What is IoT? lot sensors
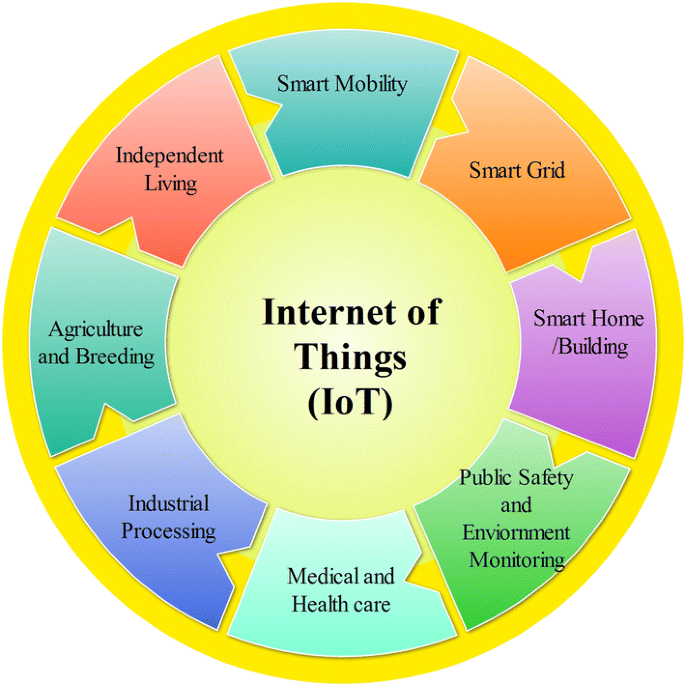
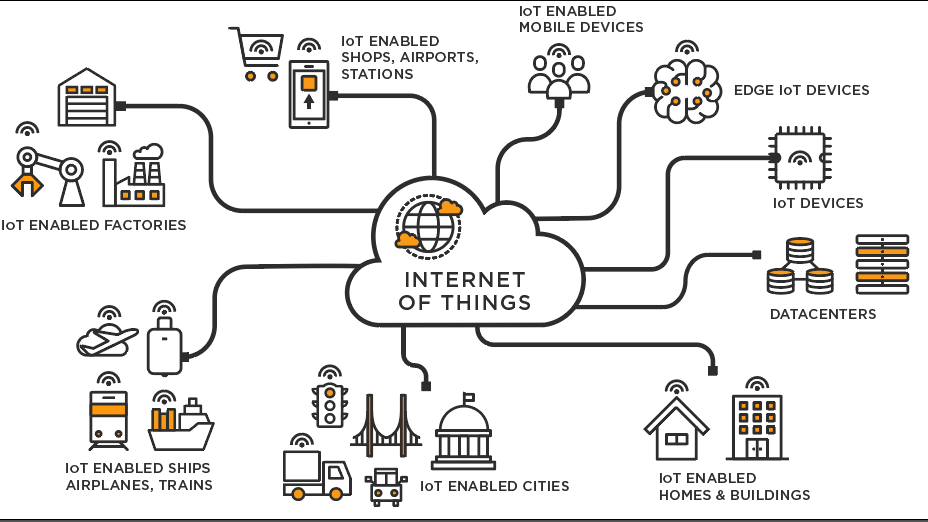
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of devices and motion sensors. These items connect and share iot data online. They use various sensors linked with network technology.
This creates a big web. It lets people, machines, and objects connect anytime and anywhere.
The main features of IoT focus on easy information sharing between objects and processes. These can be summed up as clear perception, dependable data transfer, and smart processing.
The Role of IoT Sensors
In an IoT ecosystem, two key parts are important: communication networks and connected devices. These devices mainly include sensors and actuators.
The basic layer of the IoT system has sensors. These sensors collect data about the environment. This data is a vital signs link to connect with higher layers, such as gateways and the network infrastructure.
