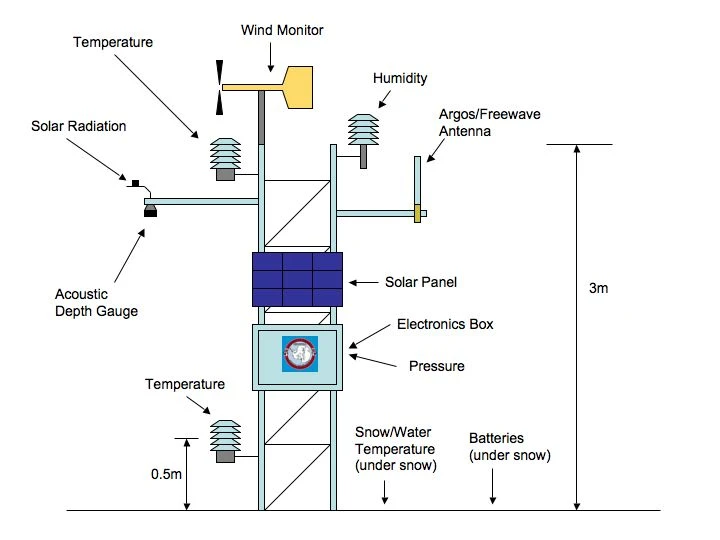
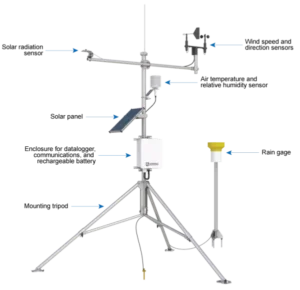
Automated Weather Stations
A weather station is a key tool that collects, studies, and processes weather data. These devices give accurate weather information quickly. This helps people make choices in many areas.
Remote locations weather stations use special sensors and tools to watch and record weather observations conditions. They measure things like temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind speed, wind direction, rainfall, sunshine duration, and solar radiation.
