wind measuring instrument
The anemometer tower has wind measurement tools to measure wind. It includes an anemometer instrument for accurately measuring wind. There is a wind vane sensor and software too. It also has a thermometer, a barometer, a hygrometer, and more.
An anemometer is a tool that measures wind speed and pressure. There are different types of anemometers. These include rotary anemometers, heat-dissipating anemometers, acoustic anemometers, and ultrasonic wind speed sensors.
Most wind farms use rotary anemometers. We can divide these devices into two types: wind cup anemometers and propeller anemometers.
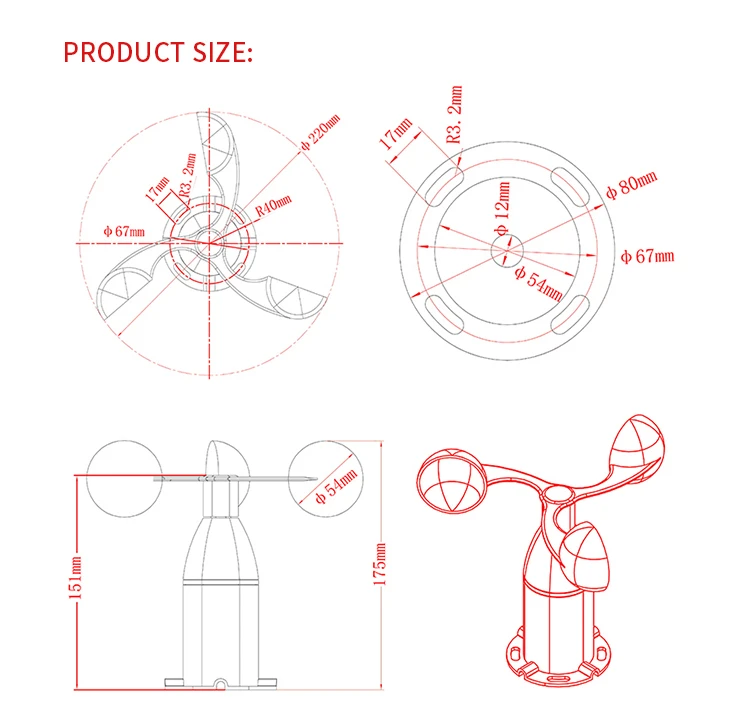
A precise wind gauges cup anemometer has three or four hollow shells shaped like hemispheres or cones. Attach a three-pronged bracket that makes a 120° angle or a cross-shaped bracket that makes a 90° angle. Make sure the concave sides of the cups all face the same way.
The team attaches the whole cross arm to a vertical axis. When the wind blows, the wind cups spin around the axis. Their speed matches the wind speed.
Another type of rotary anemometer is the propeller anemometer wind. It has a three-blade or four-blade propeller at the front of a wind vane.
This wind speed meter design helps it align with the wind direction all the time. The blades spin around a horizontal axis. Their speed matches the accurate wind speed.
wind speed meter measuring
The design of the wind alarms tower affects where we place wind speed measuring devices at different heights. To lessen the “tower shadow effect” from the anemometer tower, attach the ultrasonic anemometer to a sturdy support.
This support should reach out from the tower’s main structure and stay a safe distance away. For a truss wind tower, this distance should be more than three times the tower’s width. For a cylindrical wind tower, it should be more than six times the tower’s diameter.
You need to set the anemometer’s mounting bracket horizontally. Also, keep the angle between the bracket and the wind direction between 30 and 90 degrees.
The radiating anemometer works by linking the heat loss of a heated object to the air speed around it. This feature allows the device to measure wind speed, but users mainly use it to detect low wind speeds.
Acoustic anemometers have no moving parts. They respond quickly and measure wind speed from any direction. However, they can be quite expensive. Most people use rotary anemometers to measure wind speed.
Wind Vane Sensor
The wind direction sensor is the most common tool for finding wind direction. It includes types like single-wing, double-wing, and streamlined models. A wind vane has an unbalanced design with four main parts: the tail, pointing rod, counterweight, and main shaft.
The center of gravity lines up with the supporting shaft’s axis. This lets the wind vane sensor turn freely around the vertical axis.
Wind vane installing
The technician installs the wind vane sensor at the right height on the anemometer tower. You must attach it to a sturdy beam. This beam should be more than three times the width of the truss wind tower.
The installation should be six times the diameter of the round tube wind tower. Align it with the main wind direction. Place the beam at a 90° angle to this direction. Adjust it horizontally.
You also need to adjust the wind vane for the local magnetic declination. Ensure it points to true “north.”
You can also show wind direction using angles. Use true north as the starting point and rotate clockwise. An east wind is 90°, a south wind is 180°, a west wind is 270°, and a north wind is 360°.
Wind measurement software
The main job of the instrument for measuring wind speed software is to record data. It tracks wind speed, direction, temperature, and pressure. This wind data comes from sensors on the wind tower. Collecting this wind readings data helps the wind resource engineer analyze the wind resource information.