How Wind Speed and Direction Sensors Operate
Wind sensors have been important for measuring wind speed and direction for a long time. They help in farming, building, flying, and clean energy. Coda Electronic Tech Co., Ltd (CodaSENSOR) is a well-known maker. They make high-performance sensors for many different uses.
Applications of Wind Sensors
Wind speed and direction sensors are used in many fields. These include weather stations, wind turbines, ships, airports, and sports events.
Their accurate data is useful for several tasks. It helps with weather forecasting. And it also helps to check the environment. It is also important for checking air quality and looking at wind resources.
Understanding Wind Speed and Direction Sensors
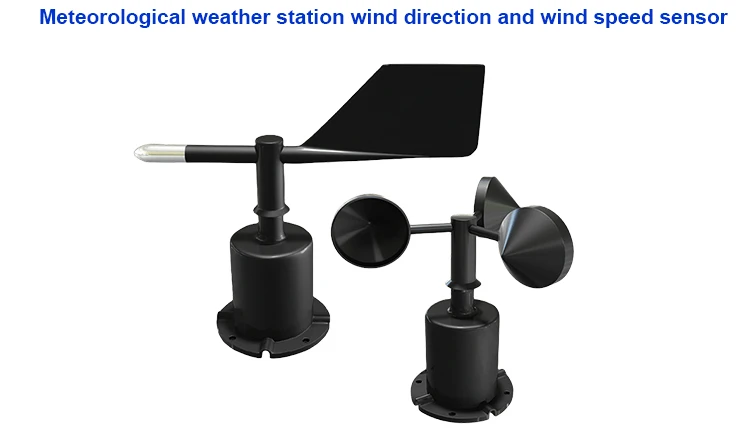
Wind sensors have two main parts. One part is called an anemometer. It measures how fast the wind is blowing.
A wind vane shows wind direction. Here’s a closer look at how each part works:
Anemometer
An anemometer measures how fast the wind blows. It usually has cups on a horizontal or vertical shaft. The wind makes these cups spin.
The speed they spin is directly related to how fast the wind blows. The device measures wind speed by checking how fast it spins.
An alternative type is the sonic anemometer. It uses sound waves to check how fast the wind is blowing. This technology measures how long sound waves take to move between paired transmitters and receivers.
It works in different directions. By looking at these travel times, you can find out the wind’s speed and direction.
The wind vane shows which way the wind is blowing. It often has a flat plate or a pointer shaped like an arrow. This pointer spins freely around a vertical axis. Its tip always points where the wind is blowing.
A potentiometer or magnetic sensor converts this rotational movement into an electrical signal, which is then processed to define the exact wind direction.
Choosing the Right Wind Sensor
Choosing the right wind sensor is key for getting accurate readings for your work. Here are important things to think about when making a choice:
– **Accuracy:** Choose sensors with low error margins. Aim for 1% accuracy in wind speed and 2 degrees in wind direction.
– **Response Time:** Different tasks need different response times. “Find out the response time your application needs before selecting a sensor.”
– **Durability:** Check the environmental conditions where the sensor will be used. Choose models that are built to last. They should resist rust and perform well in both hot and cold temperatures.
– **Output Interface:** Make sure the sensor’s output works with your data logger or monitoring system needs.
– **Cost-Effectiveness:** Balance the need for affordability with accuracy and reliability. “Find sensors that work well and are priced fairly.”
CodaSENSOR Wind Sensors
CodaSENSOR focuses on making wind sensors. These sensors use advanced digital circuits and have strong features to reduce interference. These devices can manage issues like radio waves, electromagnetic interference, and sudden voltage spikes.
Their sensors have protection against polarity. They work with many power supplies and meet ICE and CE (EMC) standards.
CodaSENSOR is excellent for work at high altitudes. It is useful in construction, port machinery, and wind power. It shows 58 years of engineering expertise.
Final Thoughts
Wind speed and direction sensors are essential for accurate weather monitoring and many professional uses. Knowing how these sensors work and looking at key selection factors helps make smart choices.
This guarantees top performance and dependability. Check out CodaSENSOR’s wide range of products. They offer advanced tools to measure the wind. This helps to make your operations better.