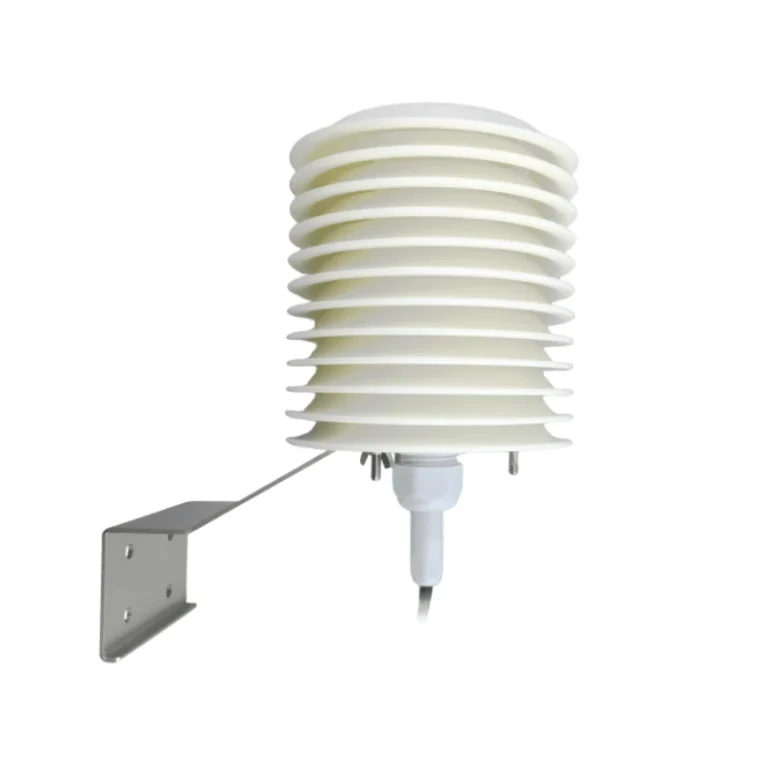
How does ambient air temperature sensor work? | ambient temp
An air temperature sensor measures the temperature around it. This device checks the air temperature and shows it as a number. The display usually shows this number in degrees Celsius (°C) or degrees Fahrenheit (°F).
Engineers and technicians use these sensors in many places. You can find them in home appliances, industrial machines, weather systems, and smart homes.
Ambient Temperature Sensor Working Principle
Ambient air temperature sensors operate based on different physical effects. Among them, the thermoelectric effect and resistance changes are more common. Here are some of the most common types of ambient temp sensors:
1. Thermocouple:
A thermocouple is made of wires from two different metals, like copper and conchoidal copper. When the metal joints are at different temperature of the surrounding environment, an electric effect happens. This effect makes a voltage at the joint.
The temperature of the air difference is linked to the electromotive force. Scientists can measure this force to find out the temperature range.
2. Thermistor:
The resistance of a thermistor changes with temperature refers. Most thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient (NTC). This means their resistance goes down as the temperature goes up. By measuring the resistance, the device can find the surrounding temperature.
3. Integrated temperature sensors:
Modern digital sensors often combine parts that sense temperature, process signals, and output data into one small chip. These sensors measure temperature using special features of semiconductor materials. They do this by checking electrical factors like current or voltage in the semiconductor.
4. Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs):
Scientists often use metals like platinum, nickel, or copper. They do this because a metal’s resistance changes when the temperature changes.
5. Infrared Sensors (Infrared Sensors):
Check the temperature by looking at the infrared light from the object. You can do this without needing to touch it.
working process:
1. Sensing: The sensor detects changes in the air temperature around it.
2.The device changes the temperature into an electrical signal. This signal can be a change in voltage or resistance.
3. Processing: The electrical signal is changed into a digital value. A microprocessor or analog circuit reads this value.
4.The air temperature value can be shown on a display, data logger, or remote monitoring system.
Ambient Temperature Sensor Scenarios:
1. Smart Home:
The sensor works in a smart thermostat control ambient system. It automatically adjusts the air conditioner or heater based on indoor changes. This keeps your living space comfortable all the time.
2. Meteorological monitoring:
Weather stations use sensors to track changes in temperature. This information helps with weather forecasting and research.
3. Industrial automation:
In industrial production, the temperature sensor plays a key role. It checks and control system the highly sensitive temperature in the production area. This helps keep a stable environment and ensures product quality stays consistent.
