What Is PM Sensor and How Does It Work? | particulate matter sensors
Air quality has a big impact on human health and the environment. Many people do not know about the pollutants that harm it. A big pollutant is particulate matter in the outdoor air, or PM. This is worrying because it can get inhalable into the lungs and even the blood.
To solve the problems of PM, technology has created PM sensors. These sensors help monitor air quality in real-time.
This article explains how dust sensors work. It also talks about their uses. Finally, it shows why they are important for better air quality awareness.
Understanding Particulate Matter
Particulate matter is made up of tiny particles or droplets in the air. These can be breathed into the lungs. The fine particle come in different sizes and types. They include dust, dirt, soot, smoke, and liquid drops.
PM is usually classified based on how big its particles are. PM10 includes particles that are 10 micrometers or smaller. PM2.5 includes particles that are 2.5 micrometers or smaller. These two types are the most talked about in air quality studies.
PM10 particles can irritate the lungs. However, PM2.5 is more worrying. It can go deep into the lungs and enter the blood. This creates bigger health risks.
Sources of PM come from nature and human actions. Natural sources include dust storms, wildfires, and volcanoes.
These events send many small particles into the air. Human activities, like car emissions and factories, also increase PM levels. Burning fossil fuels is another big cause of PM.
Urban areas often have high amounts of tiny particles in the air. This is caused by heavy traffic, industrial work, and other city activities.
Research shows that being exposed to PM can cause serious health problems. These include breathing issues, heart diseases, and even early death.
Vulnerable groups like children, the elderly, and those with health impacts issues are affected more than others. It is important to watch and lower PM levels. This helps protect public health and meet air quality standards.
Particulate matter sensors are essential for managing air pollution. They give real-time information about airborne particles. This helps both the authorities and the public act fast to improve air quality.
What Is a PM Sensor?
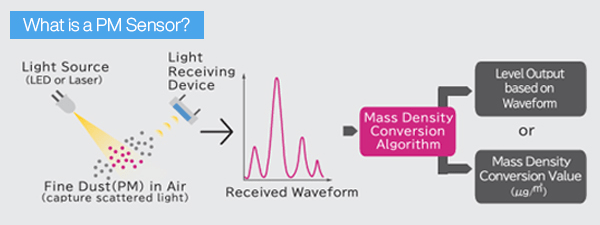
What is pm measurement ?A particulate matter sensor is a device that finds and measures PM levels in the air. These high quality sensors come in different sizes, designed to measure, and technologies. They all aim to give accurate air quality measurements. Most dust sensors use light-based methods, like light scattering.
During operation, a beam of light goes through a sample of air. When particles are present, they scatter the light. The sensor measures how much light is scattered. It then calculates the amount of particle diameter in the air.
Dust sensors come in many types. Some are small devices you can hold in your hand. Others are more advanced systems. These advanced systems are used in air quality networks or industrial setups.
High-end sensors often work with larger environmental monitoring systems. These systems collect data from various sources to study pollution trends closely.
These sensors can be set up to find different sizes of particles. They can measure PM10, PM2.5, or very small PM0.1 particles, based on what is needed. The sensitivity and calibration of a sensor affect how accurate its measurements are.
As air pollution around the world grows, we need to make and use sensors for tiny particles. Governments need these tools to follow the rules. Businesses use them to check air quality at work. People use sensors to keep track of their health.
Particle Sensors are not just useful. They help people learn more about air pollution. They also urge communities to act for cleaner air for all.
How PM Sensors Function
Particle Sensors mainly work by scattering light, but they use different technologies for this. The process begins when air is pulled into the sensor.
As air moves through the device, particles inside it interact with a strong beam of light. Light scatters based on how big the particles are and how many there are. This scattering is the basis for measuring how many particles are present.
Two common ways to detect PM are laser scattering and filter-based methods. Laser scattering sensors use a laser to make a focused light beam. When particles enter the sensor chamber, they scatter the laser light in different directions.
The sensor looks at how bright the scattered light is. It uses this to find out how many particles are in the air. The results are shown in units like micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m³).
