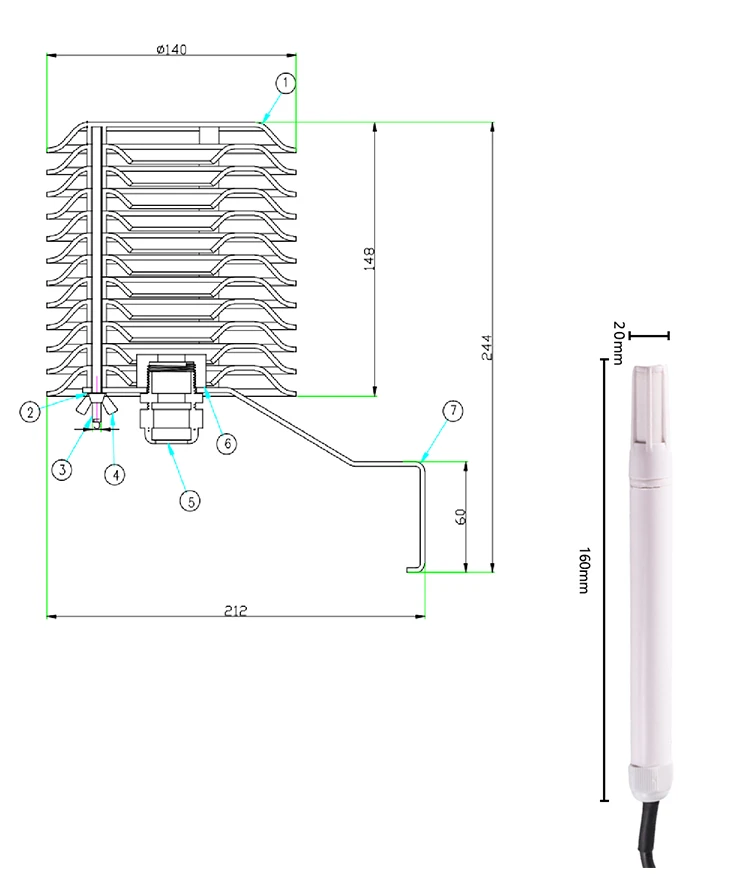
What is the most effective sensor for measuring air temperature?
An air temperature sensor, also called a room temperature sensor, measures and tracks air temperature. It is used in many fields. These include cars, heating and cooling systems, home appliances, medical devices, and environmental monitoring.
Basic Operating Principle of Air Temperature Sensors
The main idea of air temperature sensors is how heat relates to resistance, voltage, or current. A common part used is the thermistor.
This device changes its resistance when the temperature changes. When the temperature goes up, the thermistor’s resistance goes down. When the temperature goes down, the resistance goes up. By measuring the change in resistance, you can find the air temperature accurately.
Choosing the right air temperature sensor depends on the needs of your application. You should consider factors like accuracy, response time, cost, size, power supply, output signal type, and environmental conditions. Here are some common air temperature sensors, each with its own pros and cons:
Thermocouple:
– Pros: Fast response time, widely used in industrial settings.
– Cons: Limited temperature range, requires extra cold junction compensation.
Thermistor:
– Pros: Cost-effective, ideal for low-temperature measurements.
– Drawbacks: Slow response time and limited temperature range.
Semiconductor Temperature Sensor (STS):
– Pros: Very integrated and quick response time.
– Cons: Restricted temperature range, higher cost.
Thermopile Temperature Sensor:
– Pros: Provides high accuracy and works well in a wide range of temperatures.
– Cons: More expensive.
Fiber Optic Temperature Sensor (FOTS):
– Pros: Allows for non-contact measurement and is not affected by electromagnetic interference.
– Cons: It is costly and needs a complicated installation.
Infrared Temperature Sensor (Infrared Temperature Sensor):
– Benefits: measures without contact, quick response time.
– Drawbacks: Strongly affected by environmental conditions, needs calibration.
Dew Point Sensor:
– Benefits: can measure dew point temperature.
– Drawbacks: It costs more and is sensitive to the humidity around it.
When choosing an air temperature sensor, several factors need to be taken into account:
– Accuracy and precision: The necessary level of accuracy and precision will dictate the type of sensor needed.
– Temperature range: Check that the sensor works well in the expected temperature range for the application.
– Response time: In dynamic settings, sensors with quick response times are essential.
– Durability and reliability: Look at the environmental conditions. Choose a sensor that can handle the expected stresses.
– Cost: Balance performance needs with budget limits.
– Make sure to test how well the sensor works in the real environment where you will use it.
– Power source and output: Choose how to deliver power, the type of output signal, and more.
– Setup and upkeep: Check how easy it is to install and maintain.
The best air temperature sensor fits the needs of the application. It should focus on accuracy, response time, durability, and cost. RTD sensors are often the best choice for precise tasks. On the other hand, thermocouples and thermistors provide reliable performance at a lower cost.
Integrated circuit temperature sensors work well in electronic devices. Infrared sensors can take measurements without touching the object. In the end, the choice should consider these factors. This will make sure the selected sensor fits the needs of the specific application.