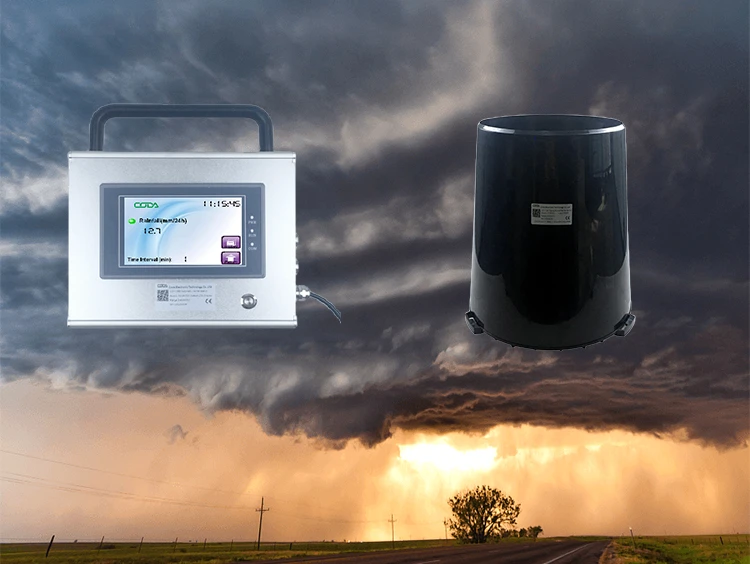
what does a rain gauge measure | rainwater sensor
A rain gauge sensor measures how much it rains in a certain unit area. It is also known as a rain gauge or rain sensor. Its main job is to collect and measure rainwater.
It does this based on size and height. We use these sensors for both manual and automated rainfall measurements.
Standardized rain gauge sensors are important for people like meteorologists, hydrologists, and environmental scientists. They help experts track rainfall trends and patterns. People also use them in practical ways, not just for science. You will manage irrigation controllers, flood warning systems, and weather monitoring stations.
There are several types of rain gauge sensors. Each type of sensor is made for specific uses. The most common ones are:
– **Tipping Bucket Rain Gauges:**
These gauges have a bucket that tips over when it collects a certain amount of water. This provides precise measurements of rainfall.
– **Weighing Precipitation Gauges:**
These gauges rain detection by weighing the water they collect.
– **Optical Rain Gauges:**
These optical rain sensor devices use laser or infrared beams to find raindrops. They measure rainfall by looking at the size of the drops and how often they fall.
The main idea of all rain gauges is to collect and measure rain. Traditional rain gauges have a simple design. They work well for getting accurate readings.
Traditional Rain Gauge Working Process:
1. **Rainwater Sensor Collection:** A round container with a wide opening collects rainwater. Usually, meteorologists or workers place the gauge on flat ground in an open area. This is done to keep it away from trees or buildings. This helps make sure we collect clear water.
2.**Funneling System:** Presence of rain goes through a funnel into a narrow tube or measuring cylinder. This setup gives accurate measurements, even for small amounts of rain.
3. **Measurement Scale:** The measuring tube cylinder has a clear scale. It is marked in millimeters or inches. This shows the total rainfall.
4. **Recording Data:** We check the water we collect regularly. Depending on the device, we may write down readings and empty the system. Some devices use sensors to log data automatically.
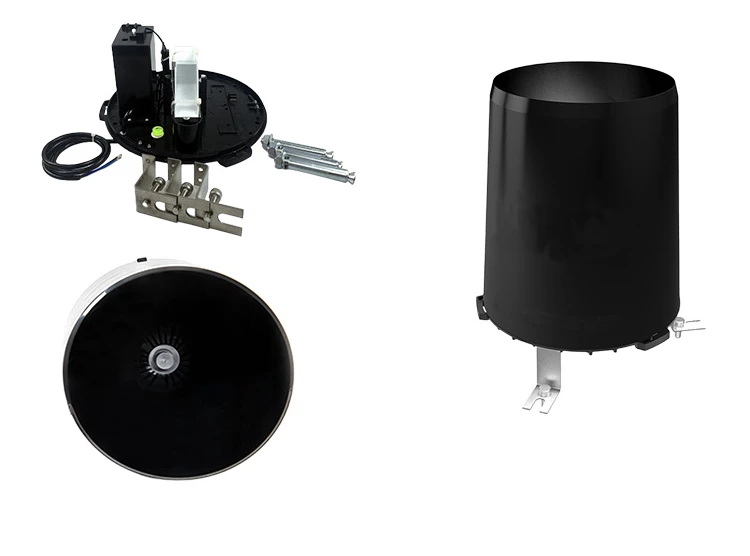
Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge: How It Works
The tipping bucket rain gauge is a common tool used to measure rainfall. It works using a simple see-saw or tilting bucket irrigation system.
1. **Rain Collection:**
At the top of the device, you will find a funnel. This funnel gathers rainwater and sends it into one of two small buckets. Each bucket can hold a set amount of water, usually between 0.2 and 0.5 mm.
2. **Tilting Mechanism:**
When one bucket fills with water, it tips over. This empties the first bucket. Then, the second bucket can collect the rainwater.
3. **Switch Activation:**
Every period of time a bucket tips, it turns on an internal switch, like a reed switch. This notes the event as a certain amount of rainfall. Each tip shows a certain amount of rain.
4. **Calibration for Accuracy:**
The device needs to be adjusted for accurate measurements. Calibration checks how much water is needed to tip each bucket. This amount depends on the design of the gauge.
5. **Data Collection:**
The total number of bucket flips shows how much rain has fallen over time. We can record rainfall this data in two ways.
We can do it by hand. Or, we can use a data logger or weather station. This lets us watch things in real-time.
conclusion
Tipping bucket rain gauges are popular. They are simple, reliable, and easy to take care of. They give clear rainfall measurements. They work well for both manual and automated monitoring.
Automatic rain gauges with sensors can measure rainfall and record data on their own. These advanced devices give real-time measurements and let us monitor rainfall continuously.
A rain gauge’s main job is to collect and measure rain. It provides key information to weather experts and water scientists. These experts need correct information about rain patterns and trends.
Rain gauge sensors are key tools for measuring rainfall. This information is useful in many areas. It helps with farming, water management, weather forecasting, and disaster planning.