Filter-based methods work by passing air through a filter that traps particles. After a set time, the filter is weighed to find the mass of collected particles. This method gives accurate data on PM concentration. However, it is usually slower and not as good for real-time monitoring as optical techniques.
Modern particle sensors often have extra features. These features include temperature and humidity measurements to make them more accurate. Environmental factors, such as humidity, can greatly affect how particles behave. This extra data helps make readings more accurate.
In recent years, new technology has made dust sensors cheap and easy to carry. This helps more people check air quality. These tools help people see how much air pollution they are exposed to. This helps people understand and encourages communities to deal with pollution issues.
As we monitor air quality more, it helps us make better policies. These policies aim to lower harmful particles in the environment.
Applications of dust Sensors
Particle Sensors are used in many industries and sectors. They are useful tools in many situations. One of their key roles is in public health monitoring.
Governments and institutions use sensors to measure tiny particles in the air. This helps them follow the air quality rules made by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). With accurate air quality data, authorities can take steps to protect public health. They can also tell residents about pollution levels and give warnings during important situations.
In cities, dust sensors are important for planners. They help manage traffic and control pollution. By placing sensors in key spots, planners can find areas with high pollution levels, known as hotspots.
With this data, they can change traffic routes, create green zones, or expand public transport. These steps aim to reduce vehicle emissions and improve air flow in crowded areas.
Dust sensors are also very important in industrial applications. Factories use these devices to check emission levels. This helps them follow environmental rules.
Accurate measurements help industries lower their impact on air quality. They also help them meet tougher emission rules.
More people are aware of indoor air quality now. This has led to a higher demand for dust sensors in homes and businesses. Bad indoor air can lead to serious health issues.
These sensors help find dust, pet hair, smoke, and allergens in buildings. By giving useful information, particulate matter sensors allow users to take action. They can make ventilation better or change the filters. This helps make living and working spaces healthier.
Particulate matter sensors are widely used in research. Institutions studying climate change, environmental science, and public health depend on these devices. They help gather important air quality data.
This research helps us see how air pollution affects health. It also supports efforts to solve environmental problems.
The use of particulate matter sensors in smart city projects creates exciting opportunities. Cities can connect sensors to the Internet of Things (IoT). This helps them build smart systems. These systems give real-time information about air quality.
This data gives citizens knowledge. It helps them make informed choices about outdoor activities based on pollution levels. This can lead to healthier living habits.
Challenges and Future Directions
While particulate matter sensors have made great progress, their use and effectiveness still face some challenges. A major issue is how accurate and reliable low-cost particulate matter pm sensor are.
These devices make it easier to monitor air quality. However, their measurements are often less precise than high-end options. Differences in calibration, sensitivity, and environmental factors can cause big inconsistencies in the recorded data.
Another challenge is that there are no standard ways to measure PM. Different manufacturers use various techniques and calibration methods. This leads to differences in data from various devices.
The lack of uniform standards makes data analysis harder. This creates challenges for regulatory agencies and researchers. They find it difficult to combine information and make reliable conclusions about air quality.
Public awareness and understanding are key challenges. Dust sensors provide quick data, but it is essential to share their meaning with the public. People must know how PM readings affect their health and what steps they can take to improve air quality. Educational campaigns and outreach are crucial for turning this information into action.
New developments in particulate matter sensors technology look promising. Innovations are lowering costs and making sensors more sensitive. They also use advanced tools like machine learning to analyze large data sets more accurately.
These tools can help predict pollution levels. They use past data and current conditions to make better forecasts.
Researchers are looking for ways to check air quality. They want to use sensors for dust along with detectors for other pollutants. These systems will give a better view of air quality. They would help us see how different pollutants work together.
Regulatory measures to reduce emissions and improve air quality are very important. As more people learn about air pollution’s health effects, stricter rules on PM emissions will likely come. This highlights the need for reliable dust sensors in public and industrial uses. These sensors play a key role in tackling these issues.
In summary
Particulate matter sensors are key for tracking air quality. They give important data that helps with public health plans and personal choices. It is important to understand particulate matter.
Particulate matter sensors help us measure it. They have many uses and face some challenges. These sensors are crucial in fighting air pollution and improving health.
As technology gets better, dust sensors will be key for cleaner air. They will help us have a healthier future.