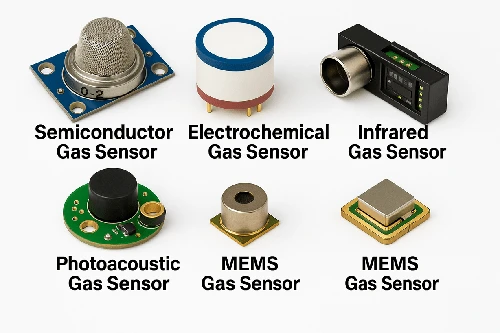
Where Are Gas Sensors Used
**Applications of Gas Sensors**
Gas sensors play a key role in many fields. They mainly measure and detect gases like carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, and argon. In factories, these devices are often used to find gas leaks.
They also check the air quality in the ventilation systems. They help find problems with the sensors.
In the medical field, gas sensors are very important. They are used to detect gases linked to tumors or smoke inhalation. The security field also benefits from using them in fire alert systems and gas sensors. These are parts of systems that sense doors and windows.
**A Brief History of Gas Sensors**
The history of gas detection goes back to 1815. British chemist Sir Humphry Davy created the “Davy lamp” to make coal mining safer. This lamp gave light without causing explosions from coal mine gas. It was an important step in dealing with gas dangers in factories.
Beyond methane, carbon monoxide is a silent threat. It is a concern because it is colorless and odorless. Canaries were used in coal mines to help detect danger early. The canaries would alert us when carbon monoxide levels were too high.
Later, they added tubes to detect carbon monoxide. These tubes became essential for modern gas detection technology. As people became more aware of the risks of low oxygen, oxygen-detection tubes were developed.
In 1926, a series of oil tanker explosions led to new gas indicators. These were developed by the Standard Oil Company of California. Portable gas sensors came out the next year.
In 1939, an interferometric gas detection meter was invented. This meter used light diffraction to measure vapors like methane and gasoline.
By 1960, electrochemical oxygen sensors were a big step forward for portable oxygen detectors. This led to their widespread use. Metal oxide sensors came out in 1968. They made it simpler to check for harmful gases.
In the 1980s, electrochemical sensors could detect different toxic gases. This led to the rise of global companies focused on gas safety tools.
**Types of Gases Detected**
Gas sensors are made to check different types of gases. These include gases that can catch fire, harmful gases, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
**Flammable Gases**
Flammable gases are some of the most commonly checked with detection tools. These gases can mix well with air or oxygen, but only up to a certain point. This can create a risk of explosion if it catches fire.
They are often seen in industries such as petrochemicals and manufacturing. Instances include hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10). They also include ethylene (C2H4), propylene (C3H6), acetylene (C2H2), and similar compounds. Toxic Gases**
Toxic gases are dangerous substances. They can harm human health and cause poisoning. There are two types of gases: irritant gases and asphyxiant gases.
Irritant gases can bother the eyes and make it hard to breathe. Asphyxiant gases lower the oxygen levels in the body.
These gases are serious threats to safety and health. Communes exempla comprehendunt monoxidum carbonii (CO), sulfideum hydrogenii (H2S), ammonium (NH3), chlorinum (Cl2), dioxidum sulfuris (SO2), dioxidum nitrogenii (NO2), oxidum nitricum (NO), et dioxidum carbonii (CO2).
**Composita Organica Volatilia (VOCs)**
VOCs are organic substances that easily evaporate at normal room temperature and pressure. These compounds are often seen as organic solvents. They are important for checking places with gasoline, diesel, paints, benzene, crude oil, and similar materials.
**How is Carbon Dioxide Measured?**
Measuring carbon dioxide is important for many uses. These include industrial processes, environmental monitoring, and safety systems. Modern CO2 detection often uses infrared sensors or chemical methods.
These methods help measure concentrations accurately. These methods keep safety rules while also making sure operations run smoothly in many areas.
**Applications of Gas Sensors**
Gas sensors change gas levels into electrical signals. Their use covers many areas, such as homes, factories, farming, healthcare, and checking the environment.