Sensors are important because they collect data from their surroundings. They are the first line of IoT operations. They change and process signals.
Then, they send these signals to the larger IoT network. While sensors have this common job, different IoT applications need specific types of sensors for different situations.
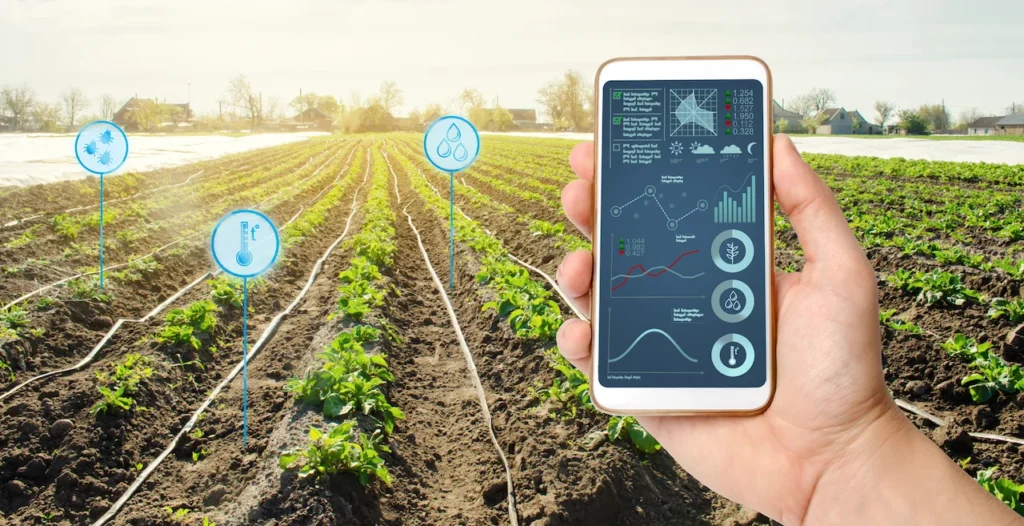
Use Case: Smart Farming & IoT in Agriculture
IoT and sensor technologies greatly help agriculture. They let farmers watch their environment in real-time. This helps them use resources well and work more efficiently.
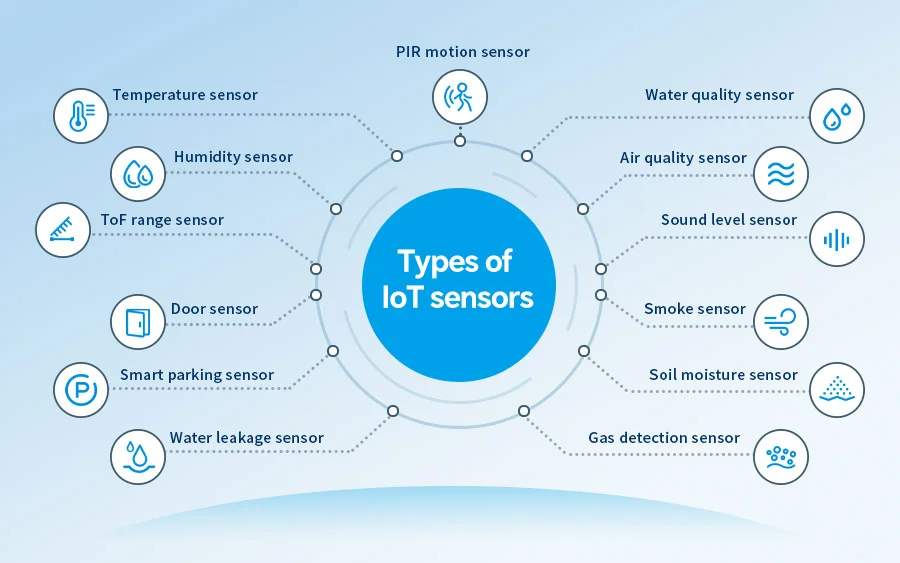
Top Types of IoT Sensors and Their Applications
1. Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors measure heat levels from different sources. They detect changes and turn them into data.