Traditional weather stations often need manual operation. However, new technology has led to automated weather stations (AWS). These stations work better and are more useful.
What Are Automated Weather Stations (AWS)?
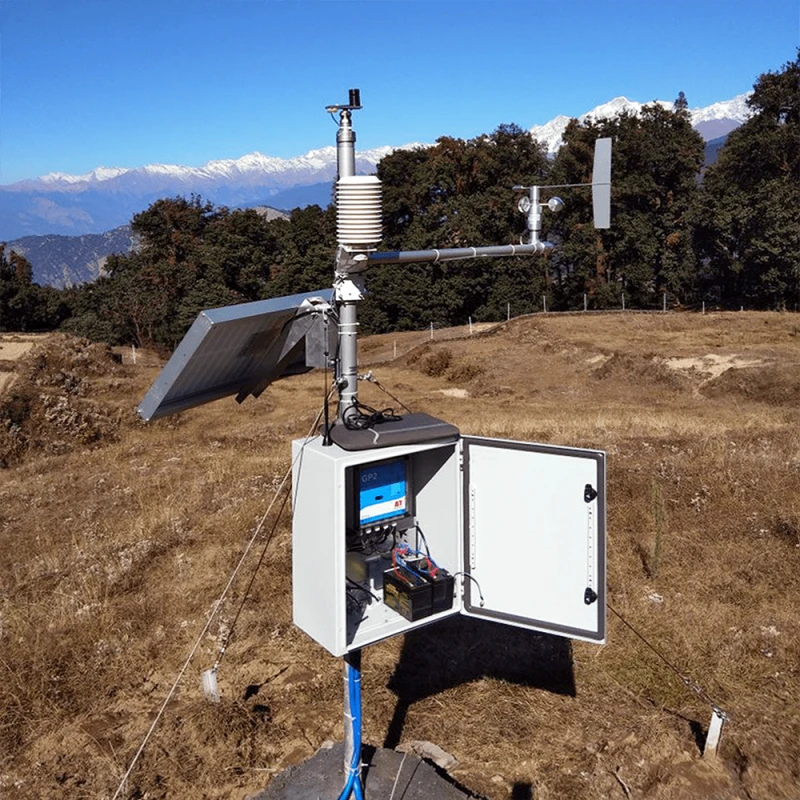
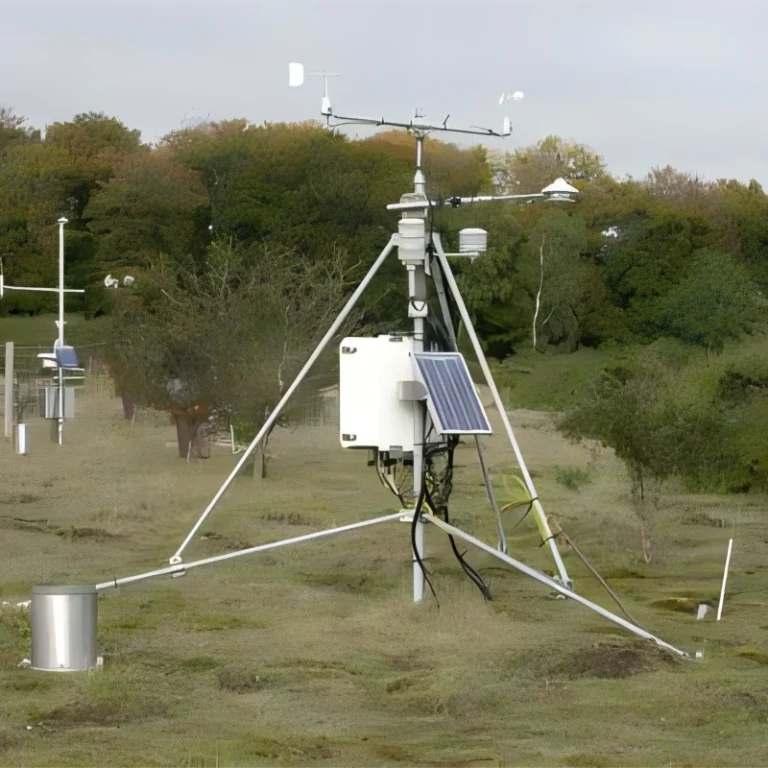
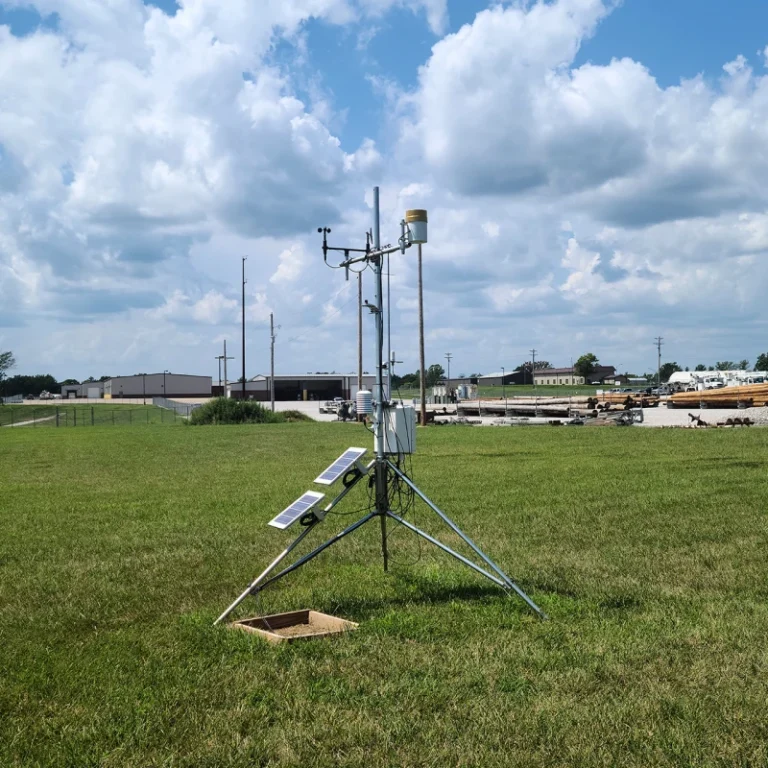
Automated weather stations are systems that work on their own. They monitor and send weather data without needing people.
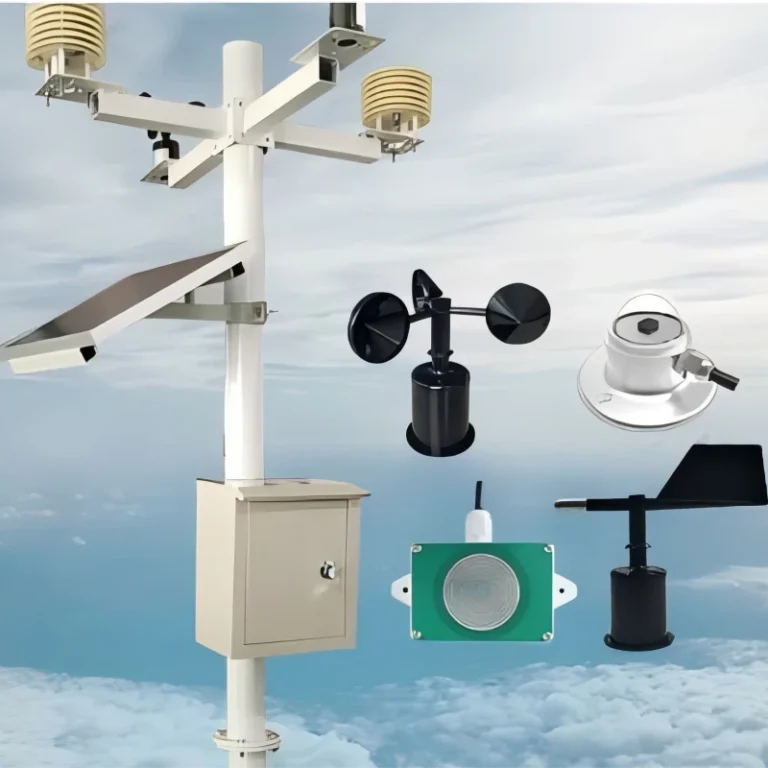
AWS has connected parts. These are weather sensors, data collectors, communication modules, and cloud integration tools. It provides real-time information on different factors.
