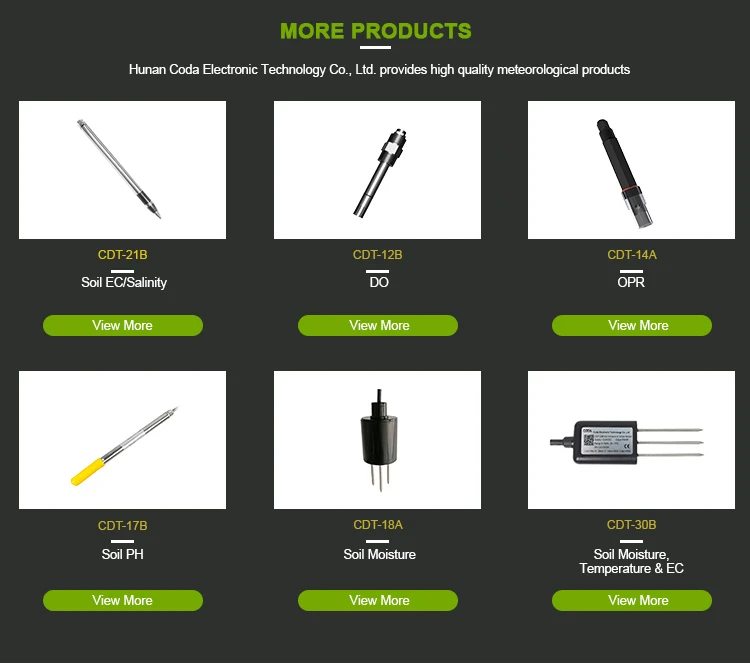
10 Types Of Soil Sensors
Soil sensors are smart tools. They check and watch different soil properties in real time. These sensors measure key factors such as temperature, moisture, pH, conductivity, organic matter, and microbial activity. They provide useful data for farming, environmental protection, geology, and other uses.
Soil sensor probe use different methods to work. These methods include capacitive sensors methods, resistive measurements, and electrodes that choose specific ions. These tools measure soil traits well. Farmers can use these sensors to water and fertilize better.
This can lead to better crop yield and quality. Environmental scientists can check for soil pollution and damage. They can then make plans to stop these problems.
Geologists look at minerals and rock formations. This helps in resource development.
Overview of Soil Sensors
Here is a list of ten common types of soil probes. It covers what they are, how they work, their features, and how to use them.
1. **Soil Temperature Sensor**
– **Definition**: A tool that checks the temperature of the soil. This is important for farming and climate research.
– **Working Principle**: It uses thermistors, like PT1000 platinum RTDs. These measures check how resistance changes to find soil temperature.
– **Characteristics**: It works in a wide range of temperatures (-40°C to 120°C). It is very accurate and works well in humid conditions for a long term time. It also provides stable performance.
– **Applications**: This device is used in farming, forestry, geology, irrigation, lawn care, highway management, and railroad work.
2. **Soil Moisture Sensor**
– **Definition**: It shows how much water is in the soil. This helps water plants and check the soil’s health.
– **Working Principle**: It works by measuring changes in the dielectric constant. It also uses two methods: capacitive and resistive.
– **Characteristics**: It gives quick answers and smooth data transfer. It also works well in different types of soil.
– **Applications**: It helps save water with irrigation. And it also takes care of greenhouses and helps with gardening. It aids in pasture management and scientific studies. It also lets you do quick soil tests.
3. **Soil Conductivity and Salt Sensor**
– **Definition**: This shows how well the soil can conduct electricity. It helps find the levels of salt in the soil.
– **Working Principle**: It uses electrodes to check how well something conducts electricity. It does this by watching how ions react in an AC electric field.
– **Characteristics**: It gives fast and precise measurements with great stability. This is good for soils that have high conductivity.
– **Applications**: This is used in plans for fertilizing, managing water, and checking for heavy metal pollution in the soil.
4. **Soil NPK Sensor**
– **Definition**: Checks nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) levels to see soil nutrients.
– **Working Principle**: It uses light and electrical tests to analyze data. It checks the nutrient levels in the soil.
– **Characteristics**: Offers real-time data that is reliable and cost-effective for smart farming.
– **Applications**: Used in precision farming, sustainable farming, and checking soil health.
5. **Soil pH Sensor**
– **Definition**: It shows how acidic or basic the soil is. This is important for how plants grow and use their food.
– **Working Principle**: It uses chemical reactions to measure pH. It checks the current from hydrogen ions in the soil.
– **Characteristics**: It provides precise pH readings that range from 0 to 14. However, it needs regular checks to stay accurate.
– **Applications**: Used in farming, gardening, and checking soil health.
6. **Soil Heat Flux Sensor**
A soil heat flux sensor measures how heat moves through soil over time and space. It helps us learn about the heat properties of soil. The sensor works by detecting temperature changes and thermal conductivity.
It uses heat flux meter principles and gives very accurate results. Even with its complex technology, it works very well. These sensors help us watch small climate areas, study weather for farming, and look at geological sites.
7. **Multi-Layer Soil Parameter Monitor**
This equipment tests soil conditions at different depths. It uses sensors for temperature, humidity, conductivity, and more. It gives detailed soil profile information for complex environments.
This helps research in farming, forestry, geology, and protecting the environment. Its many functions and strong data features make it very helpful.
8. **Soil Gas Sensor**
Soil gas sensors check the types and amounts of gases found in the soil. They check gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. They use electrochemical or optical methods to measure how gases react with sensitive parts.
This helps us learn about soil respiration and how roots function. These sensors help us study soil ecology and keep an eye on the environment in farming.
9. **Soil Water Potential Sensor (Soil Tensiometer)**
This sensor measures how much water is in the soil. It uses ceramic suction to sense water pressure. This tool helps manage soil water and design irrigation systems. It helps save water for farming and keeps the soil moist.
10. **Portable Soil Sensor**
Portable soil probes use tools to measure soil factors like temperature, moisture content, and pH levels. They are light and simple to use in the field. Their flexibility allows for quick measurement of soil conditions. This is helpful in farming, checking the environment, research, teaching, and more.
**Summary**
Soil sensors play a key role in farming and environmental science. They collect real-time data on temperature, moisture, pH, nutrients, and other soil features. These sensors use various physical and chemical methods to enhance farming practices, such as irrigation and fertilization.
This helps increase crop yield and quality. They also help protect the environment by finding soil pollution or damage. This supports sustainability.
Their variety and portability let them be used in many areas. They offer key help for making better decisions.