In manufacturing, machines need to check the air and equipment temperature. This helps keep operations safe. In agriculture, the right soil temperature is key for healthy crop growth.
Temperature sensors come in two types:
– **Contact-based:** Touch the object to feel any changes in temperature.
– **Non-contact-based:** Measure the infrared radiation that objects give off from far away. This helps us find their temperature.
Common uses are smart heating systems and checking room temperature.
2. Humidity Sensors
These devices check the moisture in the air or gases. Many industries use them, such as HVAC, weather forecasting, hospitals, and farming. They help check air quality and keep the right humidity in sensitive areas.
3. Pressure Sensors
Pressure sensors find changes in pressure and turn them into electrical signals. They have a part that responds to pressure and a unit that processes signals. Depending on how they are used, they are classified into:
– Gauge Pressure Sensors
– Differential Pressure Sensors
– Absolute Pressure Sensors
People often use these sensors in systems to find leaks. They also check water pipes to stop pressure drops.
4. Proximity Sensors
These sensors can find nearby objects or movement without touching them. They change this detection into electrical signals. These signals can start specific actions in the system. Proximity sensors are key in automation systems that need touchless features.
Engineers design proximity sensors for the non-contact detection of objects in close range. These sensors usually send out electromagnetic fields or radiation, like infrared light, to do their jobs.
They have many interesting uses. In stores, proximity sensors can see when a customer touches a product. They can then send alerts about discounts or special deals.
In parking lots at malls, airports, and stadiums, these sensors find open parking spaces. Companies also use them on assembly lines. This is common in making chemicals and food.
5.Level Sensors
Level sensors measure how much liquid or other substances are in systems. They are helpful for measuring liquids, powders, and granules.
Companies use them in many fields. These tasks include making oil, cleaning water, and growing food. A good example is waste management. In this case, level sensors measure how much waste is in bins or containers.
6.Water Quality Sensors
Water quality sensors are important. They check the properties and ion levels in water systems.
Water is vital in our daily lives and in many industries. These sensors help keep water safe and clean. They are used in many industries.
Common types of water quality sensors are:
– Chlorine Residual Sensors
– Dissolved Oxygen Sensors
– Conductivity Sensors
– pH Sensors
– Oxygen Reduction Potential (ORP) Sensors
7.Gyroscope Sensors
Gyroscope sensors measure how fast something spins around an axis. They are used in car navigation systems and anti-skid controls. They also help with motion-sensing technologies and stabilize cameras in video games.
8.Gas Sensors
Gas sensors detect changes in air quality. They can find harmful or flammable gases. Many industries use these sensors.
This includes mining, oil and gas, chemical research, and making products. For people, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide detectors are common in homes.
Popular gas sensor types include:
– Carbon Dioxide Sensors
– Carbon Monoxide Detectors
– Hydrogen Sensors
– Particulate Matter (PM) Sensors
– Nitrogen Oxide Sensors
– Oxygen Sensors
– Ozone Meters
– Ammonia Sensors
– Methane Sensors
9.Infrared (IR) Sensors
IR sensors detect environmental features by sensing infrared radiation. They can also measure heat. These sensors are used in many ways.
In healthcare iot platforms projects, they make it easier to monitor blood flow and blood pressure. Televisions use them to understand remote control signals. In art restoration, historians use infrared sensors to find hidden layers in paintings. This helps check authenticity and uncover restoration history.
10.Optical Sensors
Optical sensors change light into electrical signals and are used in many industries. In cars, they help recognize traffic signs and obstacles.
This is important for making self-driving cars. Smartphones often use light sensors to save battery power. In healthcare, these sensors help analyze breath and real time monitor heart rate.