These weather station include measure wind speed and direction, rainfall, air temperature, humidity, light levels, soil conditions, evaporation, and barometric pressure. These stations gather data and send it to central databases or cloud platforms. This makes processing and reporting more efficient.
People know AWS for many reasons. It has many functions and uses low energy. It is easy to install and can monitor fields in various conditions.
Roles of Automated Weather Stations
1. Real-Time Weather Data
AWS allows for the ongoing tracking of various weather factors. Sensors collect real-time data that gives clear insights into the current weather.
2. Data Processing and Forecasting
AWS collects data and processes it. It also analyzes the data to find trends. It looks at past weather data to predict future weather patterns. This is important for making weather forecasts.
3. Data Transmission
Advanced automated stations come with built-in communication systems. They send collected data to environmental monitoring platforms or agricultural big data platforms right away. This helps improve accuracy and speed up responses.
4. Early Warnings
In extreme weather events, AWS helps share information quickly. This helps early warning systems lower the risk of harm to people and property.
5. Support for Scientific Research
AWS provides dependable data for climate research and tracking the environment. This helps researchers and climate scientists see long-term changes in the atmosphere.
Key Functions of Automated Weather Stations
-Temperature Measurement:
AWS tracks environmental temperatures in real time. This helps with predicting the weather, farming, and planning cities.
-Humidity Monitoring:
Measuring humidity provides vital information for agriculture, water management, and related fields.
-Wind Speed Analysis:
AWS measures wind speeds. This helps predict the weather and supports wind energy projects.
-Rainfall Evaluation:
Precipitation measurements are essential for managing water resources and issuing flood warnings.
-Atmospheric Pressure Tracking:
Keeping track of atmospheric pressure makes aviation safer. It also helps improve the accuracy of weather forecasts.
Environmental Monitoring and Applications of Automatic Weather Stations
Automatic weather stations are important tools. They help us monitor the environment. They give accurate and up-to-date data for many fields. Here is a summary of important areas where these stations are used:
1. **Weather Forecasting**:
Automatic weather stations provide a lot of real-time and accurate data. This data helps make weather forecasts more accurate and timely. This is very useful for weather services.
2. **Agricultural Production**:
Farmers can use real-time weather information to plan their farming better. This helps make crops better and adjust to climate changes. It also makes farming more efficient.
3. **Urban Planning and Construction**:
Urban planners and architects use weather data to study a city’s climate patterns. This helps create infrastructure and city plans that are good for the climate.
4. **Transportation**:
Weather stations at highways, airports, and other transport hubs check the weather in real time. This makes transportation safer and more efficient.
5. **Environmental Monitoring**:
These stations are important for tracking things like air quality and soil moisture. They offer insights based on data to help with environmental conservation.
6. **Meteorological Research**:
Long-term weather data from automatic weather stations helps scientists study climate change. It also gives them better insights into weather events.
7. **Forest Fire Prevention**:
Weather data from these stations helps manage forests. It finds fire risks and helps with better fire prevention planning.
8. **Large Storage Area Microclimate Monitoring**:
Managers of large storage facilities use weather data to study local climate conditions. They also use green storage methods.
9. **Agricultural Planting Trials**:
Weather data helps farmers learn about the best conditions for growing crops. It helps make good planting plans and design experiments.
10. **Hydrology**:
These stations check rainfall and river levels. This helps predict and prevent flood risks, and supports better water resource management.
11. **Military and Aviation**:
Weather stations provide accurate weather information. This info helps military operations and aviation activities be safer by considering weather – related risks.
12. **Education and Research**:
Institutions use them as helpful tools for teaching weather science and doing experiments. This makes learning more engaging.
13. **Urban Climate Analysis**:
Automatic weather stations help planners learn about local urban climates. This information helps cities grow in a sustainable way.
Importance and Future Trends in Automatic Weather Stations
Automated weather stations are essential for today’s weather services. They are important in areas like farming, city development, transportation, protecting the environment, research, and managing disasters. They help with informed decision – making by providing reliable data.
The future of automatic weather stations depends on better technology and automation. This will help gather and process data more accurately. These systems can now give early warnings for severe weather events or natural disasters.
To keep things accurate and reliable, it is important to do regular maintenance. You should also adjust the sensors. You should also think about installation factors like the environment and safety issues.
These steps help reduce mistakes in data collection. This makes sure these systems work well to address today’s environmental and climate issues.