What are IoT sensors used in agriculture?
IoT sensors help farmers by monitoring and collecting data on different factors. These factors include soil moisture, temperature, pH, nutrient levels, and air quality. Analyzing this data can improve crop growth, reduce costs, save resources, and make smart farming more efficient.
Some specific ways to use IoT sensors in farming are:
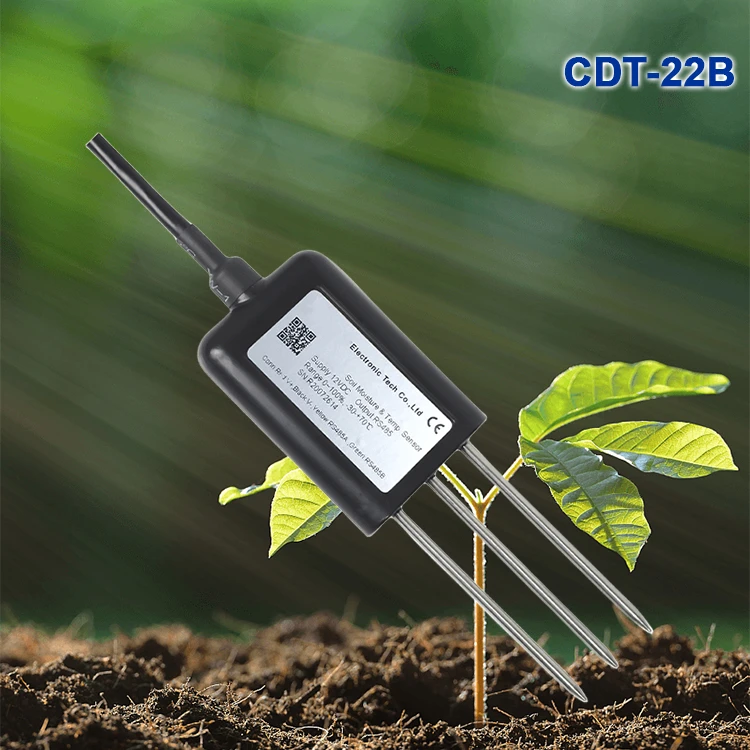
Soil moisture sensors:
These sensors check how wet the soil is. They help farmers know when to water usage their crops.
Temperature sensors:
These sensors measure soil temperature. They let us know if the soil is too hot or too cold for plants. We can also use them to check the temperature in greenhouses or other places where crops grow.
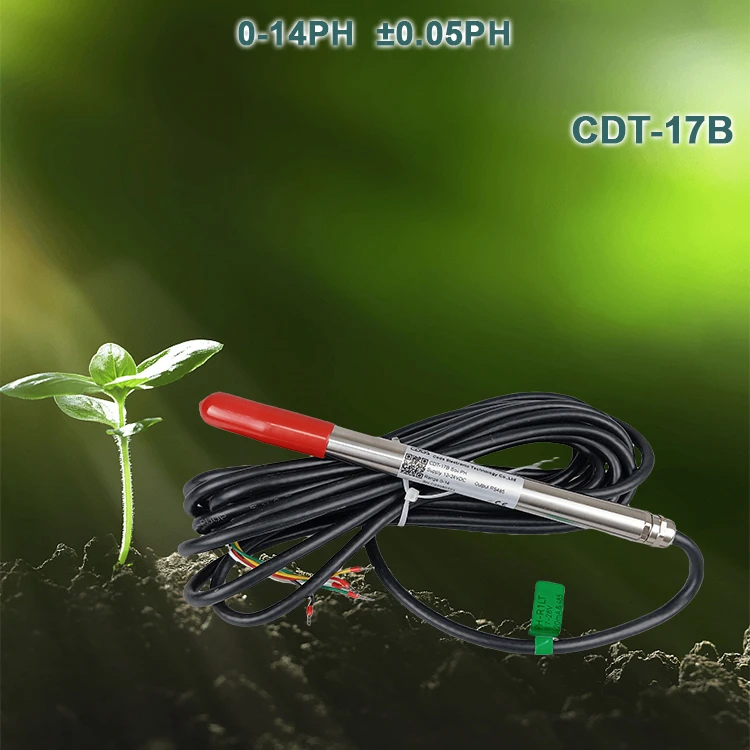
pH sensors:
These sensors check how acidic or basic the soil is. They help farmers change the pH level for healthy plant growth.
Nutrient sensors:
These sensors check the levels of important nutrients in the soil. These nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. They help farmers know when to use fertilizers for better crop growth.
Air quality sensors:
These sensors check levels of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and humidity in greenhouses. They help keep the air quality good for plant growth.
Farmers can use precision agriculture iot sensors to gather data on various farming factors. This helps them make better data driven decisions about their crops. It also boosts overall farming technology efficiency.
In addition to the sensors mentioned above, iot technology also uses these sensors in smart agriculture solutions:
Weather Sensors:
This tool tracks weather factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, rainfall, and air pressure. This information helps us predict weather changes and plan for farming.
Light Sensors:
You can measure light intensity in fields. This helps you check if plants get enough light. It also shows when to change shading or add more light.
Soil Firmness Sensor:
This measures how firm or hard the soil is. This is important for understanding soil structure. It helps prevent soil compaction and find the best tillage practices.
Water Level Sensors:
This tool is used to check water levels in the soil. It is important for smart irrigation systems. It helps ensure proper water distribution and management.
Drone and helicopter sensors: People add many agriculture sensors to these flying iot devices. These include high-resolution cameras, infrared sensors, and multispectral imagers. They use these tools to check crop growth, soil health, and environmental conditions over large farmland areas.
These sensors connect with internet of things iot solutions systems. They collect real time data. This helps farmers make better decisions and improve crop conditions yield and quality.