11.Smoke Sensors
Smoke sensors find smoke in the air and measure how much there is. They are very important for fire safety. They work by measuring changes in internal resistance. This happens when smoke particles are present.
The device sends a signal that shows how much smoke is in the air. People often use these sensors in malls, hotels, warehouses, and smart homes. They are simple to set up and work well.
12.Image Sensors
Image sensors have parts that are sensitive to light. They change light images into electrical signals. These signals match how bright the light is. These sensors are important for many technologies that need to capture visual information.
The photosensitive device is the key part of an industrial camera. The image sensor has two main types: CMOS and CCD.
The CCD is made in a special way. This design gives it many advantages. It has a high signal-to-noise ratio. It also provides great transparency and better color reproduction.
These features make CCD sensors the best choice for fields like transportation and medical imaging. The benefits of CCD imaging are useful in many fields. High costs and power use limit its use and slow down market growth.
Both CCD and CMOS sensors have distinct advantages tailored to different scenarios. CMOS technology is improving a lot.
The costs for high-end CMOS sensors are also going down. These changes will make CMOS more important in the future. This is especially true for high-definition cameras in the security industry.
Many areas use image sensors. These include digital cameras, medical imaging devices, and night vision equipment. Thermal imaging systems, radar, sonar, media rooms, biometric systems, and IRIS-based devices also use them.
13.Chemical Sensors
Chemical sensors are tools that find different chemical compounds. They change their amounts into measurable electrical signals.
Chemical sensors are like our sense of smell and taste. However, they can do more than what humans can do. They can find substances that we cannot see or smell, like hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO).
Many industries use these sensors to keep an eye on the environment. They help manage processes and find harmful chemical leaks. This can happen if someone plans it or if it occurs by chance.
People use these sensors to detect explosions and radiation. They are also useful in space station work, recycling medicines, and different lab settings.
14.Sound Sensors
Sound sensors find, measure, and study sound waves. These sensors use a special type of microphone. It is called an electret condenser microphone. It is very sensitive to sound vibrations.
When sound waves reach the microphone, they cause its electret film to vibrate. This changes its capacitance.
This change creates a small voltage that matches the sound wave. It turns this into a measurable voltage wide range of 0 to 5 volts. The system converts the data from analog to digital. It then sends this data to a computer using a data collector.
Researchers use sound lot sensors to monitor noise in smart cities. They check noise on busy roads, at industrial sites, and near construction areas. They also check noise levels in cities and neighborhoods.
15.Accelerometer Sensors
Accelerometer sensors are smart devices designed to measure acceleration forces. Their structure usually has masses, dampers, elastic parts, sensing elements, and adaptive circuits.
These sensors help robots and other systems know their position in an environment. They can tell if the robot is going up a hill, down a hill, falling, or staying still in the air.
Common types of accelerometers include capacitive, inductive, strain gauge-based, piezoresistive, and piezoelectric sensors. They are used in smartphone features, vibration measurement systems, car controls, diagnostics, and free-fall detection in electronics.
People use them in different areas. These include aerospace iot technology and tools that detect motion for athletes. You can also find them in consumer gadgets. Also, monitoring systems for factories and construction sites use them.
16.Light Sensors
Light sensors are devices that can detect light energy. They can sense light from ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths and turn it into electrical signals. These sensors usually have photosensitive parts. They fall into four types: ambient light sensors, infrared light sensors, sunlight sensors, and ultraviolet light sensors.
They are very important in electronic devices like wearable health gadgets and smart lighting systems. Modern electrical measurement tools now offer high accuracy.
They work well with computers for real-time data processing. Light sensors are important tools. They measure both electrical and non-electrical things.
Conclusion
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, many new types of sensors are appearing. Sensors are important parts of IoT device systems. They gather data such as temperature, humidity, pressure, motion, and sound.
This data helps us see changes in the environment and events. When picking an IoT sensor for a system or device, think about your application and user needs. This will help make sure performance and usability are good.