4. Agriculture:
Sensors in greenhouses and fields help farmers check the temperature. This helps them plant and take care of crops better.
5. Medical equipment:
This device checks a patient’s body temperature. It helps doctors find and treat various diseases.
6. Transportation:
In cars, planes, and other vehicles, we check the engine temperature. This helps keep driving safe.
7. Residential and commercial buildings:
In homes and businesses, sensors automate heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. These systems check indoor and outdoor temperatures in real time. This allows for automatic changes to keep a comfortable environment and save energy.
8. Electronic equipment:
Types of ambient temperature sensors are used with devices like computers and servers. They check the temperature around them to stay cool. These sensors work with fans and cooling systems to keep safe temperatures. This helps the equipment last longer and perform better.
Sensor values:
1. Better Comfort: Smart home systems keep indoor room temperature nice. This helps everyone inside feel good.
2. Improve Productivity: In factories, tracking temperature in real-time helps keep the production area stable. This boosts productivity and improves product quality.
3. Reducing Energy Use: The smart thermostat has a temperature sensor. It automatically adjusts the air conditioner or heater. This cuts down on energy waste when indoor temperatures change.
4. Scientific research and prediction: In weather monitoring, sensor data plays a key role. It helps forecast the weather and aids scientific research. This data is useful in many areas of production and daily life.
Higher ambient temperature sensors are important. They provide accurate and real-time temperature data. This helps make the system and equipment work better. It also keeps the right environmental conditions and supports automated control processes.
These sensors save energy efficiency by tracking temperature. They help equipment last longer. They also promote safety and comfort. Plus, they support research and forecasting.
Installation:
Proper installation is key for accurate temperature readings and the long life of air temperature sensors. Here are clear guidelines for different installation situations. These guidelines cover where to place the sensors, how to mount them, and what environmental factors to consider.
1. Optimal Location Selection
Avoid Direct Sunlight
Sunlight can cause “solar loading.” This occurs when the sensor takes in heat and shows false high temperatures. To prevent this, place the sensor in shaded spots, like under eaves or inside a radiation shield.
Outdoor sensors should be placed in a Stevenson screen. This is a white box with slats. It blocks direct sunlight but lets air flow.
Minimize Heat Sources
Keep at least 1–2 meters away from:
Heaters, air conditioners, exhaust vents, and machines that give off heat.
Dark surfaces, like black roofs and asphalt, give off heat.
Indoor sensors: Do not place them near radiators, kitchen stoves, or electronic devices like computers and TVs.
Ensure Air Circulation
Install in open spaces where air can flow freely (not in corners, closets, or enclosed boxes).
Place outdoor sensors at least 1.5 meters above the ground. This helps avoid temperature changes from the ground, like heat from pavement.
2. Mounting Height and Orientation
Standard Height for Accuracy
Outdoor installations: Install at a height of 1.2 to 1.5 meters above the ground. This is the average height of a person used to measure air.
Indoor installations: Place them 1.5 to 2 meters above the floor. Keep them 10 to 20 cm away from walls. This helps stop heat transfer from surfaces.
Orientation Guidelines
Place the sensor where it is less exposed to strong winds. If the sensor is unshielded, make sure the wind chill does not block airflow to it.
For sensors with a specific detection angle, like infrared models, aim the sensing part at the target area. This could be the center of a room.
3. Environmental Protection
Weatherproofing for Outdoor Use
Use sensors that have an IP65 rating or higher. This will help them resist rain, dust, and humidity.
Put a protective cover or shelter, like a ventilated plastic box, to keep out rain and snow. This will let air in.
Shielding from Moisture and Corrosion
In humid areas, such as bathrooms and greenhouses, choose sensors that are waterproof. Choose materials that do not rust, such as stainless steel or ABS plastic.
Do not install in places that get wet often, like near sprinklers or gutters.
Summary:
Researchers divide measure ambient temperature refers into two types based on how they work: direct contact and non-contact. Direct contact sensors, like thermistors, thermocouples, and RTDs, need to touch the object. This contact helps them give accurate temperature readings.
Non-contact sensors, such as infrared temperature sensors, do not touch anything. They measure temperature by sensing the infrared radiation from the object.
These sensors change temperature changes into electrical signals. Circuits then process these signals to show a temperature accurate readings. Their role is important in many fields. This includes home appliances, car systems, industrial monitoring, and research in science.