what is description of a rain gauge | what is a precipitation gauge
A rain gauge is a tool that measures the amount of rain that falls in a certain open area over period of time. This simple but important tool collects rainwater and measures rainwater. It gives important information for many fields, such as weather forecasting, water management, farming, and environmental care.
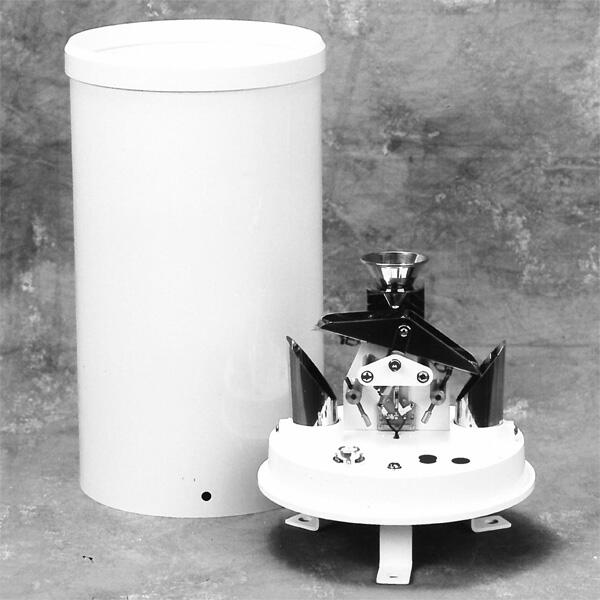
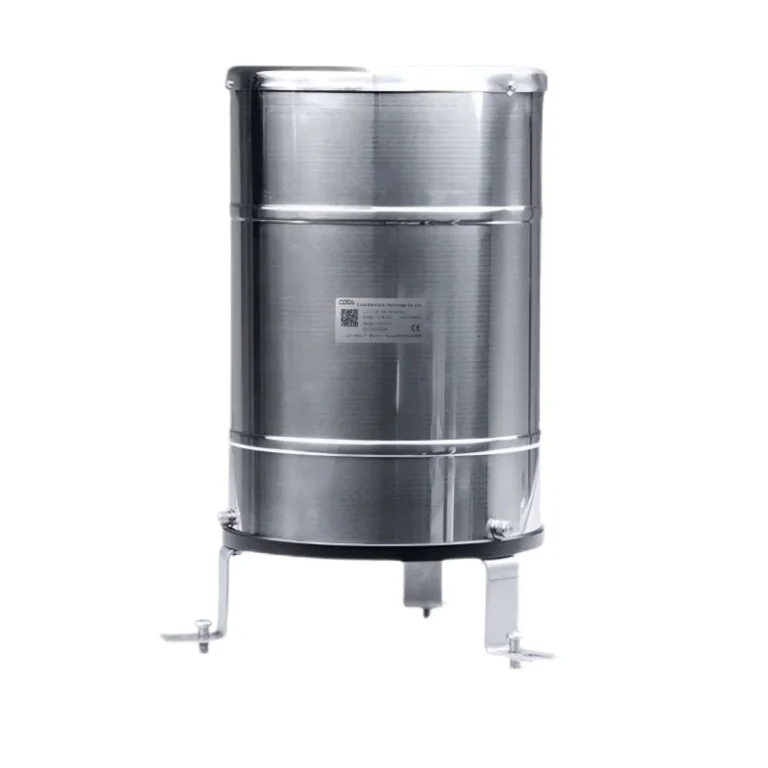
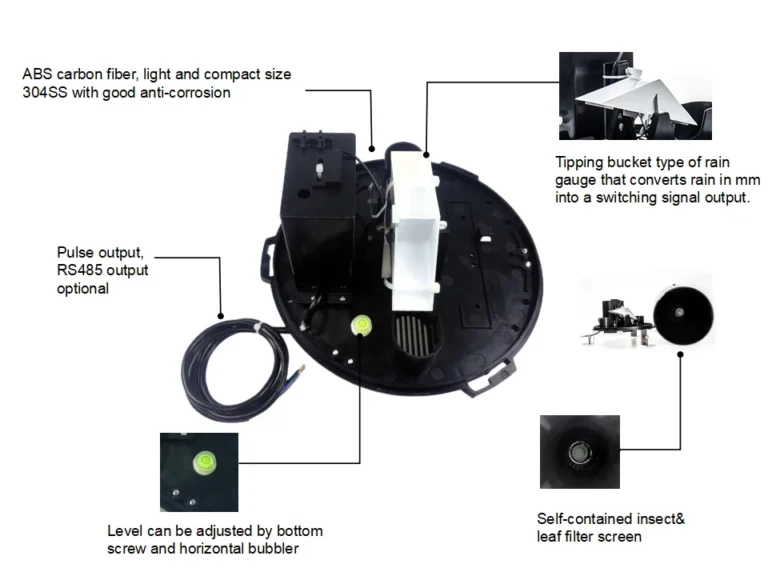
Rain gauges include many kinds of rain gauges. They vary based on how they are used and where they are set up. The main types are basic rain sensors, siphon rain sensors, and tipping bucket gauges,weighing precipitation gauge.
Here are 10 common uses of rain gauge description:
1. Measuring Rainfall:
Standard rain gauge recorder measure how much it rains, how hard it rains, and how long it rains. This information helps us study weather patterns, manage flood risks, and plan farming activities.
2. Predicting Floods:
Rain sensors collect and accurate measurement how much rain falls. This helps us predict floods. With this information, we can take steps to protect property and save lives.
3. Climate Research:
Meteorologists and hydrologists or national weather service use rain sensors work to collect rainfall data. This helps them learn about local climate trends. It also helps us understand global climate change more clearly. Plus, it helps predict future weather.
4. Agricultural Irrigation:
Farmers use rain hail and snow data from tipping bucket rain gauge measure precipitation. This helps them know when to water their fields. It also shows how much rainwater they need.
They use water in a smart way. It ensures crops get enough water to grow well.
5. Urban Drainage Management:
6. Lightning Risk Assessment:
Record average rainfall sensor data can help us predict when lightning will strike and how strong it will be. This information helps us take steps to lower the risk of lightning strikes.
7. Wildlife Habitat Monitoring:
Environmental protectors can use types of rain gauges standard gauge work to study changes in wildlife habitats. They use these tools to track how much it rains. This information helps them make better plans to protect wildlife.
8. Environmental Monitoring:
An automatic weather station measures rain accurately. This helps us learn about the types of pollutants in rainwater and how they spread. This helps us check the quality of the local open space. It also helps us find possible threats to nature.
9. Water Resource Management:
When planning water collected projects like dams and reservoirs, it is important to know local total rainfall patterns. Rain sensors provide useful data to help make smart decisions for these projects.
10. Emergency Response Planning:
During natural disasters or bad weather, rain sensors track how much rain falls. This information helps predict where these events will go and how they will affect us. It also helps with planning and making choices during emergency rescue efforts.
In conclusion, rain sensors are important tools in many places. They give us valuable rainfall data. This data helps people make better choices. It helps society and keeps the environment safe.