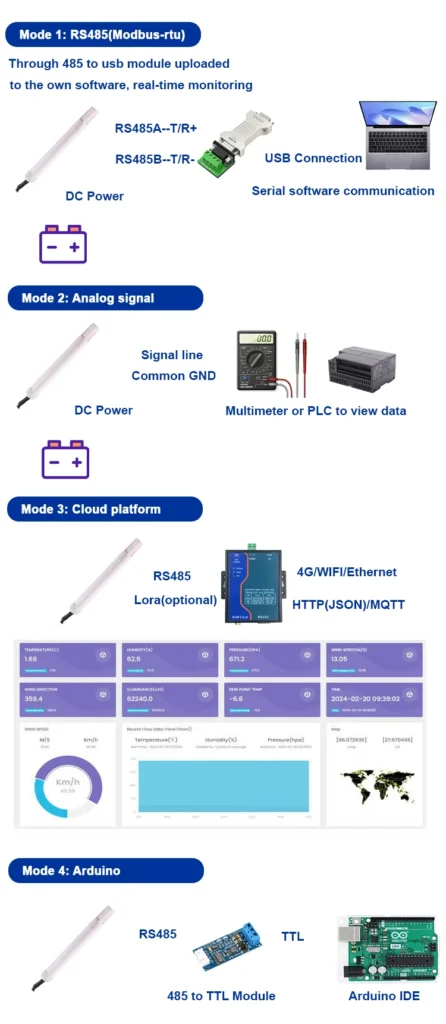
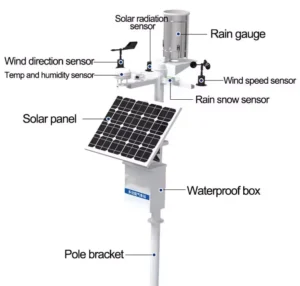
How to Select the best ambient temperature sensor ?
An ambient temperature sensor is a tool crafted to gauge the temperature of the surrounding area. It measures air temperature and shows it in a clear format. This is usually in degrees Celsius (°C) or degrees Fahrenheit (°F). By continuously sensing changes in the environmental temperature, the sensor delivers real-time monitoring and conveys this information through electrical or digital signals. Many everyday devices use these sensors. You can find them in household appliances, industrial machines, weather systems, and smart home technologies.
How Ambient Temperature Sensors Work
Operatio sensoris temperaturae ambiens pendet ex variis principiis physicis, ut effectus thermoelectricus aut variationes resistentiae. Below are some commonly used types of ambient temperature sensors and their underlying mechanisms:
1. **Thermocouple**
Two wires of different metals, like copper and constantan, make a thermocouple. When the two points where these metals join have different temperatures, they generate an electric potential (thermoelectric force). The temperature difference links to this voltage difference. The sensor can calculate the temperature by measuring this voltage.
2. **Thermistor**
A thermistor’s resistance fluctuates with temperature changes. Most thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient (NTC), meaning their resistance decreases as the temperature rises. By determining its resistance value, you can accurately calculate the ambient temperature.
3. **Integrated Temperature Sensors**
Modern sensors usually combine different parts into one small chip. These parts include temperature-sensitive elements, signal processing circuits, and output components. These sensors exploit the electrical properties of semiconductor materials to derive temperature by measuring parameters like current or voltage changes within the semiconductor.
4. **Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)**
RTDs utilize the principle that the electrical resistance of certain metals changes with temperature. People typically employ materials like platinum, nickel, or copper for this purpose, offering high precision and reliability.
5. **Infrared Sensors**
Infrared sensors measure ambient temperature without direct contact by detecting the infrared radiation emitted from surrounding objects. This type of sensor is especially useful in non-contact applications.
Working Process of Ambient Temperature Sensors
1. **Detection**:
The sensor identifies changes in ambient temperature.
2.**Conversion**: Temperature changes translate into electrical signals, such as voltage or resistance alterations.
3. **Processing**: The system processes the electrical signals and changes them into digital values. A microprocessor or analog circuit can then interpret these values.
4. **Output**: Devices like monitors, data loggers, or remote systems display the final temperature value.
Scenarios for Ambient Temperature Sensors
1. **Smart Homes**:
These sensors are key to smart thermostat systems. They allow air conditioners or heaters to adjust automatically based on indoor temperature changes. This ensures a comfortable living environment.
2. **Meteorological Monitoring**:
Weather stations and related equipment utilize these sensors to monitor ambient temperature fluctuations, providing valuable data for weather forecasting and research.
3. **Industrial Automation**:
During industrial processes, ambient temperature sensors regulate and monitor the production environment’s temperature. This ensures product quality and operational stability.
4. **Agriculture**:
In greenhouses and farmlands, these sensors assist farmers in monitoring temperature conditions, supporting efficient crop management and planting strategies.
5. **Medical Equipment**:
They are used to monitor patient body temperatures, assisting in disease diagnosis and treatment.
6. **Transportation**:
Ambient temperature sensors are employed in vehicles, airplanes, and similar transportation systems to monitor engine temperatures, enhancing operational safety.
7. **Residential and Commercial Buildings**:
These sensors are essential for automating HVAC systems by providing real-time indoor and outdoor temperature data. This aids in maintaining a comfortable environment while conserving energy.
8. **Electronic Equipment**:
Computers, servers, and other electronic devices use temperature sensors to avoid overheating. These sensors work together with fans or cooling systems. This promotes efficient performance and extends the life of the equipment.
The Value of Ambient Temperature Sensors
1. **Enhanced Comfort**:
By maintaining optimal indoor temperatures in smart homes, these sensors contribute significantly to occupant comfort.
2. **Increased Productivity**:
In industrial contexts, real-time ambient temperature monitoring ensures a stable environment, improving productivity and maintaining high product quality.
3. **Energy Savings**:
Smart systems lower energy use by automatically changing heating or cooling based on temperature changes from sensors.
4. **Scientific Research and Prediction**:
Meteorological data provided by these sensors supports weather predictions and scientific studies, aiding various aspects of daily life and production.
Sensor Types
Ambient temperature sensors can function via two primary methods—contact or non-contact operation:
– **Direct Contact Sensors**: Such as thermistors, thermocouples, and RTDs. These require physical contact with the target object for accurate measurement.
– **Non-Contact Sensors**: Infrared temperature sensors measure temperature by detecting emitted infrared radiation without requiring physical interaction.
Conclusion
Ambient temperature sensors turn temperature changes into electrical signals. The system processes these signals into readable values. These sensors are essential tools in many areas. People use them in home automation, car systems, industrial controls, weather forecasting, medical diagnostics, scientific research, and more. They ensure energy efficiency, enhance equipment reliability, improve living conditions, and support informed decision-making for both everyday applications and specialized industries.