**Gas Sensors in Homes**
Research by the World Health Organization shows that indoor air pollution can be 2 to 5 times worse than outdoor air. People spend over 80% of their time indoors. This makes it important to check indoor air quality. In homes, gas sensors help detect leaks of natural gas, propane, and harmful gases from cooking.
These sensors can be added to microwaves. They detect gases that come out while cooking. They also help to control the cooking process on their own.
You can install carbon dioxide sensors, smoke detectors, and ozone sensors in homes, offices, meeting rooms, and entertainment venues. These devices can help automate air purifiers or turn on fans. In some tall buildings, gas sensors are used to find early fire risks. This helps make sure alarms and responses are quick.
**Gas Sensors in Industries**
In factories, gas sensors are important for finding harmful emissions and keeping people safe. They are commonly used in the petrochemical industry. They help monitor harmful substances. These substances include carbon dioxide, ammonia, chlorine, and nitrogen oxides.
In the semiconductor and microelectronics industries, harmful gases are found. These include organic solvents and phosphine. In the energy sector, hydrogen sensors find hydrogen gas.
This gas comes from the breakdown of transformer oil. These applications help protect workers’ health and ensure operations run smoothly.
**Gas Sensors in Agriculture**
In greenhouses, gas sensors check levels of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and ethylene. This helps make the best conditions for plants to grow.
Low carbon dioxide levels can slow photosynthesis. This can limit how plants grow. We might need to add more carbon dioxide by hand.
Carbon dioxide sensors are used to keep the right levels in greenhouses. This helps fruits and vegetables grow well.
**Gas Sensors in Livestock Farming**
Livestock farming creates a lot of gases. These include hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and carbon dioxide. These gases come from animal breathing and the decay of organic materials.
High levels of these gases can harm the health of farmworkers and animals. Gas sensors are used to measure gas levels. They help with airflow to prevent any harmful effects.
**Gas Sensors in Medicine**
Gas sensors are used in medical devices like ventilators and anesthesia machines. They help keep track of important signs in patients. Carbon dioxide sensors help us learn about a patient’s breathing health.
They measure the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in their breath. This data helps us measure blood oxygen levels correctly. This helps healthcare providers quickly deal with breathing problems.
**Gas Sensors in the Food Industry**
Gas sensors play a pivotal role in food production and transportation. During packaging, inert protective gases are injected to extend shelf life. Gas sensors check that the gas levels in packaging meet quality standards during testing and sampling.
Transporting perishable goods like fruits and vegetables needs the right gas levels. This helps slow down their metabolic activity. Lowering oxygen levels from 21% to about 2% can reduce metabolism by around 30%. This helps keep things fresh during transport.
**Gas Sensors in Environmental Monitoring**
The need for checking the environment is growing. This has led to more people using gas sensors around the world. These sensors detect harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and hydrogen chloride. They help make sure people follow environmental rules better.
Carbon dioxide sensors help measure greenhouse gas levels for climate research. Air quality sensors also measure the amount of tiny particles in the air. This helps us learn about pollution levels. As environmental problems grow around the world, the need for gas sensors keeps increasing.
Gas sensors play a key role in many industries. They can find harmful gases and help take action. Their uses are growing quickly. They help protect health indoors and tackle global environmental issues.
Environmental Sensors List and Applications
Gas Sensor Applications in the Automotive Industry
Cars use different sensors, and gas sensors are very important. Statistics show that gas sensors make up over 50% of the sensors used in car engines. From an outside view, vehicle exhaust has harmful substances. These include nitrogen oxides (NOx), tiny particles (PM), and hydrocarbons (HC).
To cut down pollution and boost performance, different gas sensors are used to find these substances. Their main goals are to improve fuel burning efficiency, make energy use better, and lower harmful emissions. In modern cars, common gas sensors include those for nitrogen oxide, ammonia, and particulate matter.
Pollution sources inside vehicles come from their parts and materials used in the interior. Toxic pollutants like formaldehyde, xylene, and benzene pose threats to human health. Another dangerous gas found in cars is carbon monoxide.
It mainly comes from engine emissions and exhaust systems. It can also build up when you use air conditioning in parked cars.
Carbon monoxide is a gas that has no color and no smell. It can build up inside a car. This buildup can lead to serious issues. Long exposure can cause poisoning or even death.